File
advertisement

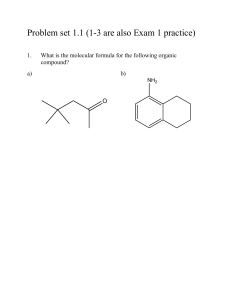
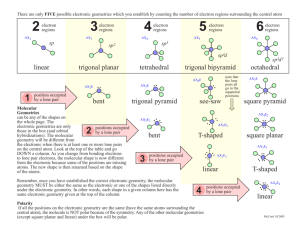
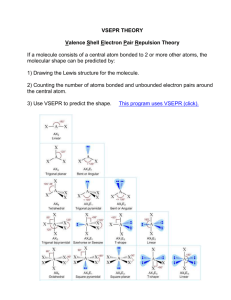
Once you’re in, you’re in. When the bell rings, voice at zero, working on the Do Now in Do Now Form. Pick up daily handouts. Pick up a Do Now Form. Pick up turned back docs. Pick up a white board, 1 sock, 1 dry erase marker. Keep your marker in the “parking spot” until further instructed. Do Now 10/8/2013 • Draw the Lewis dot structure for the following two IONIC bonds – Sodium and Oxygen – Magnesium and Iodine • Write the noble gas configuration for the following – Aluminum – Iron Do Now 10/7/2013 • Draw the Lewis dot structure for the following two IONIC bonds – Sodium and Oxygen – Magnesium and Iodine • Write the noble gas configuration for the following – Aluminum – Iron Tutoring and Makeup Work • Tuesday/Thursday this week; Wednesday at Lunch • THREE weeks left in the quarter – if your name is on the board , you owe me a quiz or a test!! • If you have a zero and you think you turned it in I have passed it back to you and you need to turn in again either graded or with proof it was turned in on time for full credit Grade Example • Test 1 – 80 • Quiz 1 – 100 • Test 2 – 75 • Report 1 – 0 • Report 2 – 0 • Test 3 – 77 Average = 55% • Test 1 – 80 • Quiz – 100 • Test 2 – 75 • Report 1 – 50 • Report 2 – 50 • Test 3 – 77 Average = 72% Test 1 – 80 Quiz 1 – 100 Test 2 – 75 Report 1 – 80 Report 2 – 90 Test 3 – 77 Average = 84% Homework • Naming Worksheet – From Thursday last week on the back of guided notes • Bohr Test Corrections (up to 4 points) Parent Signature, corrections on the back DUE TOMORROW** • VSPER Model worksheet (underline Lewis dot, shape, bond angles)** **Graded Bohr Model Test - Hand back - Review common mistakes Upcoming Dates • 10/9/2013 – Nomenclature and Formula Quiz • 10/10/2013 – Naming and Formula Test Objectives SWBAT •Explain how covalent bonding in compounds determines its characteristics •Determine that a bond is predominately covalent by the location of the atoms on the Periodic Table •Apply the concept of electrons form covalent compound that is stable •Write names of ionic and covalent compounds •Based on Lewis Structure of a compound determine the geometry and bond angles Pop call Bonding Review – Hands up, Pair up • Metallic • Ionic • Covalent Covalent Bonding Practice • • • • • • wb 2 oxygen 2 fluorine 2 Bromine HBr SiF4 N2S3 Naming Review • Ionic – Rules? – Between what types of elements? – Compounds/molecules? • Covalent – Rules? – Between what types of elements? – Compounds/molecules? wb Ionic Naming Practice • • • • • wb NaBr Zn3P2 NH4F Pb3N2 CdSO3 • • • • • Sodium bromide Zinc phosphide Ammonium flouride Lead (II) nitride Cadmium sulfite Ionic Formula Practice • • • • Calcium Bromide Sodium Hydride Potassium hydroxide Platinum (II) sulfide wb CaBr2 NaH KOH PtS Covalent Naming Practice • • • • • • P4S5 O2 SeF6 CH4 SCl4 NF3 wb Tetraphosphorus pentasulfide Oxygen Selenium hexaflouride Methane Sulfur tetrachloride Nitrogen trifluoride VSEPR Model (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) The structure around a given atom is determined principally by minimizing electron pair repulsions. Electron pairs centered around a central atom tend to orient themselves as far apart as possible Used to predict geometry of a molecule or a polyatomic ion Predicting a VSEPR Structure Draw Lewis structure. Put pairs as far apart as possible. Determine positions of atoms from the way electron pairs are shared Determine the name of molecular structure from positions of the atoms. Steric Number 1 1 atom bonded to another atom (reference handout) Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 linear 1 lone pair 2 lone pairs 3 lone pairs 4 lone pairs Steric Number 2 2 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Lone pair means a NOT bonded pair. Steric No. 2 Basic Geometry 0 lone pair linear 1 lone pair linear 2 lone pairs 3 lone pairs Steric Number 3 3 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 lone pair 2 lone pairs bent / angular linear 3 trigonal planar 3 lone pairs Steric Number 4 4 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 lone pair 2 lone pairs 3 lone pairs bent / angular linear 4 tetrahedral trigonal pyramid Steric Number 5 5 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 lone pair 2 lone pairs 3 lone pairs trigonal bipyramid sawhorse / seesaw t-shape linear 5 Steric Number 6 6 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 lone pair 2 lone pairs Octahedral square pyramid square planar 6 3 lone pairs Steric Number 7 7 atoms, or lone electron pairs, or a combination of the two, bonded to a central atom. Steric No. Basic Geometry 0 lone pair 1 lone pair pentagonal bipyramidal pentagonal pyramidal 7 2 lone pairs 3 lone pairs Lewis Structure and VSEPR practice • • • • • Carbon Tetraflouride BF3 NF3 H2CS Carbonate ion (CO3) Finish this sheet for HW