Product and Branding Strategy
advertisement

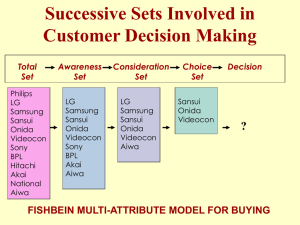
New Product Development Strategy WHY DEVELOP NEW PRODUCTS? In 1982 Timex turned down the opportunity to market "Swatches". Timex was resting on its laurels, simple low cost watches. Digitalisation revolutionized industry while Timex stuck with analog. DID NOT KEEP UP WITH WATCHES EVOLUTION FROM A FUNCTIONAL OBJECT TO A FASHION ACCESSORY. Today Global consumer owns 5 watches up from 1.5 watches 30 years ago. Move from chronometer to fashion accessory Timex then acquired Guess and Monet Jewellers Why New Products Fail? Lack of differentiating advantage – RASna JUc FIT, HLL Ayush Poor marketing plan – Yamaha RX -100, Real Value Vaccumiser, Appy, Evita, Appy, HLL Max Biscuit Target market too small – Viruddh, Livon Poor product quality – Annapoorna RTEC, Dandi Namak, Real Juice New Product – Value Proposition Value Proposition = Perceived Differential Advantage Consumer Buying Process Need Recognition Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Post-Purchase Behavior Successive Sets Involved in Customer Decision Making Total Set Philips LG Samsung Sansui Onida Videocon Sony BPL Hitachi Akai National Aiwa Awareness Set LG Samsung Sansui Onida Videocon Sony BPL Akai Aiwa Consideration Set LG Samsung Sansui Onida Videocon Aiwa Choice Set Sansui Onida Videocon Decision ? FISHBEIN MULTI-ATTRIBUTE MODEL FOR BUYING Differentiation Variable- Product After-sales Features Style Design Packaging Branding Delivery New Product Development Six categories of new products •New-to-the-world products •New product lines •Additions to existing product lines •Improvements and revisions of existing products •Repositioning •Cost reductions NEW PRODUCTS - TYPES OF INNOVATION A new product can be: Continuous Innovation. Dynamic Continuous Innovation Discontinuous Innovation NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Idea Generation Caution : Go Error / Drop Error Idea Screening Concept Development Category concept / Brand Concept Concept Testing Marketing Strategy Business Analysis Product Development Market Testing How many test cities? Which cities? Length of test? What information? What action to take? Commercialisation When / Where / Whom / How ? Product-Idea Rating Device Relative Weight Product Score Product Rating Key Success Factors (a) (b) (c = a x b) Level of Differentiation .35 7 2.45 Value for Money .25 8 2.00 Marketing strength .25 6 1.50 Competitive Intensity .15 6 .90 Total 1.00 Rating scale: 0 - 3.0 poor Minimum acceptance rate: 6.1 3.1 - 6.0 fair 6.85 6.1 - 8.0 good. New Product –Innovation Diffusion Awareness Interest Trial Evaluation Adoption New Product Adoption RATE OF ADOPTION AFFECTED BY Relative advantage Compatibility Complexity Divisibility Communicability New Product Adoption ADOPTER CATEGORIES The Product Life Cycle A life cycle plots sales of an offering or a product class over a period of time. There are FOUR main stages: 1. Introduction 2. Growth 3. Maturity (Saturation) 4. Decline The Product Life Cycle Sales Sales Profits Introduction Growth Maturity Decline LIFECYCLE STRATEGIES INTRODUCTION GROWTH MATURITY DECLINE Marketing Objective Market Development Build Brand Loyalty Convert the Competitor’s Customer Reduce Inventory Sales Low High High Low Costs High Moderate Low Low Profits Low Moderate High Low Competitors Very Few Increasing Many Few Product Basic Product Differentiate Line Extensions Reduce Variants Price Penetration/ Skimming Maintain Prices Lower Prices Lower Prices Place Selective Distribution Extensive Distribution Extensive Distribution Selective Distribution Promotion High Advertising Sales Promotion Moderate Advertising PR/Publicity High Advertising Trade Promotion Low The Product Life Cycle Product hierarchy Need family Product family Product class Product line Product type Item