Writing up your undergraduate dissertation
advertisement

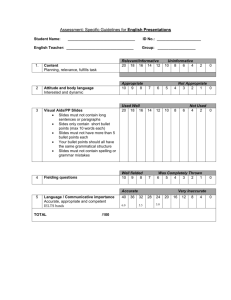
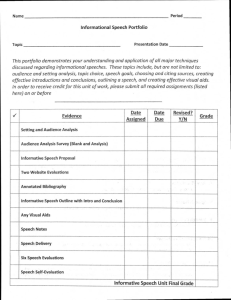
Planning and structuring your report Dr Michelle Reid Study Adviser, University of Reading Overview of the workshop • What are the features of good reports? • Writing for an audience and purpose • Sections of a report • Planning your report and writing up To start you thinking… What do you want from this workshop? Work in small groups: • Each person to write on a post-it one question they hope to have answered by the end of the workshop • Swap post-its with another group • Discuss the questions within the group and share your answers What is a report?... Reports Essays • Formally structured • Semi-structured • Informative and fact-based • Argumentative, idea-based • Written with a specific purpose and reader in mind • Not written with a specific reader in mind • Always include section headings • Written in single narrative style throughout What is a report? (cont) Reports Essays • Will sometimes use bullet points • Do not usually include subheadings or bullet points • Often includes tables or graphs • Rarely include tables or graphs • May offer recommendations for action • Offer conclusions about question Features of good reports A good report is: • Well structured • Relates results to purpose • Uses appropriate writing style • Has correct use of referencing • Answers the brief and considers the audience • Includes appropriate amount of relevant data • Uses clear expression, avoids jargon Writing for an audience and purpose Reports are informative – they are aimed at delivering information to an audience for a specific purpose. Identifying the audience and purpose of your report will help you to: – Decide what to include – Be relevant and concise – Give the audience the information they need Audience and purpose Read the report brief carefully and decide: • Who is your report for (more than one audience)? • What does the audience know already? • What does the audience want to find out? • Why does the audience want the information – what actions will they take based on the information? Audience and purpose: worked example [Suggested example] Write a report for your University’s Students’ Union on how alcohol manufacturers target students when marketing their products. Audience and purpose: worked example Who is the audience? - The Union, especially the student welfare officers, and bar / facilities managers. What do they know already? - The revenue the Union gets from alcohol sales. - How the Union runs drinks promotions. - The Union’s suppliers and their prices. (As they have the info, you may not need to tell them all this in your report) Audience and purpose: worked example What do they want to find out? - How alcohol manufacturers target the student market. - How much of their market is made up by student sales. - The advertising techniques and strategies they use to appeal to students. - Are alcohol manufacturers trying to expand their student market – future trends? Audience and purpose: worked example Why does the audience want the information? - To have a wider awareness of the topical and controversial issue of student drinking. - To discern if students are at risk from more aggressive alcohol marketing. - To consider whether the Union needs to run awareness campaigns and offer more alternatives to alcoholic drinks. A common report structure • Abstract / Executive Summary • Introduction • Literature review • Methods • Results / Data / Findings • Discussion • Conclusion / Recommendations • Bibliography / Reference List • Appendices How do your reports differ from this? Where does it go in my report?... • Does it provide background to your research? (Introduction or Literature Review) • Does it describe the types of activity you used to collect evidence? (Methods) • Does it present factual data? (Results) Where does it go in my report? (cont) • Does it interpret the results and place them in the context of the background research? (Discussion) • Does it make recommendations for action? (Conclusion) Activity: Analysing sections of a report Working in small groups – each group has an extract from a report and has to decide: • Which section of a report does your extract come from? • How do you know – what is it about the content and style that tells you this? [Use own examples] Planning Top Tips • Make an outline structure of your report headings • Group similar ideas under the same heading • Plan what goes into each section • If you are unsure where in your report some information should go…ask yourself ‘what function does this information perform?’ Where do I start? • How do you start writing a report? • Which sections do you write first and why? • What sections do you find most challenging to write and why? Where do I start? 1) Literature survey (need this to shape the course of your research) 2) Methods and Results (when you’ve done it, describe it) 3) Introduction (to establish your research questions and the purpose of the report) 4) Discussion and Conclusion (interpret your findings in light of the research purpose / question) 5) Abstract (you can’t summarise what you’ve written until you’ve written it!) What makes a good report?... • Read the brief carefully • What does the audience know and what do they want to find out? • Check which sections you need • Remember reports are meant to be informative • Write simply and precisely What makes a good report? (cont) • Spend more time on your discussion section • Make sure your references are complete and accurate • Plan your time • Proofread carefully Writing up Top Tips • Write up as you go along if possible – avoids having to write lots in a rush at the end • Have a separate sheet / file for each section and add notes when you think of them • Link your findings back to your research questions and to your background reading – do your findings confirm or contradict what others have found out? Further resources LearnHigher report writing webpages www.learnhigher.ac.uk/learningareas/reportwriting/home.htm For guides and exercises on all aspects of reports. Report writing (Napier) www2.napier.ac.uk/getready/writing_presenting/reports.html A clear and easy to follow introduction to report writing with interactive exercises on report structure and layout. Unilearning (Wollongong, Australia) http://unilearning.uow.edu.au/main.html Includes different types of report (business, technical, field, scientific) as well as sections on writing style. Any questions? Thank you and good luck with your report writing!