Conservation Strategies
advertisement

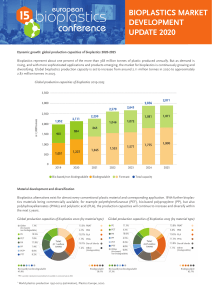
Conservation Strategies IB Geography I Part 1 Opening Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DwwOyyk iXNs • Greenpeace Ass Light • What is the purpose of this video? • How is it satirical? Objectives • To be able to discuss the reduction of resource consumption by: – conservation [Reduce] – waste reduction [Reduce and Reuse] – recycling – substitution [substituting plastics for bioplastics] Opening Activity Barriers to Sustainable Development • • • • • • • • • Poverty Renewable Technology Population Growth Tipping Point Development Education Enforcement International Consensus Habit Take 5 minutes to decide which of these barriers to sustainable development you think is most difficult to overcome and which is easiest to overcome and support answers with explanation. Conservation of Resources (defined) • The management of the human use of natural resources to provide the maximum benefit to current generations while maintaining capacity to meet the needs of future generations The Three R's Reduce: This refers to using less of a product e.g. less packaging, less energy. Reuse: This means using a product more than once. This might be returning it to a manufacturer e.g. coke bottles or selling/passing onto another consumer e.g. charity shops Recycling: The re-processing of industrial and household waste so that materials can be reused. Currently materials like paper, card, plastics, glass and some metals are recycled. 3 Rs Singalong! • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mL2gTqic _BY Conservation • Water Use Reduction Example • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GOLf2Rbx mzE#t=71 • Waste Reduction Through Recycling A lot of waste currently ends up overseas, more often than not in China. In fact demand for recyclable products is currently higher than supply there. • There are environmental and ethical issues of shipping waste overseas • Why the World’s Garbage Ends of in China • http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=fqQY6Ub32E c Recycling Deserts • Areas where rates of recycling are well below the national or regional averages Landfill vs. Incineration • A landfill is a site at which garbage/refuse is buried under layers of earth • Incineration is a waste treatment technology that involves the combustion of organic materials. Part 2 Review of Objectives/Bell Ringer • To be able to discuss the reduction of resource consumption by: – conservation [Reduce] – waste reduction [Reduce and Reuse] – recycling – substitution [substituting plastics for bioplastics] Bell Ringer: Take the next 3 minutes to answer the following IB prompt in your notebooks: Explain how there has been a reduction in the consumption of 1 resource by conservation, reuse or recycling. Today’s Case Study • First, move your desks into your elbow partner groups. You will be working with your partner on activities throughout today’s class period. • Take a moment to jot down this possible IB exam question on the essay planning tool provided: – Evaluate a strategy aimed at reducing the consumption of one resource. Today’s Case Study • To address this objective today, we will focus on strategies designed to reduce the consumption of oil by substituting plastics for bioplastics in the US. What’s the difference? • Plastics are made from oil which is a fossil fuel that produces CO2 emissions. Plastic also doesn't decay. Therefore, plastic disposal poses a difficult and significant environmental problem. • Bioplastics are plastics that are made from renewable sources such as starch, sugarcane, vegetable oil, corn oil or other substances. Some bioplastics are also biodegradable. Bioplastics also are said to have a smaller carbon footprint that regular plastic. The Strategy of Substitution • The use of common and thus less valuable resources in place of rare, more expensive resources. • Examples: – Replacement of copper by aluminum or fiber optics or PVC pipe – Replacement of Fossil Fuels with Renewable sources of energy – Replacement of Plastic with Bioplastic Unpack the Question! • With your partner, take a moment to unpack our possible IB exam question in reference to the case study we will be using: – Evaluate a strategy aimed at reducing the consumption of one resource. Case Study Sources of Evidence Video Source: • “Sustainable Spoons” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2hlFG0i1q BI#t=13 (Strength/Limitation) Close Reading Sources: • “7 Advantages of Biodegradable Plastics” Biostockpro.com (Strength) • “Sustainable Bioplastic Can Damage the Environment” The Guardian (Limitation) Close Read to Discuss Activity • After watching the video and reading the articles, have a discussion with your elbow partner using the following sentence starters: • 1. The positive aspects of bioplastics are… • 2. The negative aspects of bioplastics are… • 3. We should/shouldn’t substitute oil-based plastics with bioplastics because… • 4. Questions I still have about this issue are… Now… back to the prompt! • Using an essay planning tool, your sources (both article/video sources), and yours and your partner’s brain power, create an outline to the IB Exam question we referred to in the beginning: • Evaluate a strategy aimed at reducing the consumption of one resource. Part 3 Reuse • Plastic bags • Returning wire hangers to dry-cleaners • Donating clothes and other items to charities • Repairing household items rather than buying new • Jars/containers Overfishing • A level of fishing resulting in the depletion of the fish stock Quotas (Reduce) • Involving agreement between countries to take only a predetermined amount of a resource • Fish quotas were introduced in the EU because many of the fish stocks in EU waters were falling below unsustainable levels. • Why We need to Transform the EU’s Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1uvF8B0r mEU Fishing Quotas Advantages • They help protect critically endangered species. • This ensures the continued biodiversity of our oceans. • Ensures that food webs and chains remain intact so that other species don't become endangered. Disadvantages • Because of fishing quotas many fishermen lose their jobs • Because boats have to meet quotas, many fish (dead and alive) are thrown over board. • Fishing quotas can create an illegal trade (black market) in fish. Rationing • Very much a last resort management strategy when demand is massively out of proportion to supply • For example, people might only be allowed a very small amount of fuel and food per week Subsidy • Financial aid supplied by government to an industry for reasons of public welfare, reduces the costs for the consumers by reducing the costs for the producers • Subsidies are controversial because by making the price of a resource cheaper, demand is likely to increase which minimizes conservation efforts Product Stewardship • A system of environmental responsibility whereby producers take back a product, recycling it as far as possible, after the customer is finished with it. • Companies that participate in Product Stewardship are: – – – – Battery companies Electronics companies (computers, phones, etc) Vehicles (scrap metal, tires, parts) Mercury containing products (thermometers, fluorescent light bulbs, medical waste) Carbon Credits • Permits that allow an organization to emit a specified amount of greenhouse gases Carbon Trading • A company that does not use up the level of emissions it is entitled to, can sell the remainder of its entitlement to another company that pollutes above its entitlement. Close Read to Discuss Activity • “Let’s Stop Hiding Behind Recycling and Be Honest About Consumption” The Guardian • 4 A’s Discussion Protocol Part 4 Case Study • IB possible exam question: – Evaluate a strategy at a local or national scale aimed at reducing the consumption of one resource. • To address this objective, we will focus on researching strategies Chicago is implementing to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels in transportation. Unpacking the question: • Evaluate a strategy at a local or national scale aimed at reducing the consumption of one resource. Evaluate= to make a judgment by weighing the strengths and limitations Strategy= Transportation Strategies Local= Chicago One Resource= Fossil Fuels The Resource: Fossil Fuels Framing the Problem • The release of carbon into the atmosphere can enhance the greenhouse effect, causing global warming along with associated side effects for example: – rising sea levels – climate refugees – increased frequency and magnitude of tropical storms and desertification. The Problem in Chicago • Since 1980, Chicago’s average temperature has increased approximately 2.6 degrees. • Our current trajectory poses risks to our economy and health. • The most obvious change to come could be hotter summers and more frequent and intense heat waves. • Heavy rains and snow could become more frequent in winter and spring. Increased intensity of downpours will make travel more dangerous, flood basements, pollute bodies of water, damage crops, stress the city’s infrastructure and disrupt transportation. Urban Hotspots Sources for Evaluation • “Improved Transportation Options” from Chicago Climate Action Plan • “Chicago Climate Action Plan Progress Report” • “State Hits Brakes on City Plans for protected bike lane” by Jon Hilkevitch, Chicago Tribune