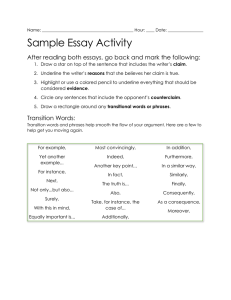
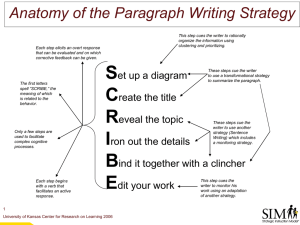
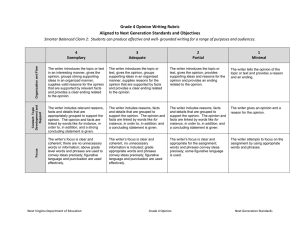
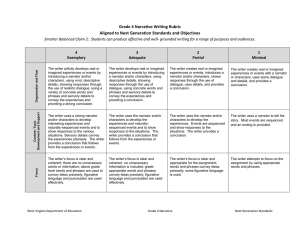
Persuasion Terms
Persuasion Terms
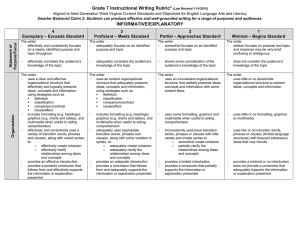
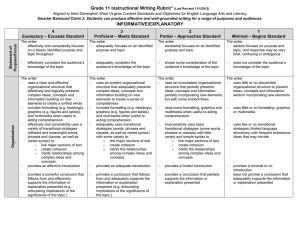
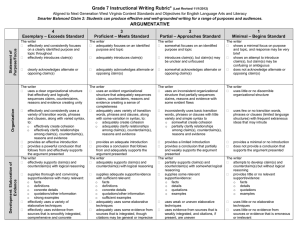
• Logos- The process of reasoning that uses logic, numbers facts and data.
• Pathos- When the writer appeals to the reader’s emotions
• Ethos- The writer tries to persuade the audience to respect and believe him; shows credibility and gives ethical appeal:
• Kairos- The writer or speaker builds a sense of urgency trying to persuade the audience to act now.
• Argumentation- Writer attempts to prove the validity of a point of view or an idea by presenting reasoned arguments.
• Persuasion- An attempt to convince someone through appeals to reason and emotion:
• Rhetoric- The art of speaking or writing as a means of communication or persuasion; the art of using language to persuade:
• Syntax- The arrangement of words in a sentence.
• Thesis- The main idea of a piece of writing;
Subject + Opinion = _____________:
• Generalization (stereotype)- When a writer bases a claim upon an isolated example or asserts that a claim is certain rather than probable.
• Diction- Word choice of a writer or speaker.
• Denotation- The dictionary and literal meaning of a word:
• Connotation- Emotional, contextual, or cultural meaning attached to a word, the implied meaning:
• Euphemism- A more acceptable and usually more pleasant way of saying something that might be inappropriate or uncomfortable.
• Deductive- Arguments that go from general to specific.
• Inductive- Arguments that go from specific to general.
• Syllogism- An argument that consists of a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion.
• Understatement- Used when a speaker wants to make a situation seem less strong or important than it really is.
• Red Herring- A distracter that draws attention away from the real issue.
• Refutation- The act of determining that something is false
• Concession- Admitting that a point in an argument is right
• Antithesis- A figure of speech in which words and phrases with opposite meanings are balanced against each other.
• Anaphora- The repetition of the same word or words at the beginning of successive phrases, clauses, sentences or lines.
• Parallelism- A balance of two or more similar words, phrases, or clauses.
• Hyperbole- An exaggeration.