Radioactive Decay
advertisement

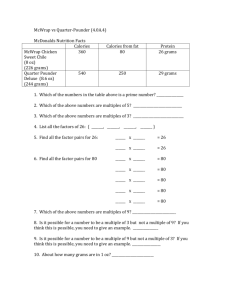
Radioactive Decay Life Science: Natural World What does DECAY mean? Rotting Death Changing from one thing to another ISOTOPE Atoms of the same element have a different number of neutrons Carbon Carbon 12 and Carbon 14 Carbon 12 is MUCH MORE STABLE than Carbon 14 How can carbon become stable? Radioactive Decay How Isotopes Help Us We can measure the amount of a radioactive element to determine the age of a fossil Each element has a HALF LIFE The amount of time it takes for HALF of the material to decay (turn into a stable element) Half Life We can figure out how much time has passed We can figure out how much of an remains Needed information: The time for one half life The amount of the material (starting and ending) How much time has passed Things to Check For: If you find it, underline it Starting material amount Ending material amount Total time Number of half lives Time for one half life Circle what you are solving for Practice with Cougartonium Cougartonium has a half life of 4 years. If an artifact started out with 10 grams of Cougartonium and 4 years have passed, how much of the Cougartonium remains? Underline the important information Practice with Cougartonium Cougartonium has a half life of 4 years. If an artifact started out with 10 grams of Cougartonium and 4 years have passed, how much of the Cougartonium remains? The Solution Starting Material Number of Half Lives 10 grams ?? Years Passed 4 years Ending Material ?? Since we know that one half life is 4 years, we know how many half lives have occurred. The Solution Starting Material Number of Half Lives 10 grams 1 Years Passed 4 years Ending Material ?? The Solution Starting Material Number of Half Lives 10 grams 1 Years Passed 4 years Ending Material ?? Since we know know how many half lives (1) and how much starting materials (10 grams), we can divide 10 grams by 2 (or multiply by ½). The Solution Starting Material Number of Half Lives 10 grams 1 Years Passed 4 years Ending Material 5 grams Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Underline the important information Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Starting Material 100 grams Number of Half lives 0 Time Passed 0 seconds Ending Material 100 grams Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Starting Material Number of Half lives Time Passed Ending Material 100 grams 0 0 seconds 100 grams 100 grams 1 x 50 grams Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Starting Material Number of Half lives Time Passed Ending Material 100 grams 0 0 seconds 100 grams 100 grams 1 x 50 grams 50 grams 2 2x 25 grams Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Starting Material Number of Half lives Time Passed Ending Material 100 grams 0 0 seconds 100 grams 100 grams 1 x 50 grams 50 grams 2 2x 25 grams 25 grams 3 3x 12.5 grams Let’s practice with on from your packet 1. What is the half life of a 100 gram sample of nitrogen-16 that decays to 12.5 grams of nitrogen-16 in 21.6 seconds? Starting Material Number of Half lives Time Passed Ending Material 100 grams 0 0 seconds 100 grams 100 grams 1 x 50 grams 50 grams 2 2x 25 grams 25 grams 3 3x 12.5 grams 21.6 = 3x 7.2 = x What to be working on 1. Half-Life Worksheet 2. Relative Dating Worksheet 3. Fun with Stratigraphy worksheet 4. Mesozoic Article 5. Ask me