Energy Flow, Part 1
advertisement

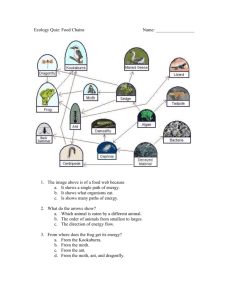
~Ecology Notes~ 1. Sun 2. Autotrophs 3. Heterotrophs 4. Decomposers ENERGY IS NOT RECYCLED!!!! The sun is the original source of energy for most ecosystems. All organisms in an ecosystem can be divided into one of two groups based on how they get their energy: Autotrophs Heterotrophs Organisms that make their own food from light or chemical energy. Include: Plants Algae Some bacteria Organisms that eat other organisms to get the energy they need to survive. Include: Humans Fish Mushrooms Organisms that eat only other animals Ex: Lions and wolves Organisms that eat only plants Ex: Rabbits and cows Organisms that eat plants and animals Ex: People and bears Organisms that feed on small pieces of dead plants and animals. Ex: worms and roly polies Organisms that use digestive chemicals to break down dead organisms Ex: Fungus (mushrooms and mold), and some bacteria In order for an ecosystem to survive, there must be a perfect balance of autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers. The autotrophs make oxygen and food for the heterotrophs. The heterotrophs produce carbon dioxide for the autotrophs and waste for the decomposers. The decomposers break down the animal waste and dead organisms and produces carbon dioxide for the autotrophs. A simple diagram to show one possible path of energy through an ecosystem. A complex diagram that shows all possible paths of energy through an ecosystem. Basically shows how all the food chains in an ecosystem connect to each other. Trophic Level = each step in a food chain or food web Each trophic level depends on the level below it for energy Only 10% of the energy is passed from one trophic level to the next. Shows the relative amount of energy being passed from one trophic level to the next. The total amount of living tissue within a trophic level A biomass pyramid represents the amount of potential food available for each trophic level As you move up a food chain, there are fewer organisms and less biomass at each level. Producers are always on the bottom.