1.2.3 Markets student version
advertisement

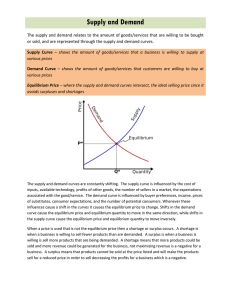
1.2.3 Markets - syllabus Students should be able to: • Describe equilibrium price and quantity and explain how they are determined • Draw, and interpret, a diagram showing the interaction of supply and demand • Show that shifts in demand and supply curves will change equilibrium • Analyse the causes and consequences of price changes Markets Bringing buyers (demanders) and sellers (suppliers) together creates a _________ Markets do not require buyers and sellers to physically meet (e.g. internet selling). Their purpose is to set a price that is acceptable to both buyers and sellers. Demand and supply In order to analyse how a market works we need to look at demand and supply curves on the same diagram. The demand curve slopes downwards, indicating that more will be purchased as price falls, while the supply curve slopes upwards, indicating that more sellers enter the market as prices rise. Draw a demand and supply curve on the same graph. Market equilibrium The price system should produce equilibrium where demand and supply are equal. This occurs at the equilibrium price. When does equilibrium occur? The equilibrium price is also known as the market clearing price. Disequilibrium When a market is not in equilibrium (disequilibrium), then there will probably be a reaction by buyers or sellers. At a high price P1, the supply OA exceeds demand OB and suppliers will not be able to sell all they have produced at this price. This is known as excess supply as supply exceeds demand and if suppliers want to sell the product then they will have to _______ the price. Market clearing price This situation is often referred to as a ‘glut’ and there is pressure on the price to fall. As the price falls demand will extend down the demand curve and supply will contract down the supply curve until they meet at price OP and quantity OQ. At this price, demand and supply are equal and it is known as the equilibrium or market-clearing price. Excess demand Similarly, at a low price of P2 demand OE exceeds supply OF. This is a condition of excess demand. This is a disequilibrium position where suppliers will sell out of stock very rapidly and there will be a shortage. The pressure on price is to rise in these circumstances and price is performing all three of its functions. Movement or shift recap? Draw a demand and supply curve. What will cause a movement along the curves? What will cause a curve to shift? Demand and supply question Price Demand Supply 1 900 500 2 800 600 3 700 700 4 600 800 5 500 900 Plot this, where is equilibrium? Summary – market mechanism So the market mechanism is the process by which market forces determine prices. The market mechanism can: cause supply to respond to changes in demand eliminate excess supply and demand signal changes in consumer tastes However it won’t necessarily ensure a fair distribution of all goods.