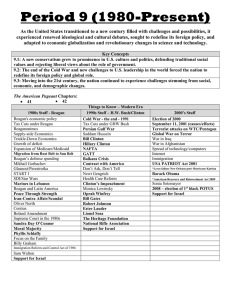
1980’s – Present
Lecture Notes
Liberalism and Conservatism
• Liberalism:
– Government should
regulate economy to
protect people from
power of business and
wealthy elites
– Government should play
a more active role in
ensuring equality of
opportunity
• Conservatism:
– Government regulations
harm a “free market”
– Oppose taxes and
government programs
that they feel come at
the expense of freedom
The Election of 1980
• Ronald Reagan (R)
defeated Jimmy Carter
(D) in a landslide
• Reagan was a strong
communicator, former
actor, and ex-California
governor
• Support came from
conservatives,
moderate Democrats
Campaign Commercials -1980
• What persuasive techniques do you see in
these campaign videos?
– What is Reagan’s message to the American
people?
– What is Carter’s message to the American people?
New Conservatism
• Newfound focus on
“traditional values”
– religious right
• “Big government” programs
of the past were scaled
down and/or eliminated
• “Free market utopians”
urged removal of business
regulations
Reaganomics
• Economic Recovery and Tax
Act of 1981 reduced income
tax rates by 25%
– Mostly benefitted upper
class, cut government income
by $747 billion
– Billions shifted from domestic
to military programs
• Environmental and business
regulations were lifted
– Corporate mergers flourished,
stock market rose
Crisis for Organized Labor
• Reagan took a “pro-business” stance in dealings
with unions
– Professional Air Traffic Controllers fired for violating a
no-strike clause
• Labor union membership declined, wages
declined
• Manufacturing jobs disappeared, personal
bankruptcies skyrocketed
Poverty Amid Prosperity
• Reagan’s policies benefitted the upper class at
the expense of the lower class
– Richest 1% saw wealth grow from 31% to 37%
– Cities were hit hard by federal funding cuts
– Middle class declined, home ownership fell
– Corporate downsizing led to lay offs in late 1980s
– Poverty climbed from 11% to 15%
– Women’s wages still fell far behind men’s
– Homelessness tripled during the decade
An Acquisitive Society
• White collar workers
prospered during the
Reagan years
• “Yuppies” symbolized
materialistic greed and
consumerism of the day
– Young Urban Professionals
Foreign Policy Adventures
• Though Reagan avoided major war, conflicts
arose in many “hot spots”
– Administration approved plan to arm Contras in
Nicaragua
– Bush authorized expansion of “war on drugs” to
Panama (Manuel Noriega)
– Middle Eastern intervention failed (Lebanon/Israel
conflict)
The Iran-Contra Affair
• U.S. began secretly selling
weapons to Iran in 1985 in an
attempt to secure release of
American hostages
– “Arms for Hostages” violated
embargo against Iran
• Money from arms sales was
funneled to Nicaraguan Contras.
– Anti-Communist rebels
• Reagan initially acted unaware,
eventually accepted responsibility.
Election of 1988
• Vice President George
H.W. Bush (R) defeated
Michael Dukakis (D)
• Bush would attempt to
continue in Reagan’s
footsteps, but faced
issues with growing
deficits
George Bush
• Americans with
Disabilities Act:
– This law banned
discrimination in
employment against people
with disabilities.
– It also required employers
to make “reasonable
accommodation” to help
disabled employees.
The Clinton Presidency
(pgs. 1006-1012)
1. How did voter dissatisfaction affect the 1992 Presidential
race?
2. Why do politicians (liberal and conservative) find it
difficult to cut entitlement programs?
3. In terms of foreign policy, why do you think US troops
were unable to complete their mission in Somalia?
4. Judging from the events of Clinton’s first term as
president, would you characterize the US in the 1990s as
politically liberal, conservative or somewhere in the
middle? Give specific examples to support your argument.
1992 Election
• Two factors helped Clinton
overcome Bush’s early lead.
1.
2.
Recession that began in 1990.
The third-party candidacy of
Ross Perot
• Balance the budget, pay off
national debt
• Most of Perot’s supporters,
however, were conservatives who
otherwise might have voted for
Bush.
• Clinton received only 43 percent
of the popular vote—the lowest
percentage for a winning
presidential candidate since
1912.
Clinton Economics
• Clinton’s support for welfare reform, coupled with an
improving economy, boosted his popularity as
president
• Republicans and Democrats worked together to craft a
tax-cut bill and the Balanced Budget Act of 1997.
– Demonstrated that Republicans and Democrats could
cooperate on important issues
• In 1998, the federal budget did not just balance. It ran
its first surplus in nearly 30 years. A budget surplus
occurs when the government takes in more money
than it spends.
– Product of the Internet boom
Clinton Scandal & Impeachment
• The primary charge was that he had illegally profited from an
investment in an Arkansas real estate development called
Whitewater. Accusations also surfaced of his having had numerous
affairs while he was governor of Arkansas.
– In May 1994, a former Arkansas state employee filed a lawsuit
accusing Clinton of sexual harassment.
• Attorney General Janet Reno appointed lawyer Kenneth Starr to
investigate the Whitewater claims. In January 1998, Starr also
obtained evidence that Clinton had engaged in an affair with a
White House intern, Monica Lewinsky, which contradicted
Clinton’s sworn testimony in the Arkansas sexual harassment case.
In September, Starr submitted to Congress a report that
recommended that Clinton be impeached.
1.
2.
Perjury
Obstructed justice by lying under oath
Surviving the Trial
• Needed 67 senators to remove Clinton from
office (2/3 majority)
– 50 Republicans (obstruction of justice)
– 45 Republicans (perjury)
– 0 Democrats
• Clinton not only survived the scandal but also
ended his presidency with a remarkably high 65
percent approval rating.
– What about the Vice President?
Election background
• November 7, 2000
– Democrat Al Gore wins
clear popular vote
– No clear winner from
electoral college
• Florida becomes the key
state
– 25 electoral votes
– Less than ½% difference
between candidates
– Recount
Terrorism
• Terrorism had been a
growing threat to the U.S.
– World Trade Center bombed
in 1993, killing six
– Bombings at U.S. embassies
in Kenya and Tanzania killed
over 200 (1998)
– U.S.S. Cole bombed in Yemen
(2000)
• Attacks were connected to
Osama bin Laden’s Al-Qaeda
network
September 11, 2001
• 4 planes were hijacked
by Al Qaeda terrorists
– 2 flew into the World Trade
Center in New York City
– 1 flew into the Pentagon in
Washington D.C.
– 1 went down in
Pennsylvania (White
House? Capital Building?)
• Foreign Policy will now be
changed forever.
Heightened Security
• Congress passed the Patriot Act
in response to the Sep. 11th
attacks
– authorized wiretapping, access of
computer records, etc.
– increased suspicion of Muslims
• Greater security measures were
taken at airports, government
buildings, public events
• Department of Homeland
Security formed in 2002
War in Iraq 2003-2011
• Key Issues:
– Weapons of mass destruction?
– Al Qaeda connection?
• Stage One:
– Traditional war March-April
2003
– Remove Saddam Hussein from
power
• Parliamentary democracy
• Stage Two
– Long term U.S. led occupation
– Violent response from
insurgents
– Major spike in U.S. and civilian
casualties
Controversy
1. Helping or creating more problems?
2. False reasons for war?
3. Fighting terrorists vs. fighting countries?
– Where are the terrorists from?