The IDEA, 504, the ADA and Assistive Technology
advertisement

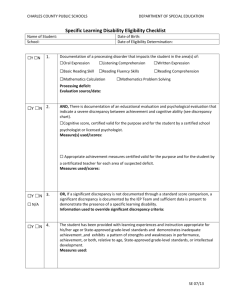
The IDEA, 504, the ADA and Assistive Technology By Randy Chapman The Legal Center for People with Disabilities and Older People www.thelegalcenter.org rchapman@thelegalcenter.org RandyChapmans Ability Law Blog Randychapman.wordpress.com Assistive technology device: Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially or off the shelf, modified or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of a child with a disability. AT Service Any service that directly assists a child with a disability in the selection, acquisition, or use of an assistive technology device. AT services include: Evaluating AT needs of student, including functional evaluation in student’s customary environment; purchasing, leasing or otherwise providing for acquisition of AT devices; selecting, designing, fitting, customizing, adapting, applying, maintaining, repairing, or replacing AT devices; AT services include; Coordinating and using other therapies, interventions, or services with AT devices such as those associated with education and rehabilitation plans and programs; training or TA for student or, where appropriate, the family; training or TA for professionals (educators, rehabilitation personnel, employers and others). Under the IDEA AT can be: Special education: specially designed instruction to meet student’s needs. related services: services student needs to benefit from special education. supplementary aids or services: aids or services provided in regular education classes or other education-related settings to enable the student to be educated with students without disabilities. Examples of assistive technology Calculators large print books adapted spoons auditory FM trainer closed circuit TV head pointers Electronic notetakers cassette recorders word prediction software adapted keyboards voice recognition and synthesis software IDEA: AT does not include: Medical device that is surgically implanted or replacement of the device; School not responsible for post-surgery maintenance, programming or replacement; but School must ensure that external components are functioning properly. Hearing Aids School must ensure hearing aids worn in school are functioning properly. IDEA: how to get AT School Assessment: IEP team must assess the student’s functional capabilities and whether they may be increased, maintained, or improved through the use of AT devices or services. [OSEP Letter to Fisher, 23 IDELR 565 (1995)] Independent assessment. Individualized Educational Program AT is a special factor, this means the IEP team must specifically consider whether the student requires AT devices and services. IEP team must approve AT device or service if: It is needed to ensure reasonable educational progress in the least restrictive setting. IEP must include: the special education and related services and supplementary aids and services. Projected date when services begin and the frequency, location, and duration of services. Special Issues Home use OK if IEP team determines the AT is needed at home for FAPE. Ownership: AT is school property, but school may transfer ownership to student. Damage: school can’t charge parents for normal wear and tear. Transition services: Included not later than on the first IEP when child turns 16 (earlier if appropriate) Postsecondary goals Transition services (including courses of study) needed to reach goals. Transition services A coordinated set of activities designed in a: Results oriented process focused on improving academic & functional achievement to facilitate moving from school to post school activities. Transition services Postsecondary education Vocational education Integrated employment (including supported employment) Continuing & adult education Adult services Independent living, or Community participation Transition services Based on individual needs, including child’s strengths, preferences, & interests and includes: Instruction, related services, community experiences, development of employment & other post-school adult living objectives; and Acquisition of daily living skills and provision of a functional vocational evaluation. Transition Services If an agency participating in the transition plan fails to provide transition services on the IEP, then the local education agency must reconvene the IEP to identify alternative strategies to meet the transition objectives. Summary of Performance For children who graduate or age out: Must provide a summary of the child’s academic achievement & functional performance; Includes recommendations on how to assist child in meeting child’s postsecondary goals. Section 504 No otherwise qualified individual with a disability in the United States …shall, solely by reason of his or her disability, be excluded from the participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity receiving federal financial assistance... Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act Prohibits discrimination by public entities. Public entities are State or local government and any department, agency, special purpose district, or other instrumentality of a State or local government. ADA Title III Public Accommodations Covers places of education and elementary and secondary private schools, day care programs. Nondiscrimination 504/ADA Disability A person has a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity. IDEA An appropriate education means providing special education and the related services the student needs to benefit from the special education program. Services developed and provided through IEP. IDEA Disability Child has an impairment (such as mental retardation, hearing impairments, speech and language impairments, visual impairments, serious emotional disturbance, orthopedic impairments, autism, TBI, OHI, or specific learning disabilities), AND because of having an impairment the child needs special education and related services. Free appropriate public education under 504/ADA Means meeting the individual needs of students with disabilities as adequately as the needs of students without disabilities are met. 504/ADA FAPE Requires Providing general or special education and related aids and services that are designed to meet the individual educational needs of students with disabilities as adequately as the needs of students without disabilities are met. Means providing accommodations and auxiliary aids and services. 504/ADA and LRE Students with disabilities receive services, to maximum extent appropriate, with students without disabilities. Includes nonacademic and extracurricular activities like meals, recess, counseling services, transportation, health services, athletics, recreational activities, clubs or special interest groups. IDEA vs. 504/ADA Eligibility means having a condition requires special education/related services. FAPE: providing special education and related services. IEP Requires having a condition that substantially limits a major life function. FAPE: meeting needs as adequately as needs of students w/o disabilities are met. 504 Plan documents accommodations and services. General education responsibility. Auxiliary aids and services Qualified interpreters notetakers transcription services taped texts readers videotext displays television enlargers talking calculators Electronic readers Braille calculators, printers, type writers telephone hand set amplifiers closed captioned decoders open and closed captioning More Auxiliary aids and services Voice synthesizers specialized gym equipment calculators or keyboards with enlarged buttons reaching devices for library use Raised line drawing kits assistive listening devices assistive listening systems TDDs Asthma substantially limits breathing Modify recess, PE Provide inhalant therapy assistance Administer medication, as prescribed Develop health care and emergency plan Provide rest periods Remove allergens Arthritis pain limits performing manual tasks Accommodate absences for doctor’s appointments Modified PE Assistance carrying books Provide modified eating utensils Notetaker, taped texts, lectures Assistive technology for writing: computer, pencil grip Supply extra set of books for home use Bathroom accommodations, locate class near rest room. Physical disability that limits walking, fine motor skills Provide assistive technology Physical therapy Assist with carrying books or lunch trays Arrange for use of ramps, elevators Relocate classes Extra time between classes Epilepsy: student has periodic seizures limit learning Monitor/distribute medications as prescribed Train staff and children and prepare emergency plan Provide rest time and academic considerations following seizures. Provide plan to makeup work do the student can catch up with peers. Parent who is blind entitled to Braille copies of: copies of IEPs parent handbook model for requesting due process information about low-cost or free legal services (35 IDELR 279) Appeal Procedures Mediation Due Process Hearing CDE Complaint Process Office for Civil Rights Complaint Court (usually must exhaust administrative procedures first) Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Response to Intervention (RTI) Before determining student has LD, assess performance in general curriculum If performance is unsatisfactory, try interventions (specialized teaching staff, smaller teacher/student ratios, more intense programming) Assess effectiveness of intervention Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Response to Intervention (RTI) Before determining student has LD, assess performance in general curriculum If performance is unsatisfactory, try interventions (specialized teaching staff, smaller teacher/student ratios, more intense programming) Assess effectiveness of intervention Response to Intervention Multi-tiered model (usually 3 tiers) A continuum of programs & services for students with academic difficulties Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Response to Intervention (RTI) Before determining student has LD, assess performance in general curriculum If performance is unsatisfactory, try interventions (specialized teaching staff, smaller teacher/student ratios, more intense programming) Assess effectiveness of intervention Response to Intervention Multi-tiered model (usually 3 tiers) A continuum of programs & services for students with academic difficulties Tier 1:Provide instructional supports in general education School personnel screen literacy skills, academics, and behavior Teachers implement research supported teaching strategies Ongoing, assessment and progress monitoring Provide different instruction based on data from ongoing assessments Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Response to Intervention (RTI) Before determining student has LD, assess performance in general curriculum If performance is unsatisfactory, try interventions (specialized teaching staff, smaller teacher/student ratios, more intense programming) Assess effectiveness of intervention Response to Intervention Multi-tiered model (usually 3 tiers) A continuum of programs & services for students with academic difficulties Tier 1:Provide instructional supports in general education School personnel screen literacy skills, academics, and behavior Teachers implement research supported teaching strategies Ongoing, assessment and progress monitoring Provide different instruction based on data from ongoing assessments Tier 2: If performance lags behind peers provide more specialized services in general education Students receive more intensive research based instruction, targeted to individual needs Student progress monitored to determine intervention effectiveness & needed modifications Parents informed and included in planning and monitoring progress General ed teachers receive support (training, consultation, direct services) from educators qualified in implementing interventions & monitoring student progress. Severe Discrepancy Standard for LD No longer required LEAs no longer required to consider whether student has severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability to determine whether student has learning disability. LEA may use a process that determines how student responds to scientific, research based intervention (RTI). Response to Intervention (RTI) Before determining student has LD, assess performance in general curriculum If performance is unsatisfactory, try interventions (specialized teaching staff, smaller teacher/student ratios, more intense programming) Assess effectiveness of intervention Response to Intervention Multi-tiered model (usually 3 tiers) A continuum of programs & services for students with academic difficulties Tier 1:Provide instructional supports in general education School personnel screen literacy skills, academics, and behavior Teachers implement research supported teaching strategies Ongoing, assessment and progress monitoring Provide different instruction based on data from ongoing assessments Tier 2: If performance lags behind peers provide more specialized services in general education Students receive more intensive research based instruction, targeted to individual needs Student progress monitored to determine intervention effectiveness & needed modifications Parents informed and included in planning and monitoring progress General ed teachers receive support (training, consultation, direct services) from educators qualified in implementing interventions & monitoring student progress. Tier 3: Evaluation by interdisciplinary team to determine eligibility for special education Parents informed of due process rights Consent obtained for evaluation to determine special education eligibility Intensive specialized instruction provided and additional RTI collected, according to IDEA timelines (60 days?) IDEA procedural safeguards apply NOTE: Parent has right to appeal refusal to assess or place in special education.