depotposter_0
advertisement
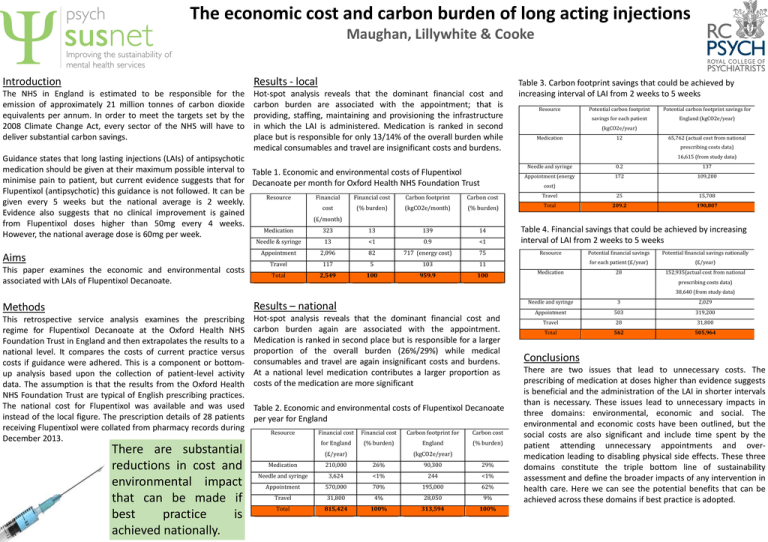
The economic cost and carbon burden of long acting injections Maughan, Lillywhite & Cooke Introduction Results - local The NHS in England is estimated to be responsible for the emission of approximately 21 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents per annum. In order to meet the targets set by the 2008 Climate Change Act, every sector of the NHS will have to deliver substantial carbon savings. Hot-spot analysis reveals that the dominant financial cost and carbon burden are associated with the appointment; that is providing, staffing, maintaining and provisioning the infrastructure in which the LAI is administered. Medication is ranked in second place but is responsible for only 13/14% of the overall burden while medical consumables and travel are insignificant costs and burdens. Guidance states that long lasting injections (LAIs) of antipsychotic medication should be given at their maximum possible interval to Table 1. Economic and environmental costs of Flupentixol minimise pain to patient, but current evidence suggests that for Decanoate per month for Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust Flupentixol (antipsychotic) this guidance is not followed. It can be Resource Financial Financial cost Carbon footprint Carbon cost given every 5 weeks but the national average is 2 weekly. cost (% burden) (kgCO2e/month) (% burden) Evidence also suggests that no clinical improvement is gained (£/month) from Flupentixol doses higher than 50mg every 4 weeks. Medication 323 13 139 14 However, the national average dose is 60mg per week. Aims This paper examines the economic and environmental costs associated with LAIs of Flupentixol Decanoate. Needle & syringe 13 <1 0.9 <1 Appointment 2,096 82 717 (energy cost) 75 Travel 117 5 103 11 Total 2,549 100 959.9 100 Table 3. Carbon footprint savings that could be achieved by increasing interval of LAI from 2 weeks to 5 weeks Resource Potential carbon footprint Potential carbon footprint savings for savings for each patient England (kgCO2e/year) (kgCO2e/year) Medication 12 65,762 (actual cost from national prescribing costs data) 16,615 (from study data) Needle and syringe 0.2 137 Appointment (energy 172 109,200 Travel 25 15,708 Total 209.2 190,807 cost) Table 4. Financial savings that could be achieved by increasing interval of LAI from 2 weeks to 5 weeks Resource Medication Potential financial savings Potential financial savings nationally for each patient (£/year) (£/year) 28 152,935(actual cost from national prescribing costs data) 38,640 (from study data) Methods Results – national This retrospective service analysis examines the prescribing regime for Flupentixol Decanoate at the Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust in England and then extrapolates the results to a national level. It compares the costs of current practice versus costs if guidance were adhered. This is a component or bottomup analysis based upon the collection of patient-level activity data. The assumption is that the results from the Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust are typical of English prescribing practices. The national cost for Flupentixol was available and was used instead of the local figure. The prescription details of 28 patients receiving Flupentixol were collated from pharmacy records during December 2013. Hot-spot analysis reveals that the dominant financial cost and carbon burden again are associated with the appointment. Medication is ranked in second place but is responsible for a larger proportion of the overall burden (26%/29%) while medical consumables and travel are again insignificant costs and burdens. At a national level medication contributes a larger proportion as costs of the medication are more significant There are substantial reductions in cost and environmental impact that can be made if best practice is achieved nationally. Table 2. Economic and environmental costs of Flupentixol Decanoate per year for England Resource Financial cost Financial cost Carbon footprint for Carbon cost for England (% burden) England (% burden) (£/year) (kgCO2e/year) Medication 210,000 26% 90,300 29% Needle and syringe 3,624 <1% 244 <1% Appointment 570,000 70% 195,000 62% Travel 31,800 4% 28,050 9% Total 815,424 100% 313,594 100% Needle and syringe 3 2,029 Appointment 503 319,200 Travel 28 31,800 Total 562 505,964 Conclusions There are two issues that lead to unnecessary costs. The prescribing of medication at doses higher than evidence suggests is beneficial and the administration of the LAI in shorter intervals than is necessary. These issues lead to unnecessary impacts in three domains: environmental, economic and social. The environmental and economic costs have been outlined, but the social costs are also significant and include time spent by the patient attending unnecessary appointments and overmedication leading to disabling physical side effects. These three domains constitute the triple bottom line of sustainability assessment and define the broader impacts of any intervention in health care. Here we can see the potential benefits that can be achieved across these domains if best practice is adopted.