Cell Biology Study Guide
advertisement

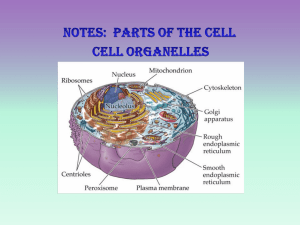
Cell Biology Study Guide Pages 107-110 1. List the four six characteristics of life: a. b. c. d. e. f. Composed of cells Complex organization pattern Use energy Have stable internal conditions Grow and change Reproduce 2. Create a flow chart in the space below showing the complex organization pattern of living things from largest (biosphere) to smallest (atom). Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Organism Organ System Atom Molecule Cell Tissue Organ 3. Which level in the above flow chart is the smallest level for living things? Cell 4. What is homeostasis? Give an example. The internal stable conditions that all living organisms strive to maintain. For example, the human body maintains blood pH within the range of 7.35 to 7.45. A pH level above or below this range can be life-threatening. For example, the human body maintains a body temperature of 37 degrees celsius. It sweats, when the temperature is too high or shivers when the temperature is too low. 5. Write a paragraph or two comparing and contrasting the two types of cells. Same • Basic unit of life • Come from preexisting cells • Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes Different • Eukaryotes are larger than Prokaryotes. • Prokaryotes lack a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles; Eukaryotes have these things. 6. What is differentiation? The process by which cells become increasingly different and specialized. 7. What are two ways that cells can reproduce? 1. Sexually 2. Asexually 8. List organelles/cell parts that all cells contain. Cytoplasm Cell Membrane DNA Ribosomes 9. List some differences between plant and animal cells. Plant Cells • Large central vacuole • Cell Wall • No flagella/cilia • Chloroplasts • No centioles (centrosomes only) • Common shape: Square, more boxy, rectangular in shape Animal Cells • Smaller vacuoles • No cell wall • Cilia and/or flagella • No chloroplasts • Centrioles and centrosomes • Common shape: Globular, circular, smooth edges 10. In the chart below are some commonly confused cell organelles. Explain the differences between the parts and their functions. Microvilli & Cilia • Microvilli are finger-like projections of the cell membrane itself. Their purpose is to increase the surface area of the cell, and they are made from the same material as the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) • Cilia are a separate structure that protrudes from the cell membrane to help with cell movement. They are made of microtubules. 10. In the chart below are some commonly confused cell organelles. Explain the differences between the parts and their functions. Mitochondria & Chloroplasts • Mitochondria are found in plant and animal cells. They convert glucose into ATP energy that the cell can use. • Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells. Through photosynthesis, they create glucose. 10. In the chart below are some commonly confused cell organelles. Explain the differences between the parts and their functions. Nucleus & Nucleolus • The nucleus is the “command center” of the cell. It houses all of the genetic information (DNA “instructions” for the cell) • The nucleolus is a small part of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. The ribosomes are sent out of the cell through holes in the nuclear membrane called nuclear pores. 10. In the chart below are some commonly confused cell organelles. Explain the differences between the parts and their functions. Rough ER & Smooth ER • The RER contains ribosomes which gives it a “rough” appearance. The ribosomes make proteins that are transported through the canal system of the RER. • The SER does not contain ribosomes, so it looks “smooth”. The SER is involved in making lipids and detoxing the cell. 10. In the chart below are some commonly confused cell organelles. Explain the differences between the parts and their functions. Cell Wall & Plasma Membrane • Plants and bacteria have a cell wall. It is located outside of the cell membrane and provides strength and rigidity for the cell. • All cells have a plasma or cell membrane. It is a semi-permeable barrier made of phospholipids. Cytoskeleton, Centriole, Centrosome • The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers (microtubules) within the cell. They give the cell support, help maintain the shape, and are responsible for movement. • The centriole is only found in animal cells. It is a pair of structures that helps with cell division • The centrosome is found in plant and animal cells and is an organelle responsible for making microtubules (the cytoskeleton). 11. Which part of the microscope is responsible for... -Holding a slide in place? Stage clips -Adjusting the focus? Fine/coarse adjustment knobs -Controlling the amount of light? Diaphragm 12. How do you calculate magnification? Show an example calculation. Ocular magnification x objective magnification = total magnification 10x (ocular) x 4x (objective) = 40x TOTAL magnification 13. Label the parts of the microscope below: Ocular lens Body tube Revolving nosepiece Arm Low power objective Med power objective High power objective Stage Stage clips Coarse Adjustment Knob Diaphragm Fine Adjustment Knob Light Source Base