File
advertisement

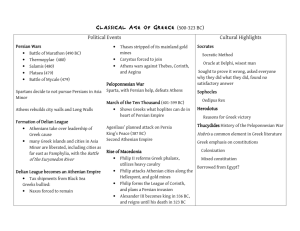
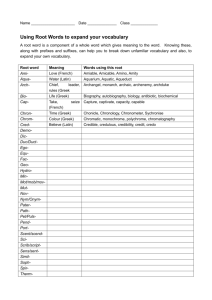
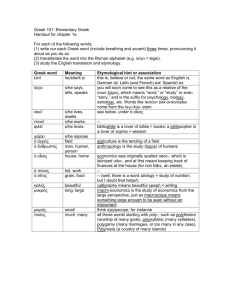
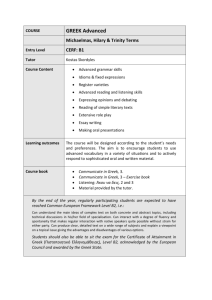
Crete • earliest center of civilization • home of the Minoan civilization • involved in trade and colonization Mycenaean Civilization • military fervor • adapted Minoan culture Dorians • little known of them • great warriors Greek Dark Ages • smaller, isolated villages • had little outside contact Homer Iliad Odyssey “Homeric Age” Greek Mythology • stories that explain beliefs • 12 chief gods and goddesses • deities lived on Mount Olympus anthropomorphic exhibiting human forms and attributes Greek Mythology polytheistic • • • • no powerful priesthood lacked otherworldliness little magic or astrology lacked a creed or system of ethics Olympic Games • honor of Zeus • physical prowess • rare examples of Greek city-state cooperation Greek Cities • polis = city • acropolis = strong city City Government • • • • monarchy = rule by one oligarchy = rule by a few tyranny = rule by force democracy = rule by the people Greek Colonization Syracuse = most important colony Greek Colonization • • • • metropolis chose a leader leader chooses site colonists and leader set sail land partitioned; laws and rituals established • new city-state on its own Sparta • southern tip of the Peloponnesus • militaristic state • state controlled every part of the citizens’ lives • oligarchy government Peloponnesian League • led by Sparta • included neighboring citystates • purpose = oppose Athenian democracy Athens • northeastern tip of the Peloponnesus • commercial power • independent and individualistic • democracy Athenian Governments • monarchy in the early days • oligarchy for a limited time Solon reforms for the common man • forbade making debtors into slaves • created the Council of Four Hundred Athenian Governments • democracy - instituted by Pericles - became the standard Delian League • led by Athens • made up of Greek citystates • purpose = offensive and defensive measure against Persia Persian Wars • Persia retaliates for colonial rebellions • focused on punishing Athens Battle of Marathon • Athenians outnumbered 3 to 1 • Athenian army defeated Persian cavalry Thermopylae • Persians outnumbered the Greeks • centered on a narrow pass Spartan Monument “Tell them in Sparta, passerby, that here obedient to their orders, we lie.” Battle of Salamis Bay • used the Athenian naval plan • a great victory for Athens Pericles His reign made Athens • the pinnacle of the ancient world’s culture • a democratic city-state Peloponnesian War • pitted Greek against Greek • a whale vs. an elephant Peloponnesian War • Phase 1: Athenian victory • Phase 2: Nician Peace • Phase 3: Persian intervention Macedonians • King Philip II Division of Alexander’s Empire • Antigonids in Macedonia and Greece • Ptolemies in Egypt • Seleucids in Syria and Persia • Chandragupta in India Greek Culture • exalted man • respected restraint and balance • appreciated beauty, strength, and freedom Greek Motto “Nothing in excess, and everything in proportion.” Hellenic = Greek culture the cradle of Western culture Hellenistic = like the Greek Greek culture conquered the world humanities a formal study of human thought and culture Greek Focus • philosophy and science the human mind and • literature reasoning human life powers and activity • sports • art height of human physical performance beauty and perfection of the human form. Philosophers • lovers of wisdom • believed man was basically good Socrates • asking questions and analyzing answers • Virtue is knowledge, and ignorance produces evil. Plato • most famous student of Socrates • established the first school of philosophy and science anarchy breakdown of government and order Plato’s Republic those with desire • needed virtue = temperance those with spirit • needed virtue = courage those with reason • needed virtue = knowledge Plato’s view of reality • something must be permanent to be truly real • reality lay in the next world • physical world = shadows of next world Aristotle • Plato’s most famous student • believed reality lay in this world • best work dealt with logic syllogism a way of reasoning Aristotle’s Organon the syllogism • three parts: major premise, minor premise, conclusion • Formula= a implies b c implies a therefore: c implies b example 1) All Greeks are human. 2) Aristotle is Greek. 3) Therefore, Aristotle is human. example a b 1) All Greeks are human. c a 2) Aristotle is Greek. c b 3) Therefore, Aristotle is human. false example a b 1) All cows have four legs. c b 2) My cat has four legs. c a 3) Therefore, my cat is a cow. Epicureanism • proposed by Epicurus • promoted avoiding pain and fear to achieve happiness and pleasure Stoicism • proposed by Zeno • promoted that man accept his fate and exercise self-control Pythagoras • philosopher and mathematician • universe could be explained in mathematical terms • Pythagorean Theorem Hippocrates • “Father of Medicine” • illnesses come from natural causes Euclid “Father of Geometry” Elements Archimedes discovered the principle of the lever Archimedes “Give me a spot to stand on and a lever long enough, and I will move the earth.” Eratosthenes • calculated the circumference of the globe • formulated the lines of latitude and longitude Herodotus • “Father of History” • chronicled the Persian Wars Thucydides • wrote about the Peloponnesian Wars • works were even more accurate and objective Sophocles • wrote tragedies Aristophanes • wrote comedies Greek Art Urns • used to hold cremated remains • decorated with scenes of everyday life, great events, or the gods Greek Art Sculpture Three phases • archaic • classical • Hellenistic archaic period Egyptian influence classical period height of Grecian achievement Hellenistic period simple beauty replaced with frenzied emotion classicism governed by reason, restrained and orderly, universally true, good and beautiful and . . . harmonious with society Greek Art Architecture • height during the “Golden Age” • copied by future generations Greek Columns Three styles • Doric • Ionic • Corinthian