Collection of Flash Websites
advertisement

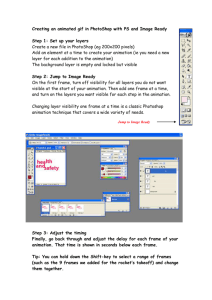
Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) RESEARCH... I am going to research on 2D animation techniques, software and graphic novels to present an overall idea of animation. Animation ‘’Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D or 3-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. The effect is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon of persistence of vision, and can be created and demonstrated in several ways. The most common method of presenting animation is as a motion picture or video program, although there are other methods.’’ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Animation History of animation... There have been early attempts to capture motion drawings in the past, such as pre-historic cave paintings; where there are several images of animals with multiple legs in superimpose positions. This was clearly attempting to illustrate motion. A 5,000 year old earthen bowl was found in Shahr-i-Sokhta (Iran). This bowl has five images of a goat painted on the sides. It has been said that this was an early example of animation; however in the years of this bowl being made, no equipment that would show the images in motion yet existed, that’s why this series of images could not be referred to as ‘animation’. The Chinese invented a zoetrope-type device in 180AD. The phenakistoscope, praxinoscope and the flip book were invented during the 19th century and I will go further and more detailed into these animation devices later on in the research. These devices did show the appearance of movement from a sequel of images but animation did not improve much until further down the line when cinematography was invented. Georges Melies was one of the first people to use special-effect films. His idea was to stop the camera rolling to change something in the scene and then continue rolling the film once the changes were made. This technique was later called ‘stop-motion animation’. This image shows an Egyptian burial chamber mural, approximately 4000 years old, showing wrestlers in action. Even though this may appear similar to a series of animation drawings, there was no way of viewing the images in motion. It does, however, indicate the artist's intention of depicting motion. Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) Traditional animation... Traditional animation was the process used for most animated films in the 20 th century. Firstly the designer would draw the animation, after which the drawings would be photographed and put into life with special editing programs and software’s. To create the illusion of movement, each drawing has to slightly differ from the previous image. After this process is completed, the animator’s drawings are traced/photocopied onto seethrough acetate called ‘cels’. These cels are filled with paints in the assigned colours on one side of the image. Once the images are placed on the cels, they are then photographed one-by-one onto motion picture film. Now, in the 21st century, animators’ drawings and backgrounds are either scanned or drawn directly into a computer system due to the improving technology. Some other forms of traditional animation are full animation, limited animation, rotoscoping and live-action animation. Examples of traditionally animated feature films: Pinocchio (U.S, 1940) Animal Farm (U.K, 1954) Akira (Japan, 1988) Examples of traditionally animated films which were produced with the aid of computer technology: The Lion King (U.S, 1994) Sen to Chihiro no Kamikakushi (Japan, 2011) Les Triplettes de Belleville (U.K, 2003) Stop motion... I have found the above images on Google Images. Stop motion animation is used to describe animation created by physically manipulating real-world objects and photographing them one by one, frame by frame until they create the illusion of movement. There are many different types of stop-animation, usually named after the resources and type of media used to create animation. Computer programs and software are completely suitable to create this type of animation. Below I will mention a few examples. Examples of stop motion: Puppet Animation – e.g. The Tale of the Fox (France, 1937), The Nightmare before Christmas (U.S, 1993), Corpse Bride (U.S, 2005), Coraline (U.S, 2009). Puppetoon Clay – e.g. The Gumby Show (U.S, 1957-1967), Morph (U.K, 1977-2000), Wallace and Gromit (U.K, 1989), The Trap Door (U.K, 1984) Cut-out Animation – e.g. Monty Python’s Flying Circus (U.K, 1969-1974), Fantastic Planet (France/Czechoslovakia, 1973), Tale of Tales (Russia, 1979) Silhouette Animation – e.g. The Adventures of Prince Achmed ( Weimar Republic, 1926), Princes et princesses (France, 2000) Model Animation – e.g. Jason and the Argonauts (1963), King Kong (1933) Go Motion – e.g. The Empire Strikes Back (1980), Dragonslayer (1981) Object Animation Graphic Animation Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) Computer animation... Computer animation surrounds a variety of techniques and methods, the combining factor being that the animation is created all digitally on computer software. 2D animation... 2D animation figures and characters are created and/or edited on computer software using 2D bitmap graphics or created and edited using 2D vector graphics. This includes automated and computerized versions of the traditional animation methods such as interpolated morphing, onion skinning and interpolated rotoscoping. 3D animation... This type of animation is digitally modelled and manipulated by the creator/animator. In order to manipulate a mesh, it has to be given a digital skeletal structure that can be used to control the mesh. This process is called rigging. Many other techniques can be applies, ones such as mathematical functions, simulated hair or fur, effects like fire and water ant the use of motion capture. Toy Story (U.S, 1995) is the first ever feature-length film created and rendered using entirely 3D graphics. TASK ONE. I have been asked to research different types of 2D animation techniques and their inventors. (see task 3 for motion comics) The Phenakistoscope The Phenakitoscope, also known as the ‘’spindle viewer’’ was invented in 1832 by a Belgian physicist named Joseph Plateau. Plateaus’ was originally inspired from the past work of Michael Faraday and Peter Mark Roget. Faraday had previously invented a device which he called ‘’Michael Faraday’s Wheel’’ which consisted of two discs that span in opposite directions from one another. Plateau took a step forward and changed Faraday’s invention into his phenakistoscope. The phenakistoscope uses a large spinning disc which is attached vertically on to a handle. Both disks are mounted on the same axis. Around the disk a series of images is drawn precisely to make the images look like they are a sequence of movements. The user will spin the disc and look at the reflection of the disc in the mirror through the slits which will give the illusion of motion. You can find a clip of the phenakistoscope in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oE3fBDYJKZk On the left side is an image of the famous Joseph Plateau. Born: October 14th, 1801 in Brussels, Belgium Died: September 15th, 1833 in Ghent, Belgium Nationality: Belgique Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) The Zoetrope The Zoetrope was invented by a British mathematician, William Horner, in 1834. When Horner invented this device he originally named it daedalum (‘’wheel of devil’’) however it was later changed by William F. Lincoln to zoetrope (‘’wheel of life’’). The zoetrope was based on the phenakistoscope; however it was more convenient as it didn’t require the use of a mirror and allowed more than one person to use it at the same time. Horner’s invention was later forgotten for near enough 30 years until 1867. This invention consists of a large cylinder with craved vertical slits in the sides. Inside the cylinder there will be a sequel of images from a video or film. As the cylinder spins, the user will have to glare through the cut-out slits, at the images on the opposite side of the cylinders interior. The slits keep the images from blurring together and therefore create the illusion of motion. A Chinese inventor Ding Huan has created the earliest elementary zoetrope around 180 AD, long before Horner which means Horner used Ding’s amazing idea and improved it in the best possible way. You can find a clip of the zoetrope in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-3yarT_h2ws On the left side is an image of the famous William George Horner. Born: 1786 in Bristol, U.K Died: 22nd September 1837 in Bath, U.K Nationality: British The Praxinoscope The praxinoscope was invented in 1877 by a Frenchman Charles Reynaud. This machine was the first to overcome picture distortion which is caused by viewing through the moving slots. These devices quickly overcome the popularity of the zoetrope as the vision was much better. Just like the zoetrope, the praxinoscope, used a strip of images positioned around the inner surface of a large spinning cylinder. However, the praxinoscope used inner circle mirrors placed so that the reflections of the images appear stationary in position as the wheel was spinning; this made it a big improvement from the zoetrope as the image created more of an illusion of movement and also a brighter and less distorted image. You can find a clip of the praxinoscope in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ez_UJAafRMs On the left side is an image of the famous Charles Reynaud. Born: December 8th, 1844 in Montreuil, France Died: January 9th, 1918 in Ivry-sur-Seine, France Nationality: French Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) The Kinetoscope The kinetoscope was an early motion picture exhibition device. It was invented by Thomas Edison in 1888. It was designed to view films but only for one person at a time through a window of a cabinet housing. The kinetoscope was designed to introduce the basic approach which was taken to be later developed into cinema projection and video. This device creates the illusion of movement by conveying a strip of perforates film bearing a sequence of images over a light source with a high speed shutter. You can find a clip of the kinetoscope in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mIkLok-BYIk On the left side is an image of the famous Thomas Edison. Born: February 11th, 184 in Ohio, U.S.A Died: October 8th, 1931 in New Jersey, U.S.A Nationality: American The Flip Book The flip book was invented by Max Skladanowsky in 1894. This was a book with a series of images which change gradually from one page to the next, and once the pages of the book are turned rapidly, the image create an illusion of movement, animation and motion. Many flip books have been illustrated and colourised for children, however some are also used by adults and present photographs rather that drawings. Skladanowsky was the first to exhibit his photographic images in a flip book in 1894; however the first drawn flip book appeared in September 1868 and it was designed by John Barnes Linnett. You can find a clip of the flip book in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AslYxmU8xlc On the left side is an image of the famous Max Skladanowsky. Born: April 30th, 1863 in Berlin, Germany Died: November 30th, 1939 in Berlin, Germany Nationality: Polish The Zoopraxiscope The zoopraxiscope was a device designed to display motion pictures. This device was created by Eadweard Muybridge in the early days of 1879. This device was considered the first ever movie projector. The zoopraxiscope projected imaged by spinning glass disks in a fast succession to produce the impression of motion. The stop-motion images were initially painted onto the glass disks as silhouettes. In 1892-94 a second series of disks were made, but this time photographs were printed onto the disks and were coloured in by hand. You can find a clip of the zoopraxiscope in action by visiting this link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NPFUUcl0A28 Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) On the left side is an image of the famous Eadweard Muybridge. Born: April 9th, 1830 in Kingston, U.K Died: April 8th, 1904 in Kingston, U.K Nationality: British Cel Animation Cel animation is a traditional form of animation used in the making of cartoons and animated movies in which each frame is hand-drawn. Full-length feature films which are produced using this type of animation will require approximately a million drawings to be made into a movie. Cel animation is very popular within cartoons; however producers no longer use the old method of handdrawn animation but instead they rely on computers and digital technology to help in the making process. This type of animation takes extremely large amounts of time to prepare and requires the producer to be organized and have an eye for details. A cel is a sheet of transparent cellulose acetate used as a medium for painting animation frames. It is transparent so that it can be laid over other cels and/or a painted background, then photographed. (Source: The Complete Animation Course by Chris Patmore.) The process of cel animation... Once an idea pops up in the producers head; they will produce a storyboard, which will later be used to visually present idea to the rest of the team. An animatic is created to sort out the film’s timing and to see if it will work. When both, the story and the timing, is approved the team will each work to create the scenes and characters for the story. At the time of drawing, the actors record the movie audio and the animators adjust the lip movements of the characters to fit the track. Later on when the audio, images, movement, timing, sounds and scenes is finished the director puts all of this information on a dope sheet. The main animator makes sketches of the key frames in the scene, and then passes the sketches to an assistant animator who cleans up the rough linework and adds some details which may be missing. When the drawing is complete the sheets are given to an in-betweener who draws the rest of the action on separate sheets in order to finish the action drawn on the animator’s key frames, he also determines how many drawings are needed. Once all of the drawings are finalized, a pencil test is carried out to determine whether all of the movements flow appropriately and that nothing is missing. Once the pencil test is finished, a cleanup artist traces all of the frames to ensure the work is consistent from frame to frame and that everything is neatly done. Once that is finished, the inker will transfer the drawings onto cels before they are colourized. If the images are done digitally on computer software most of the above actions are carried out by one person. When all of the above is done, a photographer will photograph the backgrounds along with the matching cels according to instructions on the dope sheet. All of the audio and footage is then synchronised and edited all together. Then the film is sent to a lab to be made into a film project or put on video. Layers in cel animation Layers in cel animation Example of cartoon made with cel animation process Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) TASK TWO. I have been asked to research Flash software and how it is used creatively. I will also include examples of good work produced on Flash. Adobe Flash is multimedia software used to add animation, video and interactivity to web pages. Flash can be used to produce advertisements, games and flash animations. It has been recently positioned as a tool for Rich Internet Applications (iPhone, iPad, iPod, computer applications) Flash manipulates vector and raster graphics to provide animation of text, drawings and also still images. Animations produced on Flash can be displayed on computer systems and devices by using Adobe Flash Player. Flash originated with the application SmartSketch which was developed by Jonathan Gay. Screenshots of Adobe Flash program found on Google Images Flash Animations also know as Flash cartoon is an animated film creates using Abode Flash (or similar animation software). Most Flash animations are saved in a .swf file format and can be viewed using Flash Adobe Move Player. Flash animations produce movement from a sequence of images, drawings or photographs. There are many television series, commercials and online shorts produced by Flash animations. Most internet users in the late 1990’s still had the weak internet bandwidth of 56 Kbit/s, as of this, many Flash animation producers employed limited animation or cut-out animation when creating projects for we distribution. This allowed producers to release shorts and other interactive experiences which were under 1MB; these included both audio and animation. One of the first examples is the first episode of ‘The Goddamn George Liquor Program’ which was released in 1999 at only 628kB. Flash animations are usually distributed in the World Wide Web; which means they are often referred to as Internet cartoons, online cartoons or webtoons. Animations on the internet can be interactive and created in a series. Examples of Flash Animations: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Utl1jqGtryI http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOXhYqtk_-0&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YpkEXsQXGmQ&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XSGBVzeBUbk http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sJMemIVjLa0 ‘’Flash is able to integrate bitmaps and other raster-based art, as well as video, most Flash films are created using only vector-based drawings which often result in a somewhat clean graphic appearance. Some hallmarks of poorly-produced Flash animation are jerky natural movements (seen in walk-cycles and gestures), autotweened character movements, lip-sync without interpolation, and abrupt changes from front to profile view.’’ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flash_animation Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) Collection of Flash Websites: http://www.wechoosethemoon.org/ http://moodstream.gettyimages.com/ http://www.mono-1.com/monoface/main.html http://www.agencynet.com/ http://www.marcecko.com/#/ http://www.gettheglass.com/ http://www.syfy.com/tinman/oz/ http://www.louisvuittonjourneys.com/legends/ http://waterlife.nfb.ca/ http://okaydave.com/ http://www.saizenmedia.com/reinvented/ http://lecaid.com/ Flash Vector Graphics is the use of geometrical primitives such as points, curves, lines and shapes or polygon, which are all based on mathematical equations, to represent images in computer graphics. Vector graphics are based on images that are the result of mathematical functions. Vector images are made up of tracks that are linear paths which lead through points called control points. Each of these points is placed in a fixed position on the x and y axes of the work plan. Each point is a sort of database containing information about the location of the point in the space and the direction of the vector (which is what defines the direction of the track). Can be assigned a colour, a shape, a thickness and also a fill to each track. This does not affect the weight of the files in a substantial way because all information resides in the structure. Example of an animated banner Screenshots of animated ads Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) In interactive animation, you can enjoy the animation as well as participating in the flow of the animation. Some interactive animations are games some are pop ups. In some of them you might be able to choose the actions and things to say for an animated character, in some of them you may have to make a move to score a point etc. Collection of animation screenshots: Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) There are four main animation publishing formats these are the following: FLASH SHOCKWAVE QUICKTIME SWISH In Adobe Flash the frame rate is the rate at which the animation is played, it represents the number of frames displayed in a second. If a frame rate is too slow the animation will appear to be rougher than at a higher frame rate; however an animation with a frame rate set too hight may negatively affect the preformance by shortening the animation or use a large amount of processing power from the viewer’s computer. An animation set to 12 FPS plays 12 frames each second. If the animations’ frame rate is set to 24 FPS the animation will appear more smoothl than 12 FPS. TASK THREE. A motion comic is a form of comics combining elements of print comic books and animation. (Wikipedia definition) Lions Gate released Saw: Rebirth comic as an animated film version in 2005, this was one of the very first examples of an animated comic created to tie into a film franchise. The first motion comics released were produced by Warner Bros, the owner of DC Comics to correspond with the film premiers of The Dark Knight and Watchmen releasing an adaption of Batman: Mad Love and Watchmen: Motion Comics, adapting the comic books of the same name. Marvel Comics also begun producing animated comics beginning with Astonishing X-Men and a Spider – Woman series. They have also recently announced the coming up adaption of Extremis. Top Ten Motion Comics: (according to ToplessRobot) 1. Iron Man: Extremis 2. The Walking Dead 3. Batgirl: Year One 4. Superman: Red Son 5. Spiderwoman: Agent of S.W.O.R.D 6. Batman: Black and White 7. Astonishing X-Men: Gifted 8. Watchmen 9. Peanuts 10. Axe Cop A graphic novel is a narrative work in which the story is conveyed to the reader using sequential art in either an experimental design or in a traditional comics format. The term is employed in a broad manner, encompassing non-fiction works and thematically linked short stories as well as fictional stories across a number of genres. (Wikipedia definition) Graphic novels are usually longer and more lasting formats that comic magazines, they are generally sold in bookstores and comic book shops. Even libraries have now taken interest in graphic novels even though they once ignored comic books. Some describe graphic novels as "a fictional story that is presented in comic-strip format and presented as a book.", however in the publishing sector some may say that a graphic novel cannot really be called a novel. Graphic novels are sometimes called long comic books. These books usually cover fictional material in comic book form through the use of sequential illustrations. Unlike traditional comic books, graphic novels are longer and tend to cover a story from start to end, instead of ending with the traditional cliff-hanger which comics Paula Aleksandra Rapsiewicz Unit 65: Web Animation for Interactive Media (Adobe Youth Voices: Motion Comics) usually end in. First exampled of graphic novels were comic book classics in the United States in the 1940’s. Novels such as The Three Musketeers were put into the framework of a comic book, intending to make younger readers understand the book more thoroughly. Top Ten Graphic Novels: (according to The Guardian) 1. It’s a Good Life, If You Don’t Weaken (Seth, 1996) 2. Shortcomings (Adrian Tomine, 2007) 3. Ethel & Ernest (Raymond Briggs, 1998) 4. Persepolis (Marjane Satrapi, 2003) 5. Fun Home (Alison Bechdel, 2006) 6. From Hell (Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell, 2000) 7. Black Hole (Charles Burns, 2005) 8. Blankets (Craig Tompson, 2003) 9. Alice in Sunderland (Bryan Talbot, 2007) 10. The Castafiore Emerald (Herge, 1963) Some other examples include: V for Vendetta by Alan Moore Maus by Art Spiegelmans Palestine by Joe Sacco Bibliography: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Animation http://courses.ncssm.edu http://www.google.co.uk/imghp?hl=en&tab=wi http://animatedtv.about.com/od/thesimpsonsfaq/a/celanimation.htm http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/cel_animation.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adobe_Flash http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vector_graphics (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_comic) http://www.toplessrobot.com/2011/06/the_10_best_motion_comics.php (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphic_novel) (http://www.guardian.co.uk/culture/gallery/2011/oct/30/ten-best-graphic-novels-in-pictures#/?picture=381058847&index=9 https://www.adobe.com/devnet/flash/learning_guide/animation/part02.html Cracking Animation: The Aardman Book of 3-D Animation by Peter Lord & Brian Sibley