Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
advertisement

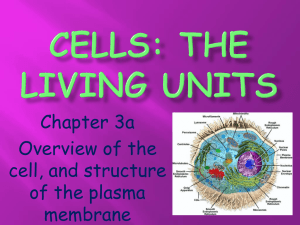
Ch 7.2 Plasma Membrane • Yesterday we talked about things all cells have. One of those things was the plasma membrane. • Can you remember the other two? • Lets review from yesterday Two Basic Cell Types Prokaryote • no nucleus • no organelles • mostly unicellular • very small in size • ex. bacteria, archaebacteria Eukaryote • contains nucleus • contains organelles (membrane-bound structures within cell) • mostly multicellular • ex. plants, animals, yeast ALL cells have 1. plasma membrane 2. Ability to break down molcules 3. genetic material • Plasma Membrane- a boundary that controls what leaves and enters the cell. Why is it important to control what leaves and enters the cell??? • All prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a plasma membrane • Surrounds the cell, providing protection and support • Helps a cell maintain homeostasis, by regulating what enters and leaves the cell • Selectively Permeable: Only allows certain materials through The plasma membrane has 4 main components. 1.Phospholipid Bilayer 2.Transport proteins 3. Cholesterols 4.Carbohydrates Structure of the Plasma Membrane • The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer – two layers of phospholipids are arranged tail to tail. Lipids – make up the lipid bilayer a. Hydrophobic region (between layers) b. Hydrophilic region (inside and outside the cell) Hydrophilic = Water Loving Hydrophobic= Water Fearing Other Components of the Plasma Membrane Within the Phospholipids there are 3 other things. Do you remember???? • Transport proteins • Cholesterols • Carbohydrates Other Components of the Plasma Membrane 2. Transport proteins - create tunnels through which certain substances enter and leave the cell. Other Components of the Plasma Membrane 3. Cholesterols contribute to the fluidity of the plasma membrane in that they prevent the fatty-acid tails from sticking together. Other Components of the Plasma Membrane 4. Carbohydrates attached to proteins stick out from the plasma membrane and help identify the cell It looks like this Fluid Mosaic Model • http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/me mb.htm • The components of the plasma membrane are in constant motion sliding past each other. • The phospholipids in the bilayer create a “sea” in which other molecules can float, hence “fluid” and “mosaic” because there are many components which appear as a pattern or a mosaic. Ok what??? • Fluid mosaic model- All the parts of the plasma membrane are moving all the time Review/Study Questions • How does the plasma membrane help maintain homeostasis? • What does it mean if something is selectively permeable? • What makes up the plasma membrane? • Why are the phospholipids arranged like they are? Plasma Membrane Poster On your BLANK PAPER complete the following: 1. Title: Plasma Membrane 2. Draw a plasma membrane in color (page 188!)) 3. Label the: * Phospholipids * Proteins * Carbohydrates * Cholestrols * Inside the cell * Hydrophobic areas in BLUE (water fearing!) * Hydrophilic areas in RED (water loving) 4. In the lower RIGHT corner, write your name Questions on Back – Define plasma membrane – What is the plasma membranes function? – Tell me what the cholesterol does – Tell me what the transport protein does – Tell me what the carbohydrate does