Self Catalytic Alloys for Hydrogen/Oxygen Recombination in Light
advertisement

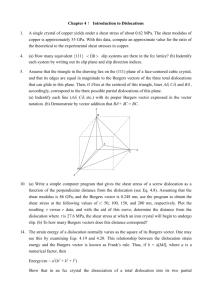
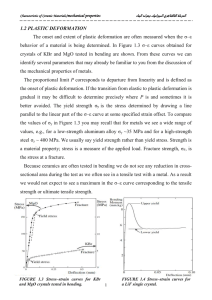
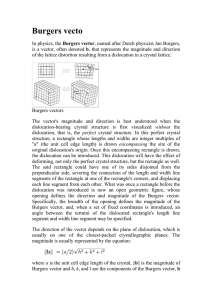
Dislocation Lecture Summary for 22.71 on 10_4_2012 Elliott Fray Outline • What is a dislocation? – Localized and Non-localized deformation – Characterizing dislocations – Dislocation types • Stress field of a dislocation – Edge type , Screw Type • Slip Systems • Applications What is a dislocation? • A dislocation is a discontinuity at which a material’s crystal lattice shifts from an un-sheared to a sheared state • Dislocations enable a material to deform under shear stress levels ~ 1/10,000 of its theoretical yield stress Localized and Non-Localized Deformation Dislocation Line 𝜀𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 = 𝜀𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐 + 𝜀𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐 • Crystals deform by dislocations 1 atomic layer thin (𝜀𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐 ) • Energy stored in the material after deformation is localized around the dislocations Characterizing Dislocations • Burgers Vector – The burgers vector is a property of a dislocation which characterizes its orientation – The burgers vector closes the circuit in loop in an imperfect crystal Characterizing Dislocations • Burgers Vector Dislocation Line 𝜇 = 𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 − 𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 – Dislocations with the same signs tend to repel, dislocations with the opposite signs tend to attract ( −𝜖 , −𝑏) ↔ ( −𝜖 , −𝑏) Same, Stress fields repel one another ( 𝜖 , 𝑏) ↔ ( 𝜖 , −𝑏) Opposite, Stress fields repel attract one another A few Dislocation Types Screw Dislocation Edge Dislocation b Mixed b • Edge – b is perpendicular to the dislocation line • Screw – b is parallel to the dislocation line Stress Field of a Dislocation • Screw Dislocation • Edge Dislocation • Packing of dislocations is limited by the range of the stress field surrounding a dislocation (R1) 𝐸(𝑅1) 𝐿 = 𝐸𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐 𝑅𝑜 + 𝜇𝑏2 4𝜋 𝑅1 ln(𝑅𝑜) where Ro~b Slip Systems • Materials tend to slip first along the closest packed plane – Smallest burgers vector: b – Largest spacing between planes: do • Alternatively one can find the directions of slip from the line tension 𝜼= 𝐸𝑠𝑒𝑙𝑓 𝐿 ~ 𝜇𝑏2 4𝜋 𝑅𝑠𝑐𝑟𝑒𝑒𝑛 ) 𝑅𝑜 ln( Minimize this to find slip systems → 𝐺𝑏2 Close packed plane of FCC Crystal or 𝜼 = 𝛼𝐺𝑏2 where α = 0.5-1 Applications • FCC materials tend to yield more before failing than BCC systems due to the large number of possible slip directions • FCC Aluminum Alloys are commonly used in nuts for traditional rock climbing Nut Placing gear during trad climbing Thanks! References – – – – – Dr. Meredith Aronson (2001). Materials Science and Art of Archaeological Objects. Retrieved from: http://www.ic.arizona.edu/ic/mse257/class_notes/disclocation.html Dr. Ulrich T. Schwarz (2004). Research Topics – Semiconductor Optoelectronics. Retrieved from: http://www.physik.uniregensburg.de/forschung/schwarz/research.html UC Santa Barbara Materials Research Lab. Finding the Burgers Vector of a Dislocation. Retrieved from: http://www.mrl.ucsb.edu/~edkramer/LectureVGsMat100B/99Lecture11VGs/ University of Cambridge. (2012). Slip in Close Packed Cubic Crystals. Retrieved from: http://www.doitpoms.ac.uk/tlplib/slip/slip_in_ccp.php Iwona Erskine-Kelliw (2009). Trad Rock Climbing Gear. Retrieved from: http://www.flickr.com/photos/iwona_kellie/4584634424/