What is HAZUS-MH? - Texas Hazard Mitigation Package
advertisement
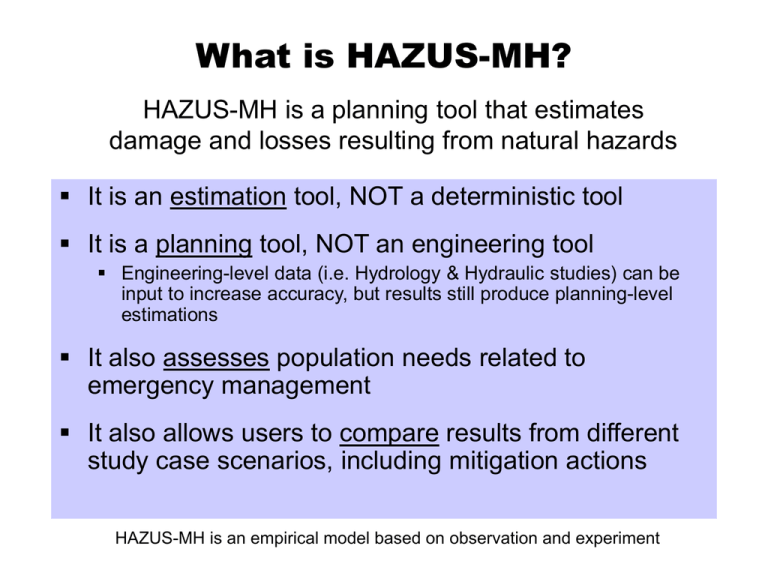
What is HAZUS-MH? HAZUS-MH is a planning tool that estimates damage and losses resulting from natural hazards It is an estimation tool, NOT a deterministic tool It is a planning tool, NOT an engineering tool Engineering-level data (i.e. Hydrology & Hydraulic studies) can be input to increase accuracy, but results still produce planning-level estimations It also assesses population needs related to emergency management It also allows users to compare results from different study case scenarios, including mitigation actions HAZUS-MH is an empirical model based on observation and experiment Texas Hazard Mitigation Package (THMP) Easy to Use (less expensive) Identification Tool www.THMP.info HAZUS Loss Estimation Tool Local Hydrology & Hydraulic Studies H & H specific applications H&H Engineering Tools & Data Highly Accurate (more expensive) HAZUS-MH: Family of Products Models HAZUS-MH is a multi-hazard (MH) application Flood, Hurricane (Wind), Earthquake Data Integration Tools • Inventory Collection And Survey Tool (InCAST) • Building Import Tool (BIT) • * Flood Information Tool (FIT) Linkage to 3rd-party Models • Areal Locations of Hazardous Atmospheres (ALOHA) • Flood Waves (FLDWAV) HAZUS-MH: Technical Components Software: Custom GIS (geographic information system) Runs on ESRI products; ArcGIS and Spatial Analyst • ESRI products must be acquired separately Spatial Analyst required for Flood Model only • HAZUS-MH is free from FEMA <www.fema.gov/hazus> Current HAZUS-MH version (MR1) runs on ArcView 9.0 Data: National data sets Inventory of assets (buildings, infrastructure, population/demographics, etc.) • Users may modify data sets or model factors • Users may add their own data ArcGIS / ArcView & Spatial Analyst www.esri.com HAZUS-MH: Technical Notes Operating System Requirements Windows XP SP1 Windows 2000 SP1 – SP4 GIS Requirements ArcGIS 9.0, SP1 Spatial Analyst extension (Flood Model only) HAZUS-MH: Technical Requirements From FEMA Web Site ArcGIS and HAZUS require significant computing power and resources (Computer hard disk space varies per dramatically per User) HAZUS-MH: Methodology 5. Estimate Losses/Needs 4. Estimate Damage 3. Overlay Inventory 2. Define Flood Hazard 1. Define the Geographic Area for Analysis HAZUS-MH: Models FLOOD HURRICANE EARTHQUAKE HAZUS-MH: Methodology MODEL Hazard Inventory Building Stock Essential Facilities High Potential Loss Facilities Transportation Utilities Hazardous Materials Demographics/Population Agricultural Products Vehicles ANALYSIS Damage Assessment Flood Hurricane/Wind Earthquake RESULTS Direct Loss Economic Business Interruption Shelter Social Casualties Loss Essential Facilities Estimation Functionality Transportation Utilities Water System Performance PARAMETERS & SCHEMES Emergency Response Power Transportation HAZUS-MH Methodology FLOOD HAZARD Frequency Discharge Depth/Elevation Velocity Duration DIRECT DAMAGE General Building Stock Essential Facilities High Potential Loss Facilities Transportation Facilities Lifelines INVENTORY Buildings Infrastructure Population Land Use INDUCED DAMAGE Fire Following Flood Hazardous Materials Release Debris Generation DIRECT LOSSES INDIRECT LOSSES Cost of Repairs/Replacement Income Loss Crop Damage Casualties Shelter and Recovery Needs Supply Shortages Sales Decline Opportunity Costs Economic Loss HAZUS-MH: Levels of Analysis Link HAZUS with Hydraulic Model 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% bu Su D en se U rb an rb . rb . bu rb . bu Su ed . Su ht M Lig O pe n/C oa st al 0% Damage Distribution of Terrain 45% Percentage of Area Community-specific Damage Functions Flood Depth Level 3 Number of Buildings by Specific Occupancy User Modified Data 120 100 Building Count Level 2 (most users) Modify Building Inventory 80 60 40 20 0 RES1 Level 1 Level 1 RES2 RES3 RES4 RES5 RES6 FIT (add local H & H) Applications in Mitigation Planning & Emergency Management Emergency Preparedness Response & Recovery HAZUS-MH Loss Reduction (Mitigation) HAZUS Applications: Emergency Preparedness Develop emergency response plans • Temporary housing • Debris removal • Emergency power and water • Emergency medical services • Evacuation/emergency route clearance Organize response exercises HAZUS Applications: Mitigation Mitigation Assessment • Identify ‘at-risk’ communities Mitigation Measures • Strengthen existing structures • Strengthen window/door openings and siding Mitigation Programs • Adopt and enforce hazard-resistant building codes • Land use planning HAZUS Applications: Response and Recovery Post-disaster damage assessment and groundtruthing Response planning for critical transportation outages Identify critical infrastructure Recovery action planning Long-term economic recovery planning Benefit Summary HAZUS-MH allows user to: • IDENTIFY vulnerable areas that may require planning considerations • ASSESS level of readiness and preparedness to deal with a disaster before disaster occurs • ESTIMATE potential losses from specific hazard events (before or after a disaster hits) • DECIDE on how to allocate resources for most effective and efficient response and recovery • PRIORITIZE mitigation measures that need to be implemented to reduce future losses (what if) FEMA: Ordering HAZUS www.fema.gov/hazus • • • • HAZUS-MH Overview Brochures/Materials Order Information Application Case Studies • • • • National Conference Info FEMA/EMI Training Schedule General Contact Info Technical Support/FAQ’s Flood Hazard Model Initial Step: Create/Open Study Region RIVERINE 2. Generate Stream Network 1.Define Topography 4. Run Hydrology 3. Define Study Case Segment Shoreline COASTAL 5. Compute Hazard Enter 100-yr Elevation Final Step: Run Analysis & View Results Initial Step: Create a Study Region Inventory Square Footage Inventory Dollar Exposure Flood Hazard HAZUS computes: • Floodplain Boundary • *Flood Depth Grid* Floodplain Boundary Flood Water Elevation Normal Water Elevation (main channel) Flood Water Elevation - Ground Elevation = Flood Depth Vertical Datum: Sea Level 1. Define Topography 2. Generate Stream Network 3. Select a Study Case 4. Run Hydrology 5. Compute Hazard (Run Hydraulics) Final Step: Run Analysis View Results by Results Table View Results by Map View Results by Attribute Table REMEMBER! units are in thousands of dollars (derived from HAZUS Tables) View Results by Summary Report