Electrical Engineering
advertisement

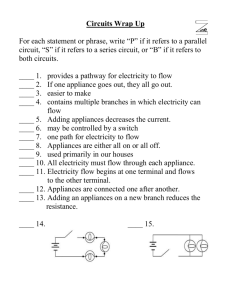
Electrical Engineering Grade 10 ST May 2012 Electricity • Static electricity: the jumping of electrons from one object to another causes static electricity. • However, because the movement doesn’t last, this form of electricity is not capable of supporting our electrical devices • Current electricity is the steady flow of electrons which lights our homes and streets and runs our household appliances and electronics. Electrical Engineering • Electrical engineering involves the designing and developing of electrical objects and electrical systems • Electrical Engineering covers two main areas: – Electricity – Electronics • All electrical appliances, like a toaster and electronic devices, like computers depend on ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS Electricity vs. Electronics • The main difference between electricity and electronics lies in the design of the circuits – An electrical circuit provides a path in which a constant source of electrons can flow. Cont... Electricity Electronics Electrical components are made up of materials that are conductors like metals and alloys Electronic components are made up of materials called semiconductors like silicon Electrical components are larger and are designed for more powerful circuits with higher intensity like motors Electronic components are very small and are designed for circuits with lower intensity The conduction is not finely controlled The electrical conduction is finely controlled allowing electronic devices to process information Working on an electrical field in a house would belong to the field of electricity Working on a computer circuit would belong to the field of electronics Examples • Electronics – Cell phone – TV – Computers • Electrical devices – car motor – toaster – ovens AC vs. DC • Not quite... • Direct current is electrical current which supplies a constant flow of electricity in the SAME direction. – A battery is a common example of DC current • Alternating current is electrical current which comes from a generator. As the electromagnet is rotated in the permanent magnet the direction of the current alternates once for every revolution. – A power plants generate AC current at a rate of 60 Hz, which means the electrons move back and forth at a rate of 60 times per second. – AC current is easy to transport over long distances Electrical functions • Power Supply: • Conduction: • Insulation: • Protection: • Resistance: • Controls: