PROTOZOA Lab
advertisement

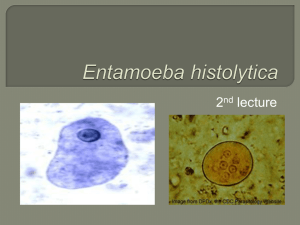
Presented By: Dr. Shaymaa Abdalal Medical Parasitology Demonstrator INTESTINAL PROTOZOA Numerous protozoa inhabit the gastrointestinal tract of humans . Entamoeba histolytica can become a highly virulent and invasive organism that causes a potentially lethal systemic disease. Giardia lamblia can cause severe acute diarrhea which may lead to a chronic diarrhea and nutritional disorders INTESTINAL PROTOZOA Intestinal protozoa are transmitted by the fecal-oral route . exhibit similar life cycles consisting of a cyst stage and a trophozoite stage INTESTINAL PROTOZOA www.tulane.edu Giardia lamblia Disease: GIARDIASIS Distribution: worldwide distribution and is the most common protozoan isolated from human stools. Giardia lamblia Definitive host : man Habitat: intestine. upper portions Infective stage: cysts. of the small Giardia lamblia trophozoite Characteristic features : Two nuclei (Nu). Central karyosomes (k). median bodies (MB). Axonemes (Ax) . Four pairs of flagella (Fg). An adhesive disk (AD). www.tulane.edu/~wiser/protozoology/notes/intes.html Giardia lamblia trophozoite Morphology: Size : 12-15 X 5-10µm. Shape: Pear or Tear Drop www.tulane.edu/~wiser/protozoology/notes/intes.html Giardia lamblia trophozoite Giardia lamblia cyst Characteristic features : Four nuclei (Nu). Axonemes (Ax) . Median bodies (MB). Well-defined wall (CW) Giardia lamblia cyst Morphology : Size : 11-14X 6-10µm. Shape: Oval Giardia lamblia cyst Entamoeba histolytica Disease: amebiasis or amebic dysentery. Distribution: found throughout the world, they are more common in tropical countries or other areas with poor sanitary conditions. Entamoeba histolytica Definitive host : man Habitat: large intestine. Reservoir: no animal reservoirs. Infective stage: cysts. Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite Characteristic features : a finger-like pseudopodium (psd) . the ectoplasm (ecto). cytoplasm has a granular appearance the endoplasm (endo). a glycogen vacuole (vac). Nuclear (Nu). chromatin and a centrally located karyosome (ka). Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite Morphology : Size : 15-30 µm. Shape: an amorphous shape . Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite Entamoeba histolytica cyst Characteristic features : Chromatoid bodies (cb) . 1-4 nuclei (Nu). a glycogen vacuole (vac) . Entamoeba histolytica cyst Morphology : Size : 12-15 µm. Shape: spherical shape . Entamoeba histolytica cyst Malaria Malaria is the 5th cause of death from infectious diseases worldwide (after respiratory infections, HIV/AIDS, diarrheal diseases, and tuberculosis) in low-income countries. Malaria is the 2nd leading cause of death from infectious diseases in Africa, after HIV/AIDS. Malaria Disease: Malaria Distribution: Malaria today is usually restricted to tropical and subtropical areas Malaria Intermediate Host: man Vector (Definitive host) : femaleAnopheles mosquito habitat: RBC`s Infective stage: sporozoites . P. vivax P. Vivax ring stage Diagnostic Points: 1.Red cells containing parasites are usually enlarged. 2.Schuffner's dots are frequently present in the red cells as shown above. 3.The mature ring forms tend to be large and coarse. 4.Developing forms are frequently present. P. Vivax schizont stage schizonts of P. vivax are large and amoeboid. Schizont large may almost fill the RBC`s. Mature = 12 to 24 merozites. P. falciparum P. falciparum ring stage Diagnostic Points: Red Cells are not enlarged. Rings appear fine and delicate and there may be several in one cell. Some rings may have two chromatin dots. Presence of marginal or applique forms. No Trophosoite and schizont. P. falciparum gametocyte stage Gametocytes of P. falciparum. Figs. 27-28: Macrogametocytes (female); Figs. 29-30: Microgametocytes (male). Illustrations from: Coatney GR, Collins WE, Warren M, Contacos PG. The Primate Malarias. Bethesda: U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare; 1971. P. falciparum gametocyte stage crescent- or sausageshaped. 1.5 times the diameter of an RBC in length. remnants of the host RBC can be seen; this is often referred to as Laveran's bib. P. falciparum gametocyte stage Gametocyte of P. falciparum in a thin blood smear, showing Laveran's bib. Key Morphological Differences Falciparum vivax numerous rings enlarged erythrocyte smaller rings Schüffner's dots no trophozoites or 'ameboid' trophozoite schizonts cresent-shaped gametocytes