Mandatory Trainings
advertisement

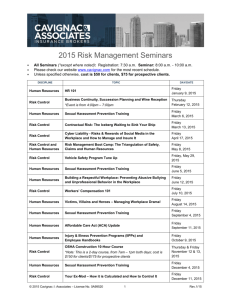
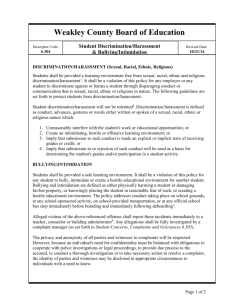
Understanding Harassment, Discrimination and Preventing Violence in the Workplace Presented by Laura Deyo Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 …prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex. Amended in 1991 to include Sexual Harassment as a form of discrimination "Title VII affords employees the right to work in an environment free from discriminatory intimidation, ridicule, and insult whether based on sex, race, religion, or national origin.” - EEOC Commission Discrimination and harassment in the workplace is strictly prohibited by a variety of federal and state laws, including, but not limited to the following: • Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 • Age Discrimination Act 1967 • Rehabilitation Act of 1973 • Pregnancy Discrimination Act (PDA) • Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, (ADA) Harassment and discrimination are illegal in the workplace when targeted toward a protected class. • • • • • • • • Age Sex Race and Color National Origin and Ancestry Religion and Creed Disability Veteran or Marital Status Sexual Orientation **State laws vary HARASSMENT: Personal or meanspirited acts which create a hostile work environment. Sexual Harassment Takes Two Forms • Quid Pro Quo: i.e. a supervisor uses his/her authority to demand unwanted attention or sexual favor • Hostile Environment: on-going language/behavior of a sexual nature. Unwelcomed jokes, pictures, emails, or physical content of a sexual nature What is Quid Pro Quo Sexual Harassment A situation in which an employee is confronted with sexual demands in return for something • The request can be • Explicit • Implicit • It only takes one sexual advance Submission to, or rejection of such conduct by an individual is used as the basis for employment decision What is Hostile Environment Harassment? Unwelcome conduct that • Unreasonably interferes with job performance • Creates offensive or intimidating work environment Examples of a sexually hostile environment • Jokes or remarks • Cartoons, posters or other graphics • Innuendos or suggestive looks Note: The behavior does not have to result in economic loss for the victim Hostile Environment Claim • The employee belongs to a protected group • The employee was subject to harassment that was unwelcome • The harassment complaint was based on a protected class • The harassment affected a term, condition, or privilege of employment and/or is so pervasive as to alter the conditions of employment and create an abusive working environment • The company or organization knew or should have known of the charged sexual harassment and failed to implement prompt and appropriate corrective action Bullying in the Workplace • Repeated, unreasonable actions of individuals (or a group) directed toward an employee (or group of employees), which are intended to intimidate and which create a risk to the health and safety of the employee(s). Bullying in the Workplace The frequent misuse of power to intimidate, degrade, offend or humiliate a worker, often in front of other employees. This can include: • • • • • • • • Excessive monitoring or “nitpicking.” Shouting or humiliation. Out-of-control practical joking. Isolation of individuals from information, outings or other opportunities. Blaming without justification. Impossible deadlines or expectations. Undermining by not giving credit to an individual, constant negative criticism or impossible assignments. Too much power given to certain individuals or groups because of position or tenure. Harassment and discrimination can take other forms of communication • E-mail • IM • Cards • Posters • Letters • Text messages Harassment and discrimination can take other forms of non-verbal communication • Innuendo • Gestures • Implied Intentions mean nothing….. When ongoing kidding of a personal nature continues or escalates after a request to stop is made, those employees may be subject to a charge of religious, racial, national origin or other discrimination. Harassment does not have to be severe to be illegal! Harassment because of someone's disability, that ranges from crude jokes, name calling, threats and intimidating, to physical assaults by fellow coworkers is illegal! All workers have a right to work in a non-hostile workplace! Create a Respectful Workplace • Follow non-harassment/discrimination and violence prevention policies and know how to report instances of bad behavior. • Do not repeat behavior that others find unacceptable. • Lead by example. • Conflict is addressed and in a positive manner. 15 • Title IX- Education Amendments of 1972 No person in the United States, shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance. • Rehabilitation Act of 1973 Prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in any program receiving federal assistance; also prohibits discrimination against beneficiaries of federal assistance. • Section 503 -in employment • Section 504- in programs • Section 508- in access to electronic and information technology • USDA Regulation 7 CFR 15 Any recipient of federal financial assistance, regardless of the amount, is subject to civil rights reviews. Further, the primary recipient of federal financial assistance is responsible for civil rights administration where the primary recipient has extended the financial assistance to another recipient. • Executive Order 13166 (2000) Improving Access to Services for Persons with Limited English Proficiency. Under Title VI and federal agency regulations implementing Title VI, recipients of federal financial assistance have a responsibility to make reasonable steps to provide Limited English Proficiency (LEP) individuals with meaningful access to their programs and activities. The Age Discrimination Act was passed by Congress in 1967 and prohibits discrimination in the hiring of employees because of age and has been used successfully by victims of age related harassment and ridicule on the job. The Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA), protects individuals who are 40 years of age* or older. (State laws vary) PROTECTING EMPLOYEES BEYOND HARASSMENT AND DISCRIMINATION Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 “An employer is obligated to furnish each of its employees a place of employment which is free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death and/or serious physical harm to its employees.” Interpreted in 1992 to include preventable workplace violence. OSHA Further States… “Employers who do not take reasonable steps to prevent or abate violence hazards in the workplace can be cited.” -OSHA Fact Sheet, 2002 “Prevention”… minimize, lessen opportunities WORKPLACE VIOLENCE: Any situation that may threaten the safety of any employee, have an impact on an employee’s physical or psychological well-being, and/or cause damage to company property. -SHRM • Harassment: Acts which create a hostile work environment • Threat: An expression of intent to cause physical harm • Physical Attack: Behavior resulting in physical assault with or without use of weapon • Workplace: Any location either permanent or temporary where an employee performs any work-related duty Who is at Risk? Research has identified factors that may increase the risk of violence including: • Those who exchange money with the public • Those who work alone or in isolated areas • Healthcare workers rank #1 • Working where alcohol is served • Working late at night • Law enforcement personnel VIOLENCE IS ANGER IN MOTION Workplace Violence Includes: • Physical altercations • Beatings • Stabbings • Sexual Assault • Threats and Intimidation • Stalking Red Flags • Irrational Communications Behavioral Precursors to Violence • Vocalized Despondency • Threats: Overt or Covert • Work Slowdown or Stoppage • Uncharacteristic Body Language • Disrespect for Others’ Personal Space • Menacing Behaviors • Recent Failed Relationship(s) • Uncharacteristic Hygiene Deficits Common Missteps in Preventing Violence • Underestimating a situation • Inconsistency in following protocol • “Covering” for coworkers • Lack of documentation • Failure to involve law enforcement Best Practices • Careful listening to minimize tension in heated encounters • Respond immediately to arguments • Self-protection strategies • Ability to maintain control and calm • Request help when needed, don’t try to handle situations that may escalate by yourself COMMUNICATION Active Listening • Minimizing a threat • An angry employees or customers may simply want to be HEARD • Clarify what you hear; paraphrase to be sure your are hearing the message • Show involvement and concern Do not make the situation worse by being confrontational. Know your organizations’ policies and when to call for assistance. Do not ignore bad behavior that can be interpreted as a threat or harassing or discriminatory. It is up to all of us to prevent harassment, discrimination & violence • Respect (For One Another) • Recognition (Of Real & Potential Problems) • Response (appropriate reporting or reaction) Additional resources are available from the EAP Go to www.theeap.com and choose from the MANAGEMENT ACADEMY or PERSONAL/PROFESSIONAL TRAINING Over 40 courses are available online, including: Preventing Discrimination and Harassment Violence Prevention in the Workplace Valuing Diversity Dealing with Difficult People