Acids Bases & Salts
advertisement

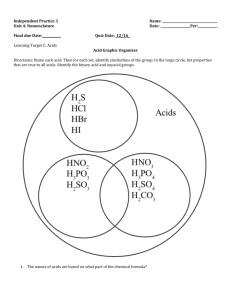
Acids Bases & Salts (Acids) an e-learning series by ycs Learning Objectives • By the end of the lesson, pupils would be able to – Define the meaning of acids – Name common acids – Explain the importance of water as solvent – Describe the physical properties of acids – Describe the chemical reaction of acids – Explain the basicity of acids Types of Acids • Mineral acids – hydrochloric acid, HCl – nitric acid, HNO3 – sulphuric acid, H2SO4 • Organic acids – ethanoic acid (vinegar), CH3COOH Definition • A substance when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions as the only positive ions HCl (aq) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) click icon H+ ion + Releasing the H ions • Water is needed for the release of H+ ions and not organic solvent. – e.g. If the gas hydrogen chloride, HCl(g), is dissolved in methylbenzene, no H+ ions would be produced. + What does the H do? • The hydrogen ion is responsible for the properties and chemical reactions of acids. • What are some properties and chemical reactions of acids? Properties of Acids • Sour taste • Turns blue litmus red • Changes the colour of indicators like universal indicator, methyl orange..etc Indicators & pH Scale • Click on the pH Scale below to learn more about indicators and the pH. The pH Scale Chemical Reactions • Acids react with metals to form salt and hydrogen gas. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Fe(s) + 2HNO3(aq) Fe(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g) Ca(s) + H2SO4(aq) CaSO4(aq) + H2(g) Chemical Reactions • Acids react with carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide gas. CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) Na2CO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) Chemical Reactions • Acids react with bases to form salt and water. NaOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + H2O(l) CuO(s) + 2HCl(aq) CuCl2(aq) + H2O(l) • This reaction is known as neutralisation and is represented by the ionic equation, – H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) H2O (l) Basicity of Acids • If an acid contains one replaceable hydrogen, it is a monobasic acid • What can you say about dibasic and tribasic? • Determine the basicity of these acids, – HCl – H2SO4 – H3PO4 Nutshell Activity • Write the chemical equations for the following reaction calcium + dilute hydrochloric acid Iron(II) carbonate + dilute nitric acid magnesium oxide + dilute sulphuric acid Nutshell Activity • Hydrogen chloride was bubbled into an organic solvent, methylbenzene. The resulting solution has no effect on litmus paper. Explain this observation. Nutshell Activity • Acids contain replaceable hydrogen. For each hydrogen replaced by a positive ion, a salt is produced. How many types of salts can be produced from a dibasic acid? • Give an example of a monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acid. Extension • To learn more about the topic on acids you can follow this link here to Chinese High School Chemistry VLE’s webpage.