Taxe - Merrillville Community School
advertisement

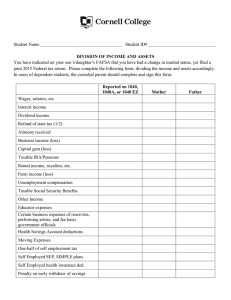
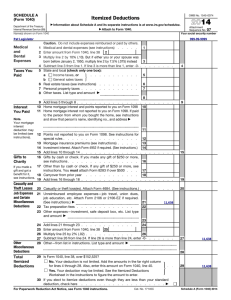
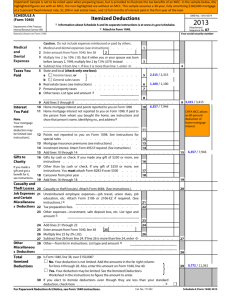
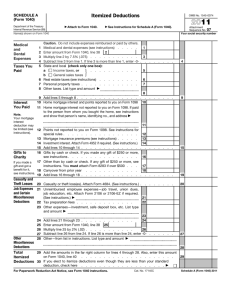
1040 Your Total Income is $9,075 (this amount changes) or more ($6,200 if you are a dependent) Earned Income Unearned Income OR Self-Employed & your Total Profit is More Than $400 April 15th unless that date falls on a weekend or holiday 1040 EZ OR 1040 A OR 1040 Wages or salaries Commissions Earned Income is Generally Shown on a Form Tips Fringe benefits and stock options Paid Sick, Holiday & Vacation Days Bonuses Health & Life Insurance Retirement Contributions Workman’s Compensation W-2 Or 1099-MISC Interest from a Savings Account Interest from Bonds Dividends from Stock 1099-INT; 1099-DIV Gains from Selling Investments Income from Rental Property Gifts & Inheritance Nothing Prizes Money from Retirement Fund Royalties In-Kind & In-Cash Transfers Other 1099 Forms Money Spent/Invested That Lowers a Tax Payers Total Income Moving Expenses if Related to Your Present Job or Starting a New Job Retirement Account Investments Tuition and Fees Student Loan Interest Total Income – Income Adjustments Who’s a Dependent? For Tax Purposes? Someone Who Lives with You More Than ½ the Year & Under 19, or 24 if student & Did Not Provide Over Half his/her own Support & Is Not Filing a Joint Return unless only for a refund Exemptions Worth $3,950 for 2014 (this amount changes) For Each: Tax Payer Dependent Over 65 Blind NOTE: Exemptions Lower AGI (Adjusted Gross Income) Income is Lowered Also By: Standard Deduction (amounts change) $6,200 for Single $12,400 for Married Filing Jointly OR Itemized Deductions—Schedule A NOTE: Use whichever is Larger Itemized Deductions-Schedule A-Examples Medical & Dental Expenses (Limited) Real Estate Taxes Paid Vehicle Taxes from Registration Donations of Money or Goods Safe Deposit Box Fees Union Dues Losses Due to Theft, Vandalism, Fire, Storm (Limited) Cost of Special Tools, Uniforms, or Protective Clothing (Limited) Business Use of Home (Home Office) (Limited) Tax Credit Lower Tax Amount If Tax Amount is Zero, Can Give a Refund More Valuable Than Deductions You owe $1,003 in tax. You are eligible for either a $1,000 tax deduction or a $1,000 tax credit. Which would you choose? Tax Credit Tax Credits are More Valuable Than DeductionsHow? $1000 Deduction—If your Original Income was $9,480, your tax is $1,003 When you deduct the $1000, $9,480 - $1,000=$8,480 is your new income Your new tax is $853 so you saved $150 $1003-$853=$150 Tax Credits are More Valuable Than DeductionsHow? $1,000 Credit—These are taken AFTER you calculate your tax Your tax on $9,480 is $1003 When you take a $1,000 credit Your new tax is $3 $1,003 - $1,000=$3 Which is a savings of $1,000 Tax Credit Examples Child Care Expenses American Opportunity Credit for College Children Under 18 Who Live With You Home Energy Savings First-Time Homebuyer Lower Income Families National Defense (Wars) Social Security Medicare/Medicaid Interest on the National Debt President , Senators and House Representatives All White House Workers Agriculture Foreign Affairs Veteran Benefits Environmental and Natural Resources Education Public Transportation Fire Fighters & Police Officers Road & Traffic Light Repair Capitol & Government Building Maintenance Congress, Governors, Mayors, State Representatives All Government Workers Garbage Collecting Healthy Drinking Water How Tax Money is Used Vote Created in 1913 16th Amendment Gave Congress the Power to Tax In 1916, Congress changed the text of the income tax law, removing the word "lawful" from "lawful business" Now ALL income, whether attained by legal means or not, was taxable. Because of this, many criminals who were guilty of other infractions were sent to prison for tax evasion. Income Payroll Unemployment State & Federal ½ of Medicare & Social Security Sales Real Estate Personal Property Tax Preparation or Help Certified Public Accountant (CPA) H & R Block IRS Tax Programs If you have a professional complete taxes, make sure they sign off on the return. If they make a mistake, the will at least cover your penalty and interest. Social Security Administration keeps track of your earnings to determine benefits you will get when retire, become disabled, or die and survivors get. IRS uses it to identify you