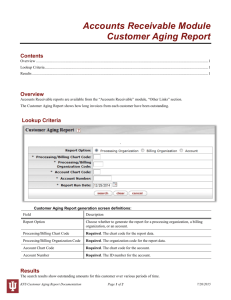
KFS Chart Features
advertisement
Building a Kuali Chart of Accounts Vince Schimizzi, Michigan State University Claire Tyson, San Joaquin Delta College Kim Yeoh, Cornell University Agenda I. Kuali Financial System (KFS) Key Chart Features – Chart – Organization – Account/Sub-account – Fund/Sub-fund – Function – Object/Sub-object – Project Code – Extended Attributes II. Laying the Groundwork – Reporting requirements – Multiple charts – Organizational hierarchies – Security/Workflow – Chart Document Routing III. Chart Experiences and Challenges – San Joaquin Delta College – Cornell University – Michigan State University Kuali Financial System (KFS) Key Chart Features KFS Chart Features Chart • An aggregation of related accounts (e.g. campus, auxiliary activities) • Individual charts report to higher level charts KFS Chart Features Organization • A unit of activity typically represented by a department (e.g. Chemistry is a department in the College of Natural Science at MSU). • Organizational structure facilitates workflow in KFS, strengthening internal controls KFS Chart Features Account/Sub-account • Specific identifier for a pool of funds assigned to a specific organization for a specific function (e.g. a grant account). • Accounts report up through organizations • Sub-accounts achieve further division of an account for internal reporting purposes Organization Hierarchy with Accounts/Sub-Accounts University Campus Division Department Program A Program B Account Account Sub-acct 1 Sub-acct 2 KFS Chart Features Fund/Sub-fund • Accounts also map to sub fund groups and then to fund groups (i.e. sub-fund is an attribute of account number). • For those that use fund accounting, an account may belong to – FUND – restricted – SUB FUND – grants / sponsored programs KFS Chart Features Function • Higher education function code is an attribute of account used in the creation of functional classification financial reports • Enables multiple views and levels of reporting KFS Chart Features Object/Sub-object • Transaction descriptor (asset, liability, fund balance, revenue, expense) • Object codes map to levels and then to consolidations • Object codes also map to object codes of higher level charts allowing for the rollup to an institutional chart for external reporting • Reports to functionality enables multiple chart of accounts KFS Chart Features Project Code • Specific transaction attribute • Established and approved at the organization level • Example: Inter-department project KFS Chart Features Extended Attributes • Can be used throughout Chart (e.g. Orgs, Accounts, Object Codes, etc.) • Implementation – Set of developer instructions to use additional table as an extension of an existing table – Can be supplemented with support tables to control related data and structure • Example – Linking otherwise unrelated organizational units Laying the Groundwork Laying the Groundwork Reporting Requirements Questions related to: • Reporting – – – – Institutional financial reporting (external) Summarized management reporting Departmental detail Online queries • Structure of Institution – Campuses (organizational units) – Fund accounting • Higher Ed Functions Laying the Groundwork Multiple Charts Questions to ask… • Does the institution need multiple charts? – For separate campuses – For Auxiliary operations • Will interfaced systems be able to accommodate multiple charts? • Does there need to be a high level chart for institutional financial reporting? Laying the Groundwork Organizational Hierarchies Questions to ask… • Should the institution model its organizational hierarchy based on: – lines of authority – lines of business (disciplines, auxiliaries, etc.) – system security schemas – reporting requirements Laying the Groundwork Security/Workflow Questions to ask… • Will the established chart accounts facilitate use of the institution’s security management tool? • Will the organizational hierarchy enable desired workflow requirements? • How can KFS hierarchies and workflow support the institution’s internal control policies? Laying the Groundwork Chart Document Routing •The routing sequence of the primary chart documents occur as follows: – Account – fiscal officer, org hierarchy, campus chart manager, university chart manager, special conditions routing – Account Delegate - fiscal officer, org hierarchy, special conditions routing – Organization - org hierarchy, campus chart manager, university chart manager – Object Code - campus chart manager, university chart manager – Sub Accounts/Sub Objects - fiscal officer, org hierarchy, special conditions routing – Project Code - org hierarchy Chart Experiences and Challenges San Joaquin Delta College Objectives • Purpose of a Financial System – – – – Data for Decision Making Financial Tracking Categorizations Reporting • Fulfill Institutional needs for financial data • Mirror Financial System Org Hierarchy to Operational Structure San Joaquin Delta College Starting with the End in Mind • Financial Reporting – Internal • Management Reports • Department Accountability • Online queries – External • GASB / FASB requirements • Federal reporting • State reporting • Other San Joaquin Delta College KFS Training / Implementation • Changes – – – – – Campus buy in Top 3 internal report wish list Hands on Training Old to New mapping What stays the same Cornell University Change Management for KFS • Decentralized campus • Significant change (not a bad thing!) • How/when to get campus involvement – Local module teams – Start up phase planning (meetings with major campus colleges/divisions) – Demos/presentations – Kuali Days Cornell University Reporting Requirements • Financial reporting (external) vs management reporting • Shadow systems • Faculty reporting • “Funding Year” reporting Cornell University Forward-looking Configuration • Support the reporting requirements at many levels – Use of extended attributes • Standardization vs flexibility – Organization level (extended attribute) – Object codes – Project code Michigan State University KFS Considerations • Multiple reporting structures vs. a hierarchical organization structure in KFS. • Object code groupings (external reporting vs. institutional budgeting vs. individual deptartment/account needs) • “User Defined” attributes • Overall change management



![[#KFSTP-1397] Collection Activity](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007301192_1-dd6f1230b3c65cff3429319b4ff035e1-300x300.png)