Chapter 1—Changing Nature of Human Resource Management
advertisement

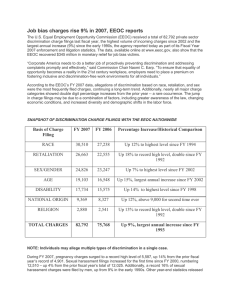
HR Hunan Ressources PRACTICE EXAM Chapter 1—Changing Nature of Human Resource Management MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. HR metrics must be linked to a. statistical analyses. b. industry outcomes. c. business performance. d. employee satisfaction. 2. All of the following are types of organizational assets EXCEPT a. social. b. human. c. financial. d. intangible. 3. You are the director of HR for a medium-sized firm. You are looking to hire a benefits specialist. You would prefer the individual to be certified in this field. Consequently, you will check applicant resumés for these initials a. OHST. b. CEBS c. CPT. d. GPHR. 4. HR professionals value their professional certification because a. certification is required in order to hold an exempt-level position in HR. b. PHR and SPHR certified professionals command higher pay. c. of the credibility certification gives them with peers and senior managers. d. certification is viewed as the equivalent of a master’s degree in HR. 5. The largest professional organization for HR generalists is a. the International Personnel Management Association (IPMA). b. the American Society for Training and Development (ASTD). c. the Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI). d. the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). 6. Emil is the assistant HR manager at a commercial construction company. Emil handles almost every aspect of human resources at the company, from employee questions about benefits to holding exit interviews. Emil is an HR a. generalist. b. specialist. c. technologist. d. unit manager. 7. Whether employees and managers of an organization behave ethically is fundamentally a function of a. professional codes of ethics. b. the relevant laws and legal guidelines applying to the organization and its industry. c. whether the organization has a code of ethics. d. the organization’s culture. 8. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act has had all of the following effects on HR EXCEPT a. HR vendors must prove that they are in compliance with the act. b. HR has had to staff the compliance verification effort involved with the act. c. HR has to check time, attendance, and payroll more closely. d. HR exempt-level professionals must have professional certification. 9. The position of vice-president of HR is open in a large paper-products manufacturing company. Two individuals are being considered, both from the internal HR function at the firm. The selection committee wants the new vice-president to be a strategic contributor to the firm. All of the following competencies are highly desirable EXCEPT a. that the candidate understands the paper-products business in all aspects. b. that the candidate be a highly detail-oriented person. c. that the candidate have personal and professional credibility. d. that the candidate understand the long-term implications of HR issues. 10. Pauline is an employee of a large city. She is the lead negotiator for contracts between the city government and the police and firefighters’ unions. Pauline is an HR a. specialist. b. technologist. c. generalist. d. interventionist. 11. The most common area for HR specialization is a. EEO compliance. b. labor/management relations. c. benefits. d. HR information systems. Chapter 3—Organization/Individual Relations and Retention MULTIPLE CHOICE 12. Applebee rewards managers who are able to retain high-performing employees. If you were a store manager, which of the following actions or behaviors would be most likely to be in your control that would improve retention of your high-performing hourly employees? a. Improve wage levels significantly for all hourly employees. b. Improve the benefits package for hourly employees. c. Base hourly employee raises on performance. d. Provide job security for hourly employees. 13. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a. One of the benefits of running call centers from countries such as India is that turnover is reduced to only that which is uncontrollable by the individual. b. Monotonous jobs, such as many call center jobs, generate high levels of turnover regardless of the country in which the call center operates. c. A disadvantage of running call centers from countries such as India is that poor performing employees tend to stay, rather than quitting, which results in dysfunctional retention. d. Workers in different countries are motivated by different core elements of jobs. Consequently, monotonous work, such as call center jobs, are considered motivating in some countries such as India. 14. Alice, a chronically tardy server at a moderately-priced restaurant, who consistently gets the lowest tips from customers, has announced that she is quitting to take another job at a newly-opened casino. This could be categorized as ____ turnover. a. disruptive b. functional c. involuntary d. predictable 15. In a/an ____ interview, individuals are asked to identify their reasons for leaving the organization. a. departure b. appraisal c. exit d. retention 16. With regard to exit interviews, which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Departing employees are eager to use the exit interview to unburden themselves about the real reasons for their leaving. b. HR typically conducts exit interviews. c. It is often more useful to contact departing employees a month or so after departure when they may be more willing to provide information. d. About half of organizations use exit interviews to make changes to aid retention. 17. Why should employers use attitude surveys? a. to identify employee needs and/or preferences b. to identify employees who are unmotivated and/or likely to quit c. as a psychological tool to assure employees that the employer cares about their opinions d. to identify jobs that can be eliminated or automated 18. Only surveys that are ____ can measure attitudes accurately. a. internally developed b. valid and reliable c. custom-designed for the specific organization d. user-friendly 19. The COO of ButtonVox is unwilling to authorize an attitude survey of employees that has been proposed by the director of HR. The COO has used several aphorisms to counter the HR director’s arguments: “Let sleeping dogs lie.” “If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it.” “Don’t ask, don’t tell.” and “This will just open up a can of worms.” The HR director suspects that the COO is most concerned that a. b. c. d. it will be difficult to keep employee responses to the survey confidential. employees will suspect an organizational restructuring is being considered. the survey results will reveal that employee compensation is not competitive. employees will expect action will be taken on the concerns identified. 20. HR managers should view absenteeism and turnover as a. unavoidable dysfunctional behaviors. b. largely out of the organization’s control. c. unrelated forms of withdrawal. d. symptoms of problems within the organization. 21. Ideally, interventions to improve retention a. should be implemented simultaneously across the organization. b. implemented in the departments least likely to have negative consequences. c. pilot tested before being implemented in the entire organization. d. initially implemented in the departments with the worst retention problems. 22. The employee attitude survey conducted by a financial services firm three months ago has been analyzed. Although employees are generally satisfied with their pay, the survey revealed strong and generalized dissatisfaction with the organization’s management style, promotion practices and training programs. As director of HR, you recommend a. sending an internal e-mail thanking employees for their cooperation and valuable feedback in the survey. b. announcing the positive survey results, while beginning to work on solutions to the problems revealed by the negative results. c. announcing the hiring of a consulting firm to address issues raised by the survey. d. communicating the positive and negative survey results to employees along with an action plan to move toward solutions of the problems revealed. Chapter 4—Legal Framework of Equal Employment MULTIPLE CHOICE 23. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a. The United States has lagged behind most other developed nations in passing laws banning employment discrimination. b. No major federal employment discrimination laws have been passed since the IRCA in 1986. c. Legislation aimed at reducing discrimination in employment has still not eliminated discriminatory practices. d. Anti-discrimination legislation impacts HR almost exclusively in the areas of hiring and selection. 24. In order to effectively defend itself against a charge of discrimination in the recruiting and selection of members of protected classes, an organization should a. provide exit interview summaries. b. keep job evaluation data. c. maintain applicant flow data. d. design subjective applications. 25. When Clark discussed his disturbing situation at work with a representative of the EEOC, the representative told him that the EEOC would make a decision as to how Clark’s complaint should be categorized. The EEOC representative explained all of the following complaint categories EXCEPT a. frivolous. b. immediate dismissal. c. needing further investigation. d. priority. 26. Yvette considers that she was passed over for a promotion because she is a woman over 40. She learned of the decision on August 1, 2007. She has until ____ to file her complaint with the EEOC. a. August 31, 2007 b. January 26, 2008 c. July 31, 2008 d. August 1, 2009 27. After the EEOC investigates a complaint and finds sufficient cause that the alleged discrimination occurred, its next step is to a. sue the employer in federal court. b. issue a right-to-sue letter to the complaining employee. c. offer mediation of the dispute to the two parties. d. decide on a remedy for the wrongdoing. 28. The ultimate authority in interpreting the EEO laws is a. the president. b. the U.S. Supreme Court. c. the EEOC. d. the Congress. 29. Orson wishes to be accepted into the management training program at his company. The company has a mathematical skills test. Orson took the test April 2 and received a score of 56%, which was below the cutoff score. The next time the test was given, October 11, Orson scored 89% and was accepted into the program. Orson had not done any studying between the test in April and the test in October. Which of the following statements is probably TRUE? a. This test had poor test-retest reliability. b. This test had poor content validity. c. This test was reliable. d. The criterion variable was invalid. 30. While Edith, the manager of HR for a large insurance company, was on vacation, her new intern decided to straighten out the bulging files in the file room. He went through all employee records and discarded all records from people who applied for jobs, but who were rejected, and he discarded all information about current employees that was more than five years old. To maintain confidentiality of the files, the intern had all the discarded material shredded. a. Everything the intern did was within EEOC guidelines. b. The intern was correct in discarding the rejected applicants’ records, but he should have kept all of the current employees’ records. c. The intern was probably within EEOC guidelines with his 5-year cut off for current employee files, but he should have retained the rejected applicants’ records. d. The intern was correct in shredding the rejected applicants’ records, but current employee records should be kept on-site for a minimum of three years, and then in a safe storage location for another 10 years in order to comply with EEOC guidelines. 31. All of the following employers must file an annual EEO-1 report with the EEOC EXCEPT a. all state government agencies. b. all employers with 100 or more employees. c. Federal contractors with at least 50 employees and contracts of at least $50,000. d. Financial institutions with at least 50 employees in which government funds are held or savings bonds are issued. Chapter 5—Managing Equal Employment and Diversity MULTIPLE CHOICE 32. The two approaches that are the basis for equal employment opportunity in U.S. organizations are nondiscriminatory practices and a. diversity training. b. affirmative action. c. reasonable accommodation. d. attribute-neutral practices. 33. Which of the following statements about research results on managing diversity is TRUE? a. Individuals with strong religious beliefs are usually the most open to the message of diversity training. b. Diversity training is most effective when it does not attempt to change worker’s personal beliefs. c. Diversity training results in employees generally believing they have expanded opportunities in the workplace. d. Diversity training reduces the level of discrimination and harassment complaints. 34. The most effective type of diversity training is one that focuses on employee a. thought patterns. b. behaviors. c. attitudes. d. perceptions. 35. A backlash against diversity efforts typically comes from ____ who believe they are set up as scapegoats for societal problems. a. white males b. middle managers c. undocumented workers d. professional women 36. In a company training program, white employees were required to play the role of a newly-hired minority employee. They acted out a scenario where the minority employee was subjected to racial taunts. This activity would be most likely to be included in a. affirmative action training. b. legal awareness training. c. cultural awareness training. d. sensitivity training. 37. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a. Managing diversity improves organizational performance on gender issues. b. Diversity has been consistently shown to increase business performance. c. Diversity of customer-contact employees increases satisfaction of minority and female customers. d. Firms with diverse workforces have higher turnover levels than firms with homogeneous workforces. 38. The most fundamental reason why PepsiCo’s diversity efforts has been successful is that a. the company is so profitable that it has ample slack resources to devote to diversity programs. b. top management is committed to diversity. c. PepsiCo has a large proportion of Latino employees. d. PepsiCo’s efforts are focused on employee attitudes and beliefs. 39. Harold and Maude both applied for a position in the firefighter training program. The cutoff test score to qualify for the training program was 560 points. Harold had a score of 601. Maude had a score of 592. The fire department brought in Maude instead of Harold because the department has almost no women firefighters. Harold feels he was denied entrance to the training program because he is a man. Harold feels this is a case of a. disparate impact. b. reverse discrimination. c. disparate treatment. d. adverse impact. 40. Clark, a member of the HR department at a large accounting firm, is comparing the number of protectedclass members who are potential workers in the appropriate labor markets in which the accounting firm hires both clerical and professional staff. Clark is doing a/an a. utilization analysis. b. availability analysis. c. representational sampling. d. market scanning study. 41. As part of affirmative action efforts a. employers establish quotas for hiring protected-class members. b. employers set goals, targets and timetables for the number and types of individuals they hope to employ in the future. c. the OFCCP will institute temporary bans on hiring any majority applicants. d. the EEOC will terminate federal contracts if employment patterns within the firm do not match the external labor market. Chapter 6—Jobs and Job Analysis MULTIPLE CHOICE 42. Odd and unusual aspects of jobs that are unique to the employing organization a. should be omitted from the job descriptions because they are not comparable across companies and industries. b. are important job requirements and should be included in the job description. c. should be eliminated because they introduce legal questions of discrimination or differential treatment. d. should be included in a job description only if they will make a difference in compensation. 43. The duty statement of a job description should start with a. a proper noun. b. an adverb. c. an action verb. d. an adjective. 44. An example of a ____ for a secretary would be "Ability to type 50 words per minute with no more than two errors." a. job description b. job responsibility c. performance standard d. job specification 45. The best source for the KSAs required for the job would be a. the ideal candidate who could perform the job excellently. b. the best-performing current job incumbent. c. an average-performing current job incumbent. d. the job incumbent who is performing the job satisfactorily. 46. You are looking for a new job and you are scanning dozens of job descriptions in a large organization where you hope to find a job. The quickest place to look in the job description to find the general responsibilities and main distinctive components of the job is in the a. identification section. b. general summary. c. essential functions and duties section. d. job specifications section. 47. What information should be provided in the job specification to ensure compliance with ADA regulations? a. b. c. d. identification of compensable and non-compensable factors. disclaimer that the job description is not a legal contract performance standards for all levels of physical ability information necessary to determine what accommodations might or might not be possible 48. Which of the following would be considered a performance standard for a clerk at a movie rental store? a. Stocks coolers of food items and snack racks. b. Operates cash register. c. Greets customer within 15 seconds of entering store. d. Files returned videos and DVDs. 49. Archie is developing performance standards for the job of pediatric nurse practitioner for a pediatrics medical practice. Archie should base these standards directly on a. the pediatric nurse practitioner job description. b. the job specifications for pediatric nurse practitioner. c. benchmark data from other pediatric medical practices. d. the professional guidelines by the pediatric nurse practitioner accreditation organization. 50. The main considerations in determining whether a task is an essential function or a marginal function of the job include all of the following EXCEPT a. the number of employees performing the task. b. the percentage of time spent on the task. c. frequency of the task. d. importance of the task. 51. At Ochre Automobile Insurance, the job of appraiser involves spending 40 percent of the time conducing “drive-by” assessments of the damage to policy-holders’ vehicles. This task would be considered a/an a. performance standard. b. essential job function. c. job element. d. job specification. ANSWER KEY 1. C 29. A 2. A 30. C 3. B 31. A 4. C 32. B 5. D 33. B 6. A 34. B 7. D 35. A 8. D 36. D 9. B 37. A 10. A 38. B 11. C 39. B 12. C 40. B 13. B 41. B 14. B 42. B 15. C 43. C 16. A 44. D 17. A 45. D 18. B 46. B 19. D 47. D 20. D 48. C 21. C 49. A 22. D 50. A 23. C 51. B 24. C 25. A 26. B 27. C 28. B