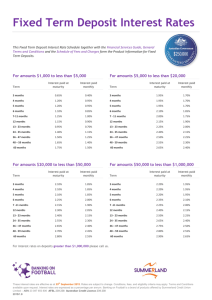
What is Strategy? - Strategic Management 3e
advertisement

Strategy Issues in Industries and Life Cycle Stages Chapter 8 Strategic Management:Value Creation, Sustainability, and Performance, 3e, 2014 Learning Objectives 1. Stages of industry life cycle and their impact on business strategy. 2. Implications of competing in fragmented or concentrated industries. 3. Value chain activities appropriate for organizational life cycle stages. 4. Risks of first mover strategy. 5. International strategy considerations. Industries Evolve Opportunity recognition New knowledge about value creation Growth in demand (and supply) Industry Stages Introduction – innovative new companies Growth – increased demand, standardization Maturity – slowed demand, commoditization Decline – substitutes abound Renewal – new customers, new segments Redefine industry boundaries Disaggregate bocks of value chain activity Redefine value Shift to complements Competing in Consolidated Industries Usually occurs during Growth and Maturity stages. Usually scale (cost containment) addresses increasing standardization. Focused differentiation can also work Mobility barriers inhibit large companies Anti-trust concerns hinder large companies Large companies blind to niche opportunities Large companies subject to margin pressure, cannot always divert resources Competing in Fragmented Industries Usually occurs When entry barriers are low, or Where value creation is locally-based (so that consolidation is ineffective) Unbundling or disaggregating value chain activity into new configurations Redefining how and where value is delivered, i.e change the game Industry "roll-ups" – creating corporate value while maintaining local presence Organizational Life Cycles Conception – innovation, strategy, finance Commercialization – production, hiring, and organizational issues Growth – scaling up, marketing, culture, pace of change and chaos Maturity – profitability, internal controls First Mover Strategy Not always successful First Mover Advantages Timing advantages Set the standard "Installed base" – creates switching costs Reputation Preemption Size advantages Scale Experience curve Scope Network First Mover Risks Expensive to pioneer new domain Technology uncertainty – standard may ultimately be different Demand uncertainty – "Will they buy?" Inertia – reluctance to modify approaches as the industry develops ("sunk cost") Dealing with Fast Growth Growth at 20+ % per year Organizational problems: chaos, paperwork, customer attention, competitive attention "Solutions" Use vision, mission, principles to unify Carefully examine value chain activities What's strategically critical, what's not Emphasis on internal coordination of activities Consider restructuring (Chapter 11) Strategic Renewal Usually needed at the Maturity Stage "Solutions" Build opportunity recognition capabilities Reconfigure resources to develop new operational capabilities that can be leveraged Develop new products / services at "platform" level – a foundation for future variations Optioned investments in innovation – a portfolio approach Retool culture and incentives to embrace change International / Global Strategy Growth into international markets is a strategic choice among alternatives Common motivations New geographic revenue opportunities Leverage value chain and resources Spread risk Achieve location-based advantages (where value creation is enhance by local presence) Leveraging Value Chain Four International Strategies Global Value added in upstream activities Efficiency through scale & scope Minor country-to-country variations Transnational Multi-Domestic Centralized Single Country Value added downstream near customer Efficiency through scale & scope is important Variations across countries are meaningful Value added downstream near customer No pressure to be efficient Variations across countries are significant Value added in upstream activities No pressure on efficiency Occurs where markets are protected or government controlled