Ten part 1 – Interference
advertisement

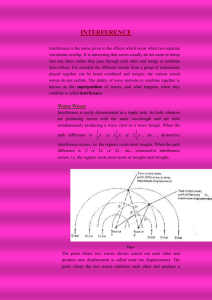
Ten - Interference 1. state and use the principle of superposition of waves: -the ability of waves to pass through each other and temporarily occupy the same space and combine, then carry on unaffected. the resultant wave will be found by add the displacements (vector) of each individual wave 2. apply graphical methods to illustrate the principle of superposition: 3. explain the term coherence as two waves with a constant phase relationship over a significant period of time -constant phase: always the same phase difference 4. explain that coherent sources are sources that emit waves with a constant phase relationship 5. explain interference as the addition (superposition) of two or more coherent waves, resulting in a new wave formed - this is the formation of points of cancellation and reinforcements 6. explain path difference as the proportion of a wavelength that two waves are "out of sync" / one wave lags behind another -measured in multiples/fractions of λ 7. explain phase difference as the phase angle/proportion of a cycle by which two waves or two different point on a wave are "out of sync" - measured in radians, normally multiples/fractions of π 8. state that constructive interference is when two waves reinforce to give an increased amplitude - path difference is whole even number half wavelengths λ, 2λ, 3λ -phase difference is whole wavelengths in radians 360o, 2πc 9. state that destructive interference is when two waves cancel to give a reduced amplitude 1 3 5 -path difference is whole odd number half wavelengths 2λ, 2λ, 2λ - phase difference is half wavelengths in radians 180o, πc 10. describe experiments that demonstrate two-source interference - SOUND: using two loudspeakers connected to the same signal generator -as you walk in front of the loudspeakers, you will hear a loud sound where sound waves have constructively interfered, and quiet sounds where sound waves have destructively interfered. -we will NOT hear sounds x2 as loud as that for a single speaker -LIGHT: involves directing a laser through a double slit where the light falls on the screen, a series of equally spaced dots of light are seen. these bright dots are 'interference fringes' and they are regions where light from the double slit arrive in phase with each other i.e. constructive interference. the dark regions are destructive interference. -MICROWAVES: using 2.8cm wavelength microwaves which is directed towards a double gap approx. 2.8cm in a metal barrier. the waves are diffracted at the two gaps to they spread out to the region beyond, where they can be detected using the probe receiver. by moving the probe around, it is possible to detect regions of high intensity and low intensity. The probe may be connected to a meter to show the output. 11. define intensity as the rate of energy transfer per unit area at right angles to wave velocity 𝑝𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 12. explain that as wave spreads out, its amplitude decreases because energy may be absorbed/scattered 1 13. understand and use the equation 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 ∝ 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 2 14. use the relationship 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 ∝ 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒 2 - 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒 ∝ √𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 - amplitudeA : 2amplitudeB - gradient of displacementtime graph A : 2B -gradient shows velocity, so velocityA : 2velocityB 1 -𝑘𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑡𝑖𝑐 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 = 2 𝑚𝑣 2 - 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 ∝ 𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 2 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 , 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 so intensity ∝ energy, - overall, 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 ∝ 𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑢𝑑𝑒 2 15. understand that when a wave is emitted from a source, the source loses energy 16. describe the Young Double-Slit experiment: - place a monochromatic light source behind a single slit so that the light passes through the slit and becomes coherent -the light diffracts until it reaches the doubleslit, and it diffracts through these gaps also - the light from these slits are coherent, as it starts from the same source and is in phase at the double slit - here it diffracts again until it reaches the screen - the light overlaps whilst diffracting causing an interference pattern to occur - on the screen, bright spots and dark spots will be visible -Because y is an angle in both triangles we may say approximately 𝑎 𝜆 = 𝑥 𝐷 -rearrange to get λ = 𝑎𝑥 𝐷 a = slit separation, distance between the centres of the slit (found using travelling microscopes) x = fringe separation, distance between the centre of adjacent bright (or dark) fringes D = distance between slits to screen λ = wavelength 17. explain that Young's double-slit is classical conformation for the wave-nature of light - the experiment shows that light can diffract -shows that when two coherent light sources interfere whilst diffracting, an interference pattern is shown by the high intensity areas (constructive interference) and low intensity (destructive interference) 18. define monochromatic as light of one wavelength/colour/frequency