HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.6.3 Context
advertisement
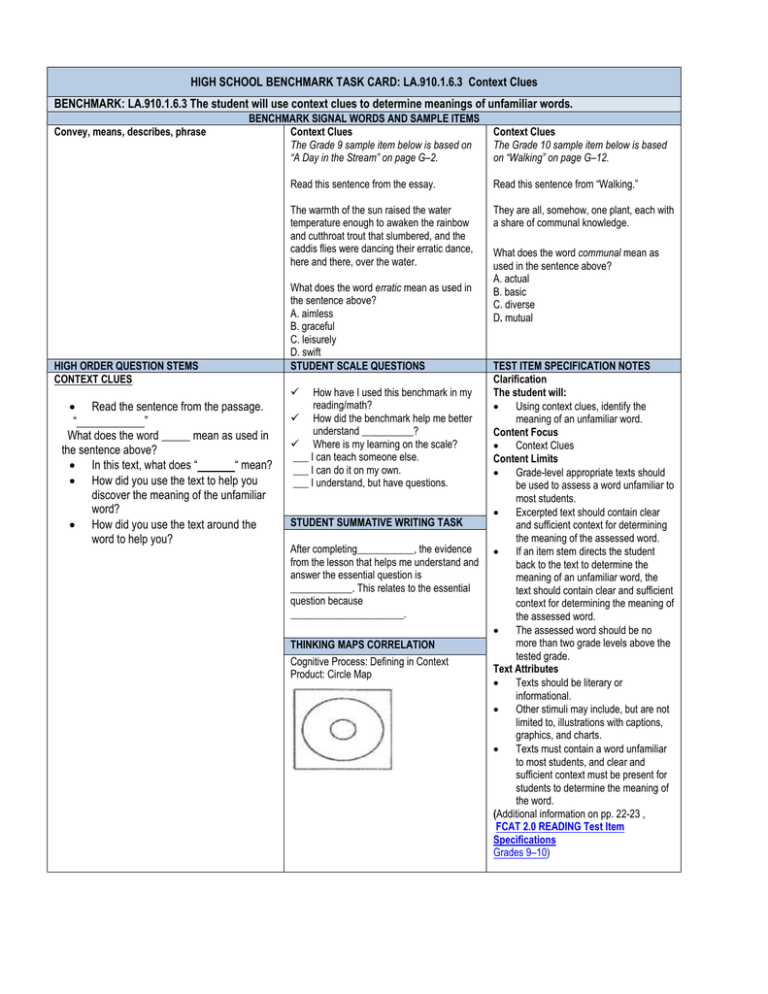
HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.6.3 Context Clues BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.6.3 The student will use context clues to determine meanings of unfamiliar words. Convey, means, describes, phrase BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS Context Clues The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A Day in the Stream” on page G–2. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS CONTEXT CLUES Read the sentence from the passage. “ ” What does the word _____ mean as used in the sentence above? In this text, what does “ “ mean? How did you use the text to help you discover the meaning of the unfamiliar word? How did you use the text around the word to help you? Context Clues The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Walking” on page G–12. Read this sentence from the essay. Read this sentence from “Walking.” The warmth of the sun raised the water temperature enough to awaken the rainbow and cutthroat trout that slumbered, and the caddis flies were dancing their erratic dance, here and there, over the water. They are all, somehow, one plant, each with a share of communal knowledge. What does the word erratic mean as used in the sentence above? A. aimless B. graceful C. leisurely D. swift STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Defining in Context Product: Circle Map What does the word communal mean as used in the sentence above? A. actual B. basic C. diverse D. mutual TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Using context clues, identify the meaning of an unfamiliar word. Content Focus Context Clues Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should be used to assess a word unfamiliar to most students. Excerpted text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed word. If an item stem directs the student back to the text to determine the meaning of an unfamiliar word, the text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed word. The assessed word should be no more than two grade levels above the tested grade. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts must contain a word unfamiliar to most students, and clear and sufficient context must be present for students to determine the meaning of the word. (Additional information on pp. 22-23 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.6.7 Advanced prefixes, Suffixes, and Root words. BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.6.7 The student will identify and understand the meaning of conceptually advanced prefixes, suffixes, and root words. Also assesses LA.910.1.6.11 The student will identify the meaning of words and phrases from other languages commonly used by writers of English (e.g., ad hoc, post facto, RSVP). BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS affix, Anglo Saxon, base word, origin of, Greek word, Latin word, Analyze Word Structure Analyze Word Structure root, prefix, suffix The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “National The Grade 10 sample item below is based Park Service Homepage” on page G–4. on “Cutting Off the World’s Roof” on page Read the section National Park Service African G–18. American History Month Observance 2008 in the National Park Service homepage. Read this sentence from the article. Jaded thrill seekers must be wondering why Culture comes from the Latin word cultura, which there are so few really tall mountain ranges came from colere, meaning “to cultivate.” Based on the on Earth, and why the ones we have aren’t meaning of the root word culture, what does the taller. “theme . . . of Multiculturalism” mentioned in this section suggest about groups of people in a society? The word jaded comes from the Middle English word iade, which means “a worn-out A. Many people in a society are responsible for horse, a nag.” Based on the meaning of the determining the customs within their group. root word, the sentence implies that some B. Different groups of people in a society will support mountain climbers have become the views expressed by its scholars. C. A society is enriched by various groups who merit A. bored with the sport of scaling Earth’s equal respect and scholarly interest. available mountain peaks. D. An informed discussion among groups in a society B. resentful of the superior skill to climb can reveal many conflicting views. Earth’s mountains shown by others. C. frustrated at their inability to successfully ascend Earth’s highest mountains. D. exhausted by their efforts to reach the summits of Earth’s highest mountain peaks. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS Roots & Affixes The origin of . What does is the root mean? , meaning STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Part to Whole/Whole to Part Product: TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Analyze affixes, or root words, or words/phrases derived from other languages, including Greek and Latin, to determine meaning in a text. Appropriate word strategies, simple analysis, and/or direct inference may be required. Content Focus Analyze Word Structure (e.g., affixes, root words) Analyze Words/Phrases Derived from Latin, Greek, or Other Languages Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should contain vocabulary for assessing the analysis of word structure and for assessing words and phrases derived from other languages, including Greek and Latin. Assessed words should be no more than two grade levels above the tested grade. If a stem directs the student back to the text to determine the meaning of an unfamiliar word, or when assessing foreign words and phrases, the text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed word or phrase. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts must contain appropriate words to assess affixes, root words, and foreign words and phrases. (For additional information , see pp. 24-26 of FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.6.8 Analyze Words/Word Relationships BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.6.8 The student will identify advanced word/phrase relationships and their meanings. Convey the meaning, pair of words, add to the idea, restates the meaning, phrase, most similar in meaning, most opposite in meaning BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS ANALYZE WORDS/PHRASES WORD RELATIONSHIPS The Grade 9 sample item below is based on The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Woman “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. with Flower/Offspring” on page G–15. Read this sentence from the article. Though swing never completely died out, it wasn’t until the late 1980s that the music experienced a true rebirth. What does the sentence above tell readers about swing music during the late 1980s? A. Swing music once again became popular. B. Swing music was rewritten into modern versions. C. Modern instruments gave swing music a new sound. D. Unpublished compositions of swing music were discovered. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS Word Relationships Which pair of words from the article best describes ______ conveyed in the pictures on page ____? How do the words _____in the title relate to the information in the article? Which phrase best describes both _____ in ____ and the speaker of ________? Analyze Words in Text What does the author mean by saying, “ ?” Which words help the author convey the meaning that ? What does the author imply by saying “ ?” Read these lines from the poem. “ “ Based on the rest of the poem, which sentence best restates the meaning of the lines above? Read the quotation from the article: “ “ What does the phrase reveal about the narrator’s view of the situation? STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Part to Whole Relationships Product: Brace Map Cognitive Process: Analogies/Relationships Product: Bridge Map Read this line from the poem “Offspring.” Face slanted upward toward a threatening sky, Which word from the poem “Woman with Flower,” if used to replace threatening, would create the most opposite image of the sky? A. eager B. nurturing C. prodding D. watchful TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Analyze the meanings of words, phrases, and word relationships by using strategies including, but not limited to, context clues and word structure. Content Focus Analyze Words/Phrases Word Relationships Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should be used to assess the analysis of words and phrases and the identification of word relationships (e.g., synonyms, antonyms). Analogies should not be assessed. When assessing Analyze Words/Phrases excerpted text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the phrase being assessed If an item stem directs a student back to the text to determine the meaning of an unfamiliar phrase, the text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed phrase. When assessing Word Relationships the terms synonym and antonym should not be used in stem construction. Wording should be most similar in meaning or most opposite in meaning; Only grade-level appropriate words found within the text should be assessed The text should contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed words. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts must contain appropriate words, phrases, and word relationships to assess knowledge of vocabulary at grade level. (Additional information on pp. 27-29 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.6.9 MULTIPLE MEANINGS BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.6.9 The student will determine the correct meaning of words with multiple meanings in context. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS same meaning, used in the same way, adds to MULTIPLE MEANINGS MULTIPLE MEANINGS the idea, most similar, most opposite, pair of The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A The Grade 10 sample item below is based on words Day in the Stream” on page G–2. “Woman with Flower/Offspring” on page G– 15. Read this excerpt from the essay. I showed him how to keep his fly from dragging, Read these lines from “Woman with Flower.” how to fish the deeper pools. He was absorbed The leaf’s inclined to find its own direction; by the whys and the hows and the execution. Give it a chance to seek the sunlight for itself. In the lines above, what does the word In which sentence does execution have the inclined reveal about the leaf? same meaning as used in the excerpt above? A. The leaf grows at an angle to find its own A. After an execution of this computer program, direction. the entire system might shut down. B. The leaf bends down to find its own B. Their plan was sound, but its faulty execution direction. caused a delay in starting the project. C. The leaf hesitates to find its own direction. C. After agreeing on the terms of the sale, the D. The leaf prefers to find its own direction. execution of the deed to the house will be finalized. D. The execution of the terms of his final will and testament should occur as soon as the judge approves it. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Multiple Meanings Read the excerpt from the passage: “ “ In which sentence does the word have the same meaning as in the excerpt above? Read the lines from the poem: “ “ In the lines above, what does the word_____ reveal about the ____? Clarification How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Compare/Contrast Product: Double Bubble Map The student will: Analyze words that have multiple meanings and determine the correct meaning of the word as used in the text. Content Focus Multiple Meanings Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should be used to assess words with multiple meanings. Words with multiple meanings should be assessed using words on grade level or not more than two grades above or below grade level. Excerpted text must contain clear and sufficient context for determining the meaning of the assessed word. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts must contain words with multiple meanings and must provide clear and sufficient context for the student to determine the correct meaning. (Additional information on pp. 30-31 , Cognitive Process: Classifying Product: Tree Map FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.7.2 AUTHOR’S PURPOSE, AUTHOR’S PERSPECTIVE, AUTHOR’S BIAS BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.7.2 -The student will analyze the author’s purpose and/or perspective in a variety of text and understand how they affect meaning. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS AUTHOR’S PURPOSE AUTHOR’S PERSPECTIVE Explain/discuss, demonstrate/show, persuade, most likely agree, most important, agree with inform/entertain, compare features, main reason, statement, probably thinks, attitude/point of most likely intended, purpose in describing, wants view, experience leads to , generates reader to think, reveal narrator’s view position, creates tone, value the most, bias Author’s Purpose Author’s Perspective The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A Day The Grade 10 sample item below is based on in the Stream” on page G–2. “Cutting Off the World’s Roof ” on page G– 18. Read this sentence from the essay. And the fish, whether six inches or ten, were praised The author of this article would most likely like precious stones. make the statement that mountains must AUTHOR’S BIAS bias, attitude/point of view, experience leads to, persuade, most likely intended, wants reader to think Author’s Bias The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A Day in the Stream” on page G–2. Which statement from the essay reveals the author’s initial bias toward her client? The author uses this comparison to A. reveal the assorted colors of fish. B. describe the various sizes of fish. C. show the client’s appreciation for each catch. D. focus on the client’s preference for material goods. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS A. move with Earth’s crust. B. crumble when faults occur. C. yield to the forces of nature. D. sink under their own weight. A. “Typical beginner, I thought.” B. “First, I turned his reel around.” C. “He looked like a model for an outdoor catalogue.” D. “The felt on his wading boots was as white as snow.” STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES AUTHOR’S PURPOSE The author uses comparison to _____. What is the most likely reason the author of _____ included the section _____ in the article? Explain how _____ uses information to persuade readers to _____. How does the author persuade the ________ to ? What is the author’s purpose for saying ? What type of article did the author most likely intend________ to be? The author discusses ________ because __________? What is the author’s purpose for writing this passage? How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. Clarification AUTHOR’S PERSPECTIVE What is the author’s point of view about ? How does the author’s experience lead to ? What words or phrases create the tone of ? The author wants the reader to think . With which statement would the author most likely agree? Which feature would the author value the most? What is the author’s attitude toward ? Which statement best describes what the author probably thinks about ? The author of this passage would most likely make the statement that ________. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because_____________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Reasoning Product: Multi-Flow Map The student will: Identify the author’s purpose or perspective. The student will analyze the impact of the author’s purpose or perspective within or across texts. Content Focus Author’s Purpose (within/across texts) Author’s Perspective (within/across texts) Author’s Bias (within/across texts) Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts used in assessing author’s purpose should contain an identifiable author’s purpose for writing, including, but not limited to, persuading, entertaining, conveying a particular tone or a mood, informing, or expressing an opinion. The author’s purpose, perspective, and bias should be recognizable within or across texts. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts may include, but are not limited to, persuasive articles, essays, editorials, and informational articles. (Additional information on pp. 33-35, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.7.3 MAIN IDEA BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.7.3-The student will determine the main idea or essential message in grade-level or higher texts through inferring, paraphrasing, summarizing, and identifying relevant details. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS MAIN IDEA/SUMMARY/PREDICTION RELEVANT DETAILS in conclusion, best summarizes, lesson/moral, essential most important, most valuable, most concern, message, primary, main, central idea supports, emphasizes, describes, characterizes, contributes Main Idea Relevant Details The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “Swing Is The Grade 9 sample item below is based on the Thing!” on page G–6. “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. Which statement best expresses the main idea of the According to the article, which musician helped article? America rediscover swing music? A. Art forms are fads that are enjoyed temporarily. A. Frank Sinatra B. Personal preferences influence musical appreciation. B. Duke Ellington C. The value of music lies in how it enhances human C. Louis Armstrong lives. D. Harry Connick Jr. D. The success of an artist is measured by future generations. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS MAIN IDEA How have I used this benchmark in my reading? Which statement best expresses the main idea of the How did the benchmark help me better article? understand the text? What is the main idea of this article? Where is my learning on the scale? What would be another good title for the article? ___ I can teach someone else. Based on all the information given, how does each ___ I can do it on my own. piece contribute to the idea that_______________? ___ I understand, but have questions. Which sentence gives the best summary? Which statement best describes the lesson/moral of this story? STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK What is the primary topic in the article? What is the essential message in the article/story? After reading ___________ (lit or informational What is the central idea of the article? text), the evidence from the text that helps me What is the main goal of ? understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential RELEVANT SUPPORTING DETAILS question because ______________________. In what ways did ______ experience ______? According to the article, which (person) helped ___? Which sentence best characterizes ‘s THINKING MAPS CORRELATION attitude toward ? Cognitive Process: Classify How does support the Product: Tree Map: Main Idea and Relevant idea that ? How can the reader prove the idea that is Details the main idea of this text? CONCLUSIONS/INFERENCES From reading the article, the reader can infer that _____ will _______. Based on the passage, which action will the narrator most likely take in the future? Cognitive Process: Infer Product: Flow Map CONCLUSIONS/INFERENCES imply, infer, might happen if, prove, concludes Conclusions/Inferences The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Cutting Off the World’s Roof ” on page G–18. From reading the article, the reader can infer that the “world’s roof ” will A. be avoided by adventure seekers. B. increase in elevation in the future. C. continue to be studied by geologists. D. be affected by major fault movements. TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Determine the main idea (stated or implied) Identify a correct summary statement Locate relevant details and facts Draw logical conclusions Make appropriate inferences Use details to make predictions beyond a text within or across grade-level appropriate texts. Content Focus Main Idea (stated or implied) Summary Statement Relevant Details Conclusions/Inferences Predictions Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts with an identifiable main idea (stated or implied) Relevant details from which students may draw logical conclusions or make inferences within or across texts. Paraphrasing should not be assessed. Items may assess a student’s ability to identify a correct summary statement. Text Attributes Literary or informational. May include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Should include a main idea (stated or implied) with relevant details Enable students to draw logical conclusions and make appropriate inferences. (Additional information on pp. 36-39 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.7.4 CAUSE AND EFFECT BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.7.4 The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS CAUSE AND EFFECT: main cause(s), factor forces, Cause and Effect main reason(s), results, conflict, might happen if, The Grade 9 sample item below is based on influences, decide to, particular action, most affected “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. by, since, as a result, led to, leads to, brings about, therefore, accordingly, effects, effect of According to the article, what is one reason for swing music losing its role as a major form of entertainment? HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS A. Swing music fans began wearing unusual clothing. B. Young people chose to attend summer music camps. C. Swing music concerts started to attract unruly crowds. D. People became interested in listening to individual singers. STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS CAUSE What caused to___? Why did happen to_____? How did the conflict between and begin? What is the main reason/cause that happens? Which factor forces/influences ? Why does the author describe the character as ______________? Why is _________ a significant event? EFFECT What was the effect of ? What were the results of _____________? What effect did _______ have on ______? After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. Cause and Effect The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Cutting Off the World’s Roof” on page G–18. What caused Nicholas Brozovic´ and his fellow geologists to first believe that glaciers influence the height of mountain ranges? A. models of mountain terrain B. analysis of prominent features C. pictures of the mountain summits D. measurements of various elevations TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. Clarification The student will: Identify cause-and-effect relationships within texts. May also need to discern a causal relationship implied in the text through the assimilation of facts and details provided. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK Content Focus Cause and Effect THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Cause and Effect Product: Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts used in assessing cause-and-effect relationships should contain identifiable causal relationships embedded in the text and/or contain sufficient facts and details to assist students in discerning implied causal relationships. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts should include an identifiable cause-and-effect relationship that may be stated and/or implied. (Additional information on pp. 40-41 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.7.5 TEXT STRUCTURE/ORGANIZATIONAL PATTERNS BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.7.5 The student will analyze a variety of text structures (e.g., comparison/contrast, cause/effect, chronological order, argument/support, lists) and text features (main headings with subheadings) and explain their impact on meaning in text. TEXT STRUCTURE: mostly explain, compare/contrast, problem/solution, argument/support, cause/effect, begins/repeats, ends/conclude, order/arranged, better understand, like, different, when, then, eventually, during, meanwhile, reasons, cause, as a result, develop the text, develop the information, additional paragraph, connection between, connect the ideas, organizes/sequence, passage/story/article, essay, flyer/list, biography, poem(s), statement, heading, section, paragraph, website, brochure HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS ORGANIZATIONAL PATTERNS Based on the main heading and subheadings, the reader can determine that the main organizational structure of the article is ____. How does the author organize the information in the passage to illustrate _________? How does the organization of the webpage help visitors find information about ______? What would an additional paragraph at the end of this passage most likely be about? What is the connection between in paragraph ____and in paragraph ? Why does the author connect the ideas of and ? Why did the author begin this passage by saying ? Why did the author use to develop this text? Why did the author conclude this passage by saying “ ?” What would happen if had been changed to ? What happened after ? How did the author organize the _______ paragraph? How does the author develop the information in this article? Which organizational pattern does the author use in this passage/article/essay? TEXT STRUCTURE How has the order in which the author arranged this passage about helped the reader understand ? This section ____ is different from the other sections of the website because it _______. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS Text Structures/Organizational Patterns Text Structures/Organizational Patterns The Grade 9 sample item below is based on The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Cutting “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. Off the World’s Roof ” on page G–18. Based on the main heading and subheadings, the reader can determine that the main organizational structure of the article is A. a comparison of Big Band music to other musical styles of the time. B. a description of the effects of Big Band era music on other musical styles. C. a chronological history of the highlights and musicians of the Big Band era. D. a listing of the artists and composers who contributed to the emergence of Big Band music. STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Compare/Contrast Product: Double Bubble Map Cognitive Process: Cause/Effect Product: Multi-Flow Map Cognitive Process: Sequencing Product: Flow Map How does Ken Howard organize the article “Cutting Off the World’s Roof ”? A. He writes mainly about his personal experiences. B. He describes differences between several theories. C. He answers questions about different mountain ranges. D. He persuades readers to accept one theory over another. TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Identify and analyze text structures/organizational patterns and determine how they impact meaning in texts. Content Focus Text Structures/Organizational Patterns (e.g., comparison/ contrast, cause/effect, chronological order, argument/support, definition/explanation, question/answer, listing/description) Content Limits Text structures found within grade-level appropriate texts should be identifiable and may include, but are not limited to, comparison/contrast, cause/effect, chronological order, and argument/support. Text features should not be assessed in this benchmark but will be assessed in LA.910.2.2.1 for literary text and in LA.910.6.1.1 for informational text. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Informational texts are more suited than literary texts toward item development for this benchmark; however, a literary text may occasionally be appropriate (e.g., one that utilizes chronological order, comparison/contrast, or cause/effect). Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Text structures must be clearly evident as indicated by signal words and phrases. Texts must contain identifiable organizational patterns. Texts may include identifiable viewpoints, positions, or persuasive arguments. Support should be objective and substantial. Paired texts or different sections within a text should include similar or opposing viewpoints, positions, or arguments. (Additional information on pp. 42-43 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.1.7.7 COMPARE AND CONTRAST BENCHMARK: LA.910.1.7.7 The student will compare and contrast elements in multiple texts. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS COMPARE: alike, main similarity, similar EXCEPT, Compare common features, shared elements, comparison, The Grade 9 sample item below is based on between, helps to illustrate, advantage, appropriate, “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. comparison, change before/after, like, just like, just as, in the same way, equally, similar, resembles According to the article, what do musicians Benny Goodman, Elvis Presley, and the Beatles CONTRAST: MOST different, different from, change have in common? beginning/end, attitude towards differ, concept relate to, distinguish characteristics, classify, disadvantage, on A. All studied music in New Orleans. the other hand, however, although, unlike, instead, B. All attracted audiences of enthusiastic fans. rather, as opposed to C. All helped to revive interest in swing music. D. All performed for soldiers serving in World War II. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS COMPARE How are and similar? Why does the author compare and in this passage? How does the comparison between and help to illustrate ? In what way is an appropriate comparison? What do and have in common? How is ‘s attitude toward like his/her attitude toward ? CONTRAST How does the narrator’s impression of _____ and ______ change throughout the passage? Explain how _______‘s opinion about ______ changed throughout _____. The ______ chart is different from the other text features because ______. How are and different? What advantage did have over ? Why did have more than ? How does the concept in article relate to the concept in the article ? Use details from and to support your answer. How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Compare/Contrast Product: Double Bubble Map Contrast The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Quest-4 Cell Phone––User Manual” on page G– 16. The CALENDAR SYMBOLS chart is different from the other text features in the user manual because it A. lists events in order of importance. B. illustrates how to input calendar dates. C. provides a key for categories of calendar entries. D. clarifies the operating instructions of the cell phone. TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Identify similarities between elements within or across texts or will identify differences between elements within or across texts. Content Focus Compare (similarities within/across texts) Contrast (differences within/across texts) Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should include elements that can be compared or contrasted and may include, but are not limited to, character, setting, descriptive language, subject, author’s purpose, author’s perspective, main idea, themes, and topics. Text Attributes Texts should be literary or informational. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Texts should provide sufficient information that establishes a clear relationship between the similarities or a clear relationship between the differences. Texts should include elements that compare or contrast. To assess this benchmark within a text, items should be based on elements that can be compared or contrasted. To assess this benchmark across texts, items should be based on two related texts that contain elements that can be compared or contrasted. (Additional information on pp. 44-46 , FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.2.1.5 ELEMENTS OF STORY STRUCTURE BENCHMARK: LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author’s use of literary elements (e.g., theme, point of view, characterization, setting, plot), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery). BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS Setting Resolution PLOT DEVELOPMENT/SETTING: main problem, lead to, The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Woman with indicates events, faces, plans to, indicates setting, creates Day in the Stream” on page G–2. Flower/Offspring” on page G–15. tone, words, phrases, add to the feeling, previously, first, How does the setting of the essay contribute to Which statement best conveys the resolution in the poem second, now, not long ago, frequently the development of the narrative? “Offspring”? CHARACTER DEVELOPMENT/POINT OF VIEW: A. The description of the creek provides an A. The daughter fulfills the speaker’s wishes. protagonist/antagonist, BEST describes, character showed, opportunity to explain how the fishing gear is B. The speaker recognizes the daughter’s individuality. feelings change, attitude/opinion, affect reactions, comments, used. C. The daughter discovers a past connection with the speaker. contribute, character’s responsibilities most likely reacted, narrator B. The abundance of fish in the wilderness D. The speaker accepts a superficial relationship with the CONFLICT: internal, external, main conflict, central conflict, stream allows for a detailed description of flydaughter. add to the feeling fishing. THEME: main subject, pair of words, main lesson learned, C. The remote dude ranch furnishes the positive result background for the fly-fishing adventure RESOLUTION: character change, solved/resolved, solution, experienced by the client. peace, conclusion D. The family vacation destination presents a location where the family members can enjoy activities together. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification PLOT DEVELOPMENT How have I used this benchmark in my The student will: How do ______’s comments contribute to the reading/math? Identify, analyze, and interpret elements of plot development of the story/article? How did the benchmark help me better development within or across texts. What events lead to the resolution? understand __________? Identify, analyze, and interpret other literary elements, such CONFLICT Where is my learning on the scale? as character development, character point of view, and What is the main conflict in the essay? ___ I can teach someone else. conflict and resolution within or across texts. When is the central conflict between ____ and _____ ___ I can do it on my own. Identify, analyze, and interpret how plot events contribute introduced in the story/poem? ___ I understand, but have questions. to conflict and resolution within or across texts. RESOLUTION Content Focus What in the passage indicates that the conflict is STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK Theme resolved? CHARACTER DEVELOPMENT How does _____'s character change from the beginning to the end of ___________? What word best describes the character? What pair of words best describes _______? How do the character’s responsibilities affect how he/she reacts? What phrase best describes the narrator’s _____? Which statement from the essay illustrates the characteristic the author appreciates most about _____? How does ___ change ____’s opinion about _____? CHARACTER POINT OF VIEW How do ____’s comments contribute to the development of the passage/poem? What is _____’s opinion of _____? THEME Which statement best describes ’s approach to life? Which sentence from the passage mostly expresses its theme? Which line from the poem clearly reveals its theme? How do the changes in the narrator’s feelings toward ___________ contribute to the theme? SETTING How does the setting add to the feeling that ______? Why is the setting at the beginning of the passage important? After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Sequencing Product: Flow Map Cognitive Process: Defining in Context Product: Circle Map Character Development Character Point of View Setting Plot Development Conflict (e.g., internal or external) Resolution Content Limits Texts should be grade-level appropriate and contain identifiable literary elements (e.g., theme, character development, character point of view, setting, plot development, conflict, resolution). Figurative language should not be assessed in this benchmark but should be assessed in Benchmark LA.910.2.1.7. Text Attributes Texts should be literary and may include, but are not limited to, fiction, nonfiction (e.g., biographies, autobiographies, personal and historical essays, diary entries, memoirs), poetry, and drama. When assessing theme, the text must have a strongly implied theme. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. To assess this benchmark within or across texts, items may be based on one text that contains a variety of literary elements; or two texts with related literary elements (e.g., theme, characterization, conflict, resolution). (Additional information on pp. 48-51, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) o o HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.2.1.7 FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE BENCHMARK: LA.910.2.1.7 The student will analyze, interpret, and evaluate an author’s use of descriptive language (e.g., tone, irony, mood, imagery, pun, alliteration, onomatopoeia, allusion), figurative language (e.g., symbolism, metaphor, personification, hyperbole), common idioms, and mythological and literary allusions, and explain how they impact meaning in a variety of texts. DESCRIPTIVE LANGUAGE: literary technique, overall tone, mood (weariness, gloomy) , create feeling, irony, imagery /setting, sensory details, alliteration, allusion, satire FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE: literary device, simile, metaphor, personification, characteristic describe, compares/applies, hyperbole, symbolism, pun, onomatopoeia HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS DESCRIPTIVE/FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE How do ______’s comments contribute to the development of the story/article? What word best describes the character? What pair of words best describes _______? What phrase best describes the narrator’s _____? Which statement from the essay illustrates the characteristic the author appreciates most about ___? How do ____’s comments contribute to the development of the passage/poem? Which statement best describes ’s approach to life? Which sentence from the passage mostly expresses its theme? Which line from the poem clearly reveals its theme? How does the author’s use of words and phrases convey meaning in the text? BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS Descriptive Language The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “A Day in the Stream” on page G–2. Read this sentence from the essay. To be with someone who was able to treasure the moment the way he did made me feel like I was exploring fly-fishing for the first time. What type of literary device does the author use in the sentence above? A. irony, expressing a contrast to the narrator’s skill at fly-fishing B. imagery, creating a vivid picture of the sport of flyfishing C. tone, emphasizing the narrator’s attitude toward her client D. onomatopoeia, using a word that sounds like its meaning STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Describing Product: Bubble Map Cognitive Process: Classifying Product: Tree Map Figurative Language The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Walking” on page G–12. Read this sentence from the essay. It was a green and sleeping bud, raising itself toward the sun. What literary device does the writer use in the sentence above? A. metaphor, comparing the sunflower to a tired child B. hyperbole, exaggerating the fast growth of the sunflower C. symbolism, representing the season of spring as a sunflower D. personification, portraying the sunflower as a person waking up TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Identify, analyze, interpret, and evaluate the author’s use of descriptive or figurative language and will determine how the author’s use of language impacts meaning in a variety of grade-level appropriate texts. Note: As recommended by Florida educators, pun should be assessed as a type of figurative language device used by authors and not as a type of descriptive language device, as indicated in the original benchmark language above. Content Focus Descriptive Language Figurative Language Content Limits Grade-level appropriate texts should contain clear examples of descriptive language (e.g., tone, irony, mood, imagery, alliteration, onomatopoeia, allusion, satire) and figurative language (e.g., symbolism, simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, pun). Idioms should not be assessed. Text Attributes Texts may be literary or informational and may include, but are not limited to, fiction, nonfiction (e.g., biographies, autobiographies, personal and historical essays, diary entries, memoirs, speeches, editorials), poetry, and drama. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. (Additional information on pp. 52-53, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.2.2.1 TEXT FEATURES BENCHMARK: LA.910.2.2.1 The student will analyze and evaluate information from text features (e.g., transitional devices, table of contents, glossary, index, bold or italicized text, headings, charts and graphs, illustrations, subheadings). BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS TEXT FEATURES: Text Features purpose, use to show, order in which arranged, aid The Grade 9 sample item below is based on understanding, opening paragraph “A Day in the Stream” on page G–2. section titled, likely to find passage, headings, illustration, photograph, titles/subtitles, heading/subheading, sections, Based on the essay “A Day in the Stream,” charts/tables/graphs, which caption would be most appropriate for diagrams/captions, italicized text, italicized print, maps, text the picture on the first page of the essay? boxes, keys/legends, stanzas A. a celebration of life B. a chance to use the new gear C. an exceptional day for fishing D. an eagerness to catch the first one HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS Why did the author use subtitles in the passage? How does the caption under the photograph help the reader to understand_____________? How does the photograph of______________ help the reader understand _______________? How do the photograph(s) and caption(s) help the reader understand___________________? From the pictures and subheadings of the article, the reader can conclude that ______. Based on the passage, which caption would be most appropriate for the picture on page _____? Explain how the (chart/ map/ diagram/ subheading/ caption/ illustration/ graph) aids the reader understands. The use of bold-print words throughout the ____ helps the reader to ___. Which statement from the passage is best supported by the diagram on page ___? STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS: How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK: After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Defining in Context Product: Circle Map Text Features The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Woman with Flower/Offspring” on page G–15. The text box that accompanies the poems “Woman with Flower” and “Offspring” was most likely included to A. provide the poet’s biographical information. B. document the poet’s publishing experiences. C. authenticate the poet’s training in creative writing. D. explain the poet’s inspiration for writing the poems. TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Identify, explain, analyze, and determine meaning from a variety of text features. Content Focus Text features Content Limits Text features should be assessed within grade-level appropriate literary fictional texts and literary nonfiction texts. Texts should include a single, identifiable text feature or should contain a variety of text features. Transitional devices, tables of contents, glossaries, bold text, and indices should not be assessed. Text Attributes Texts should be literary and may include, but are not limited to, fiction, nonfiction (e.g., biographies, autobiographies, diary entries, memoirs), poetry, or drama. Stimuli found in texts may include titles, headings, subheadings, sections, charts, tables, graphs, illustrations, maps, diagrams, captions, italicized text, and text boxes. (Additional information on pp. 54-56, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA910.6.1.1 ANALYZING TEXT FEATURES BENCHMARK: LA.910.6.1.1 The student will explain how text features (e.g., charts, maps, diagrams, sub-headings, captions, illustrations, and graphs) aid the reader’s understanding. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS titles/subtitles ,heading/subheading, ,sections, illustration/photograph ,charts/tables/graphs, diagrams/captions, italicized text/print, maps/symbols ,text boxes, keys/guide, words stanzas, aid understanding, better understand, organize information, arrange information, bullets, footnotes, table of contents, bold print, glossaries/indices, website, creator Text Features The Grade 9 sample item below is based on “Swing Is the Thing!” on page G–6. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS Why did the author use subtitles in the passage? How does the caption under the photograph help the reader to understand_____________? How does the photograph of______________ help the reader understand _______________? How do the photograph(s) and caption(s) help the reader understand___________________? From the pictures and subheadings of the article, the reader can conclude that ______. Based on the passage, which caption would be most appropriate for the picture on page _____? Explain how the (chart/ map/ diagram/ subheading/ caption/ illustration/ graph) aids the reader understands. The use of bold-print words throughout the ____ helps the reader to ___. Which statement from the passage is best supported by the diagram on page ___? From the photographs and headings of this article, the reader can conclude that A. swing music was not popular for dancing. B. several great musicians played swing music. C. swing music did not remain popular for long. D. many swing musicians played the same instrument. How have I used this benchmark in my reading/math? How did the benchmark help me better understand __________? Where is my learning on the scale? ___ I can teach someone else. ___ I can do it on my own. ___ I understand, but have questions. STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK After completing___________, the evidence from the lesson that helps me understand and answer the essential question is ____________. This relates to the essential question because ______________________. THINKING MAPS CORRELATION Cognitive Process: Classifying Product: Tree Map Cognitive Process: Compare/Contrast Product: Double Bubble Map Text Features The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Cutting Off the World’s Roof ” on page G–18 and references the diagram on page G–20. Which statement from the article is best supported by the diagram on the third page of the passage? A. “And in any case, Brozovi´c points out, it’s unlikely that faults would turn up in just the right places to make terrain taper off right above the snow line.” B. “As the Himalayan mountains come up, glaciers shear off their tops like a buzz saw.” C. “They start to form after a mountaintop pokes up past the snow line.” D. “The tallest, pointiest peaks, then, can become glacier-proof.” TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES Clarification The student will: Identify, explain, analyze, and determine meaning from a variety of text features. Content Focus Text Features Content Limits Text features should be assessed using grade-level appropriate texts that may include, but are not limited to, informational articles and functional reading materials. Texts should include a single, identifiable text feature or should contain a variety of text features. Text Attributes Texts should be informational. Texts may include, but are not limited to, grade-level appropriate informational articles and functional reading materials. Stimuli found in text may include headings, subheadings, sections, titles, subtitles, charts, tables, maps, diagrams, captions, illustrations, graphs, or italicized text. (Additional information on pp. 58-59, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10) HIGH SCHOOL BENCHMARK TASK CARD: LA.910.6.2.2 VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY BENCHMARK: LA.910.6.2.2 The student will organize, synthesize, analyze, and evaluate the validity and reliability of information from multiple sources (including primary and secondary sources) to draw conclusions using a variety of techniques, and correctly use standardized citations. BENCHMARK SIGNAL WORDS AND SAMPLE ITEMS VALIDITY AND RELIABILTY Analyze and Evaluate Information Determine the Validity and Reliability of Information supports conclusion , support /add to idea ,reasons behind , MOST The Grade 9 sample item below is based on The Grade 10 sample item below is based on “Cutting Off “National Park Service Homepage” on page G–4. the World’s Roof ” on page G–18. valid , BEST be used to ,suggest central idea , leads reader to The homepage of the National Park Service website What is the strongest evidence in support of the glacial believe, MOST accurate statement, accurate information, greatest would be useful for all of the following purposes erosion theory? benefit, credible evidence , sound argument, convincing argument , EXCEPT A. The tallest mountains are those closest to the equator. reliable, dependable evidence , relate to concept , factors EXCEPT, A. planning a family vacation. B. The faults are forty miles long and several miles deep. NOT true B. locating information about a summer job. C. Angles of mountain slopes increase below the snow line. C. comparing mountain ranges around the world. D. Rocks of similar ages appear at different heights and D. writing a research report about weather locations. conditions. HIGH ORDER QUESTION STEMS STUDENT SCALE QUESTIONS TEST ITEM SPECIFICATION NOTES How have I used this benchmark in my Clarification Based on all information given, how does each part add reading/math? The student will: to the idea that ? How did the benchmark help me better Use a variety of techniques and strategies to analyze How do and understand __________? and evaluate information within or across texts. suggest the central idea that ? Where is my learning on the scale? Identify the validity and reliability of information in a According to the information given (including the chart, ___ I can teach someone else. text by identifying supporting facts and analyzing the graph, photograph caption, etc…) about , ___ I can do it on my own. development of argument(s) within or across texts. ___ I understand, but have questions. explain ________? May also be asked to apply information from a text in a valid and/or reliable way. People who read this article will learn to/that _ ___? Identify relationships between two or more ideas or How does the concept in article relate STUDENT SUMMATIVE WRITING TASK among other textual elements found within or across to the concept in the article ? Use texts. After completing___________, the evidence from details from and to support your answer. Content Focus the lesson that helps me understand and answer What information supports the conclusion Synthesize Information (within/across texts) the essential question is ____________. This that____________? Analyze and Evaluate Information (within/across texts) relates to the essential question because Based on the passage, how does the author support the ______________________. Determine the Validity and Reliability of Information idea that the characters have a ______ relationship? (within/across texts) Content Limits THINKING MAPS CORRELATION What leads the reader to believe that_____________? Texts should be grade-level appropriate and present Cognitive Process: Seeing Analogies information in order to: Product: Bridge Map Aid the student’s determination of validity and reliability of information Express a relationship among two or more ideas; Express a relationship among ideas and certain text features; Reflect ideas that can be analyzed and evaluated. This type of information may come from both primary and/or secondary sources. Cognitive Process: Cause and Effect Synthesis should be assessed by identifying the Product: Multi-Flow Map relationships among two or more ideas. Text Attributes Texts should be informational but on occasion may be literary; both may include either primary or secondary sources. Primary sources may include, but are not limited to, eyewitness accounts of events, such as letters, journals, diaries, and historical documents. Secondary sources may include, but are not limited to, encyclopedias, books, newspapers, and magazine articles. Other stimuli may include, but are not limited to, illustrations with captions, graphics, and charts. Evidence presented in texts should be logical, internally consistent, and clearly developed by the author in order to assess the validity and reliability of information. (Additional information on pp. 60-63, FCAT 2.0 READING Test Item Specifications Grades 9–10)







