America in World War I
advertisement

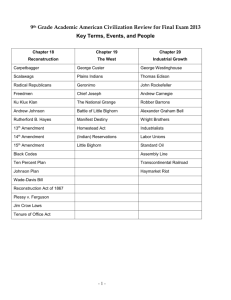
Foundations: Background to American History Bill of Rights – First 10 Amendments to the Constitution: Added to protect personal Liberty (Freedom). 1st Amendment 2nd Amendment Rights of the Accused 4th Amendment 3rd Amendment 5th Amendment – Self-incrimination: A person cannot be forced to testify Miranda v. Arizona Eminent Domain 6th Amendment - Fair Trial 7th Amendment – Trial by Jury 8th Amendment 9th Amendment – Rights to the People 10th Amendment – Rights to the States Industrialization in the “Gilded Age” Tentacles represent the reach and power Standard Oil had over the U.S. Capital, White House, State Capital and over congressmen. John D. Rockefeller and his company Standard Oil and Trusts controlled 90% of the oil refining in the U.S. and used its economic power as a monopoly to sway government decisions. Sherman Anti-Trust Act 1890 – Stop monopolies engaging in unfair business practices. Development of a national market Shipping raw materials and finished goods became less expensive. Department stores and Advertisements Population growth and railroad expansion created favorable conditions for business expansion Interstate Commerce Act 1887 – Prohibited railroads from charging higher rates for shorter routes. Conditions of labor such as child labor, long hours/low wages, unsafe conditions and lack of job security led to the rise of workers Unions. Leaders such as Samual Gompers formed The American Federation of Labor to organize skilled labor forces with similar economic interest for high par and 8 hour work days. The Workingman depicted as ‘Hopelessly Bond to the Stake’ of Monopolies and the conditions they endure. Men of logs represent entrepreneurs such as Andrew Carnegie & John Rockefeller Haymarket Affair Riot of 1886 - Union activities were often associated with violence and radical ideas. Labor leaders were blamed when a bomb exploded during a demonstration of striking workers at Haymarket Square in Chicago. Government Attitude – Business leaders contributed heavily to political campaigns so politicians shared the same out look as the business leaders. Laissez-faire – The government positions was, let it be. The fewer regulations to more successful the business can be. Not taking into account the working man or the environment. Clayton Anti-Trust Act 1914 – Prevents the restriction of unions and strikes during labor disputes. American Society in Transition New Immigrants - Southern and Eastern Europe. Catholic, Jewish, and spoke no English. Ethnic Ghettoes – Settled with those of same nationality Americanization Schools taught English. Nativism – Those “native” to the U.S. wanted to restrict immigration because new immigrants would work for low wages and take away jobs. Urbanization: The Growth of Cities & Rise of Industry Factories, workshops and new farm machinery reduced the need for farm jobs, causing movement from rural (farming) to urban (industrial). Cities Face New Problems - Overcrowding Tenements – Single room apartments without heat or lighting. Inadequate Public Services – Hospitals, police/fire department, schools, street cleaning and garbage. Transportation – Development of electric trolleys and the subway. Social Tensions – Between rich, poor, minorities and nativists. [Left] Controlled the activities of political parties in the city to ensure that their candidates were elected. Provided public services and jobs to immigrants in return for their votes. They made sure city government worked to their advantage. Boss Tweed is represented counting votes. This shows how bosses controlled the vote to his advantage. [Middle] Political bosses and politicians would work together to provide over-prices contracts to preferred business, often ripping off the tax-payer with no one taking the responsibility. [Right] The Bosses of the Senate – Notable symbolism: “This is a Senate of the Monopolist by the Monopolists and for the Monopolists.” Monopolist are piling in from their entrance while The Peoples entrance in the background is closed. Standard Oil (John D. Rockefeller) is represented as well as Steel and Iron (Andrew Carnegie) as monopolies. Chinese Exclusion Act – First federal law to restrict immigration. It reflected American/Nativist prejudices at the time against Asians. In California political leaders blamed unemployment and decline in wages on Asian immigrants. The railroads attracted an increasing number of settlers to the west. Rails often ran through Native American territories, leading to new conflicts. Millions of Buffalo were destroyed by sharpshooters traveling by train. This affected the ability of the Plains Indians to remain on the Plains. Homestead Act 1862 – Any citizen could occupy 160 acres of land if the settler “improved” the land by making a home and growing crops. The cattle industry/Ranchers began driving cattle northwards to the railroad lines in Kansas where they were able to ship cattle to Chicago to be slaughtered then the meat shipped east in refrigerated rail cars. Open Range – Unfenced land not belonging to anyone. Problems faced by farmers/Homesteaders - The Homestead Act and the sale of railroad land-grants stimulated the movements of farmers westward. Hostility from both the Indians and the Cattlemen/Ranchers The farmers would win the conflict because they came in greater numbers and were able to enclose their lands with barbed wire. When they arrived they found little rainfall, few trees, tough soil, extreme temperatures, plagues of grasshoppers and personal isolation Factors Eroding Native American Control of the West Forced Removal – Moved Indians west of the Mississippi (Mainly to Oklahoma) Nearly one-quarter of the Cherokees perished on the journey known as The Trail of Tears. Flood of Settlers – Transcontinental Railroad and the Homestead Act helped settle the west. Indian Wars Destruction of Buffalo and natural environment. The Dawes Act 1887 – Sought to speed up the process of Indians becoming Americanized. Abolished Native American tribes and gave each family 160 acres to farm. Shortcoming of the Dawes Act Threatened Tribal Ways Hunters, Not Farmers Infertile Lands – Reservation Life – Suffered malnutrition and poverty Progressive Era Cross of Gold speech by William Jennings Bryan. Democratic National Convention in Chicago on July 9, 1896. Bryan supported Unlimited Coinage of Silver to raise farm prices and make loan payments easier and increase the amount of money in circulation. He decried/disliked the gold standard, he praised farmers and denounced/blamed bankers for “crucifying mankind upon a cross of gold. Unlimited Coinage of Silver is a Populist Party platform. This is an example of how major political parties adopt popular ideas from third parties. Trusts – Companies that worked together to control the market of a particular good. Created Monopolies. Teddy Roosevelt believed there were "good trusts" and "bad trusts." He dissolved/got rid of bad trust. The trusts that were destroyed became symbols, so that other trusts would reform themselves. Theodore Roosevelt broke up Rockefeller’s Standard Oil and became viewed as a trust-buster. Roosevelt’s Square Deal Legislation Protecting the Public Health – Meat Inspection Act and Pure Food & Drug Act Regulating Transportation and Communication. Conserving the Nation’s Resources. Reasons for Farmers’ Economic Problems Agricultural Overproduction – As farmers produced more crops, food prices fell. High Costs – Railroads charged more for shorter hauls. This would lead to the Interstate Commerce Act 1887. Farmers Indebtedness – Farmers borrowed at high interest rates Natural Disasters Granger Movement – Urged economic and political reforms such as the Interstate Commerce Act. The farmers and Grange Movement supported the Populist Party. The Populist Party Platform – A Third Party Fighting for farmers, industrial workers, and miners in the battle against banking and railroad interests. Unlimited Coinage of Silver – To raise farm prices and make loan repayments easier. Direct Election of Senators – 17th Amendment Term Limits for President – 22nd Amendment Graduated Income Tax – 16th Amendment Shorter Workday – Eight hours The Populists Party represented how a Third Party can have an impact on the political process. Although they never gain a majority following, they provide an outlet for minorities to voice grievances and generate new ideas. Progressive Movement – Correct the political and economic injustices that had resulted from America’s industrialization and they wanted the government to correct the evils created by big business and political machines. Image shows Commerce, the business of America, dressed as a woman with Labor (right) standing up to Capital, the corporations (left) ready to fight. The quote say that we have become too big to fight one another. Social Gospel Movement – Emphasized a Christian Duty to help those who were less fortunate. The Social Gospel Movement is also associated with the Temperance Movement – The removal of alcohol from society. America Builds an Empire The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine declared that the United States would exercise “international police power” to get Latin American nations to honor their financial commitments to European powers and keep European powers out of Latin America. Triggering events of the Spanish – American War: Marked the end of Spain’s colonial empire and the emergence of the United States as a world power. The U.S. demonstrated its Naval strength to the world. Yellow Journalism - Newspapers sensationalized news reports De Lome Letter – Spanish Ambassador call President Mckinley weak. This angered many Americans. Explosion of U.S.S. Maine – Explosion was blamed on a Spanish Attack, which was never proved but gave America reason enough to intervene in Cuba. Theodore Roosevelt & Rough Riders – Fought at San Juan Hill and helped lead America to victory. Platt Amendment – Gave the United States to intervene in Cuban affairs at any time. American Imperialism – Represented by the American Bald Eagle stretching its wings from Puerto Rico to the Philippines. Need for Raw Materials and Markets – Make stuff, sell stuff! Nationalism – Show of power and pride! Strategic Reasons – Maintain a powerful navy to protect. Attitudes toward other Peoples – “Superior race” that should rule others. Missionaries to convert natives. Alfred Thayer Mahan & Theodore Roosevelt among the leading imperialist. Anti – Imperialism: Mark Twain and Andrew Carnegie felt imperialism violated the basic principles of self-government on which the United States was founded. Hawaii – American settlers built sugar & pineapple plantations Missionaries sent to convert natives to Christianity. 1893 – Queen Liliukalani overthrown by American landowners and Sanford B. Dole led the provisional government. 1898 - After the outbreak of the Spanish – American War, Congress voted to annex Hawaii. China – Europe established “spheres of influence” (areas where they enjoyed special privileges in the 1850s. John Hay – China was a vital market for U.S. & wanted a piece of it. Open Door Policy - Gave equal trading rights to all foreign nations. Boxer Rebellion – Chinese who opposed Western influence. Boxers threatened the live of foreigners living in China. U.S. troops were sent to China to crush the rebellion. Commodore Matthew Perry opened up Japan to western trade and influence. Japan began to adopt imperialist policies. Panama’s climate posed special challenges in building the canal. Intense heat, mountains and dense rainforest. Heavy rains caused frequent mudslides. Yellow Fever was spread by mosquitoes. The canal caused major environmental damage Reasons for U.S. Interest in the Caribbean Hemispheric Security – Keep foreign powers out of the Caribbean because they pose a threat to U.S. Security. Economic Interest – Agricultural products like sugar & provided valuable goods and investments. Need for a Canal – The Spanish – American War demonstrated the need for a canal through Central America. America in World War I ANationalism – Extreme pride in country led to rivalries between France, Germany, Austria – Hungary, and Russia. Nationalities wanted to form their own national states creating more conflict between empires. Economic Rivalries and Imperialism – Competing for territories and resources Militarism and Military Planning – Building up militaries. Belief that it was better to attack first to catch others off guard. Alliance System – Allied Powers: France, Great Britain, Russia, and America. Axis Powers: Germany, Austria – Hungary, and Ottoman Empire Assassination of the Archduke Ferdinand by Serbian nationalists ignited World War I Machine guns, poisonous gas, submarines, airplanes and tanks contributed to a new type of warfare. Machine guns halted enemy lines creating “Trench warfare.” Hundreds of miles were dug on the Western Front. Tanks were used to break through the stalemate. America Intervenes 1917 – Zimmerman Telegram – Germany promised Mexico to get back land if Mexico fought America. Sussex Pledge - Germany pledge not to sink ships. Main reason for American entry into World War I o Unrestricted Submarine Warfare – Violated the principal of “freedom of the seas.” After Germany broke its pledge, President Wilson asked congress to declare war on Germany. The Home Front 1917-1918 Selective Service Act – Required millions of Americans to register for the draft. Women and African Americans filled jobs left by soldiers. The war was paid for by higher taxes and war bonds. The war benefitted the American economy, since exports to the Allied powers increased. Espionage Act of 1917 – Made it a crime to criticize the war effort. Schenk v. U.S. – Schenk arrested for encouraging men not to register for the draft. The court ruled that there are limits to free speech. The First Amendment did not protect words that created a “clear and present danger.” You cannot shout fire in a crowded theater. The Roaring 20’s Social Tensions – The Red Scare: 1917 Communists revolutionaries, led by Vladimir Lenin seized power of Soviet Union. Communist threatened to spread their revolution to other countries. In 1919 Many Americans feared this would spread to America, causing a “Red Scare” Palmer Raids and J. Edgar Hoover – Rounded up thousands of suspected communists without warrants. Hysteria affected Italian immigrants Nicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti. The two were convicted of murder and robbery with no evidence proving guilt and were sentenced to death. Rise in Nativism (dislike of foriegners) and increased immigration restrictions. Republican Policies Favoring Big Business: Laissez – Faire High Protective Tariffs: Hawley Smoot Tariff 1930 – Designed to protect U.S. manufacturers by keeping out foreign made goods. Lower Taxes on Wealthy and Corporations – Resulted in a larger tax burden shifted to the average wage earner. Lax Enforcement of Antitrust Laws – Did very little to regulate business. Teapot Dome Scandal – Harding Administration: Secretary of Interior leased oilrich government lands at Teapot Dome, Wyoming in exchange for personal bribes. Cultural Values in Conflict Prohibition 18th Amendment – Banned alcohol. It would be repealed by the 21st Amendment. Women’s Suffrage 19th Amendment – Gave women the right to vote. Gave women a greater voice in government. The Scopes Monkey Trial – Pitted older religious beliefs against new scientific theory. Clarence Darrow and Modernism (Teaching Evolution) vs. William Jennings Bryan and Traditionalism (Creationism) The Great Depression and the New Deal Roosevelt’s Court-Packing Scheme (1937) Proposed a plan to allow the President to add a new appointment to the Supreme Court for each Justice over 70 ½ years old. This would have given him control of the Supreme Court. Viewed as an effort to upset the traditional separation of powers and would have increased the power of the presidency/executive branch. Court Packing Scheme + Increasing size of government + Serving 4 terms = Being viewed as a Dictator or King Franklin D. Roosevelt & The New Deal changed American thinking about the role of government because it was based on the belief that the – federal government bears the chief responsibility for ensuring the economy runs smoothly. Permanently increased the size of the federal government. New Deal Remedies – Relief to banks homeowners, farm owners and the unemployed. Gave jobs through government projects. Recovery to increase purchasing power by putting government money into consumers’ hands. Reform to protect individuals against risk they could not handle on their own. Created the FDIC (insures your bank deposits) and created Social Security (provides retirement income to retired people) Causes of the Great Depression – Over extension of Credit Overproduction – Consumers lacked the money to buy cars, radios, and refrigerators. Manufacturers produced more goods than they could sell. Speculation: Buying on Margin – The buyer paid only 10% of the stock’s value and promised to pay the rest when the stock was sold. Shaky Banking – Banks invested their depositors’ money in unsound investments. The government failed to regulate banking & the stock market. Restricted International Trade – Tariffs protected American markets. This made it hard for producers to sell abroad since other countries retaliated with tariffs. Stock Market Crash October 29, 1929 – Corporations could not raise funds, leading to unemployment and then people could not pay loans or rents, leading to bank failures – Thousands of people lost their life savings. Dorothea Lange’s photography was made famous because her photographs were able to capture the pain and suffering experienced by Americans during the Great Depression The Dust Bowl Farming methods, such as lack of crop rotation, cut up the top-soil and depleted the groundwater. A series of droughts in the early 1930s dried up crops and top-soil, turning the soil into dust. Unable to pay their bills farmers were forced to abandon their farms, many moved west to California. John Steinbeck documented these movements of these migrants he dubbed Oakies. America in World War II Japanese-American Relocation Executive Order 9066 Issues by President Truman Korematsu vs U.S. – Supreme Court Ruled that relocation was constitutional during time of war. Women and minorities filled jobs left by men fighting the war. This gave women and minorities a chance to prove their worth as productive members of society. Americans sacrificed everyday items such as milk, bread, and produce in order to provide for the war effort. Ration Books were issued to ensure the distribution of goods for the war effort. Many Americans planted Victory Gardens in order to increase the food supply during farm-labor shortages. Origins of World War II – Joseph Stalin, Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini World War I and the Great Depression had profound effects on Europe. High unemployment and bitterness from World War I shook public confidence and leaving people desperate for change. Leaders like Hitler and Mussolini would take advantage of the people’s vulnerability. Mussolini = Italian Fascists Hitler = German National Socialists (Nazis) Russian Revolution of 1917 - Russia became the world’s first Communists state. Failure of the League of Nations – League was too weak to resist these dictators. Appeasement Failed – Britain gave in to Germany’s demands for the Sudetenland - part of Czechoslovakia Increasing United States – Japanese Tensions Japan’s industrialization needed raw materials and markets for their industries. Japan’s military began to influence national policy. In 1931, Japan invaded Manchuria. In 1937 Japan attacked the rest of China. In 1941 Franklin Roosevelt reacted by freezing Japanese assets (money) in the United States and cutting off all trade with Japan. This pissed Japan off… Reasons for Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 “A date which will live in infamy…” Japan decided to attack Indonesia to obtain oil for their war effort. They knew this would provoke America. Japan decided to attack first. Temporarily eliminated U.S. naval power from the Pacific. United States declares war on Japan. Four days later Germany and Italy, allies of Japan, declared war on the United States. Americans were now engaged in a war on two fronts, the Atlantic and Pacific. D-Day June 6, 1944 – The invasion of Normandy, France. Led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower. Considered the largest amphibious landing crucial to the success of the allies. The Bataan Death March, 1942 The Japanese forced their prisoners to undertake a 60-mile march through the jungle and faced starvation, disease, exposure to the sun, and no water. Thousands of soldiers died. The War Turns Against Japan Navajo Code Talkers – The Navajo language is unwritten and extremely complex. The Japanese were unable to break the codes. Battle of Midway – Island Hopping U.S. Navy could decipher Japanese secret codes and knew a surprise attack by the Japanese was coming. Chester Nimitz commanded U.S. forces at the Battle of Midway. Battle marked an end to Japan’s strong hold in the Pacific Ocean. Opened up the way to drop the bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki Japan Technology in World War II Albert Einstein sent a letter to President Roosevelt telling him it was possible that Germany might be developing an atomic bomb. President Truman feared that an invasion of Japan might lead to a million American casualties. Truman decided to use the Atomic Bomb against Japan rather than to sustain such high losses. Rader was developed to detect a moving objects range, altitude and direction. Sonar was used to detect submarines Antibiotics such as penicillin to treat soldiers wounds. Jet and Rocket Engines gave fighter pilots an advantage The war was won in part by the ability of the Allies to create new technologies America in the Cold War and the Civil Rights Years 1946 An Iron Curtain fell over Eastern Europe, closing it off from the West. Trade and communication would remain limited for 40 years. 1948 A Divided Germany & the Berlin Airlift by President Truman French, British and Americans merged zones into West Germany. Soviets responded with a blockade of West Berlin, closing all highway and railroad links to the West. U.S. responded with Berlin Airlift provided supplies to a blockaded Berlin. The blockade was not successful and showed that America would not back down to Communism. The Truman Doctrine and the Origins of Containment - Truman promised to support any country fighting Communism. This policy would lead to government financial aid to Greece and Turkey, involvement in Korea and Vietnam. Cartoon symbolizes unchartered territory (shaky stick and troubled waters) for America (Shown as Uncle Sam blindfolded carrying a bag of money for Greece and Turkey) The Containment Policy also extended to Asia. China falls to Communism in 1949 led by Mao Zedong. This was seen as a crushing blow for the United States as more than 1/4 of the world’s population now came under Communist control. The Marshal Plan – Provided aid to help Europeans rebuild their economies. Farm production had been destroyed and cities had been reduced to rubble. President Truman believed that people who were desperate and miserable would be attracted to Communism. Extremely successful. It benefited the American economy in helping rebuild war torn Europe. Speed the economic recovery of Western Europe and created good will towards the U.S. Korean War, 1950-1953 Dividing line remains at the 38th Parallel Korea was divided into two zones after WWII. A Communist North Korea, a non-Communist South Korea. North Korea invaded South Korea in an attempt to unify the country under Communists rule. North Koreas aggression reminded President Truman of Germany’s aggression in WWII. The United States was able to pass a resolution sending U.N. troops, mostly U.S. soldiers, to South Korea. Led by General Douglas MacArthur American forces on China’s border brought China into the war The United Nations was successful in halting North Korea’s advance The dividing line remains at the 38th Parallel The Space Race begins with the launch of Sputnik inn 1957 It raised fears that the Soviet Union might use missiles to send nuclear bombs to the United States. The federal government started new programs in math and science education Technologies developed for spaceflight were later developed in to consumer goods, such as, cordless power tools, Velcro, Tang, and Kevlar. Led to improved communication technologies via satellites through the use of GPS and Direct TV. Loyalty Review Boards – Established by President Truman to investigate individual “unAmerican” activities, such as participation in the American Communist Party. House Un-American Activities – Congress conducted its own loyalty checks. This Committee questioned actors, directors, writers & others about possible Communist sympathies. The Rosenberg Trials – Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were charged with selling national secrets to the Soviet Union. They were found guilty and executed. The Venona Papers would later prove their guilt as well as show that some Soviet agents penetrated American government, science and industry during the Cold War. Economic Prosperity under Eisenhower and Social Conformity during the 1950’s Housing Boom – High birth rates “Baby Boom” This boom and the G.I. Bill (Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944) helping veterans led developers to build cheaper, mass-produced housing. This movement from urban to suburban led to a declining urban tax base and decaying inner cities. Economic Prosperity – Pent up consumer demand. People had money from working during the war and returning home from the war. More jobs were available. Conformity – Unusual ideas were regarded with suspicion. Impact of Geography – The building of highways and the construction of new homes after World War II allowed a shift from city to the suburbs. This would also have an impact on the environment. Replacing the habitat of local wildlife with neighborhoods would force the wildlife to die off or relocate. The Road to Equal Voting Rights Civil Rights Act 1957 – Gave federal courts power to register African American voters. Helped set the pattern for later civil rights legislation. March on Washington – Pressured Congress to pass Civil Rights Act of 1964 – Prohibited discrimination based on race and religion in businesses. It created the… Equal Employment Opportunity Commission – Businesses could no longer discriminate in employment. 24th Amendment – Eliminated poll taxes in federal elections. Selma Marches 1965 – MLK marched to demand the vote for African Americans. Demonstrators were attacked, Johnson introduced the Voting Rights Act of 1965 – Ended poll taxes, suspended literacy test and led to a substantial increase of African – American voters. The Sixties: A Decade of Protest and Change Bay of Pigs 1961 – A failed attempt to overthrow Fidel Castro who began making agreements with the Soviet Union to turn Cuba into a pre-Soviet Communist nation. Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 – Closest the World has ever come to nuclear war. Kennedy set up a blockade to prevent the Soviets to deliver the launch system for the missiles already in Cuba. Krushchev agreed to withdraw the missiles and Kennedy pledged not to invade Cuba. “This Hurts Me More Than It Hurst You” Krushchev ishown pulling missiles out of Cuba (Castos’s mouth) Kennedy and Kruschev are shown in an “Arms Race” Tensions are high. Who will push the button first? Berlin Wall 1961 – 1989 After the Bay of Pigs failure Soviet officials began construction of the Berlin Wall cutting off between East and West Berlin. Family and Friends were separated overnight for 28 years. The wall was a symbol representing the symbolic division between America and the Soviet Union. Cesar Chavez – Chicano Movement organized farm workers in California. Migrant farm workers perform seasonal farm work such as planting and harvesting grapes, strawberries and lettuce. Fought for farm workers’ rights and demanded increased wages and better working conditions. Relied on nonviolent means, using strikes, pilgrimages, and fasts (hunger strikes) to achieve his goal Organized consumer boycotts of farm products. Urged state legislatures to pass laws to improve the lives of farm workers. Chicano Mural Movement – Mexican Americans expressed themselves through a greater appreciation of their culture by painting murals in barrios (ethnic neighborhoods). Murals supported identity, justice and provided a visual presence for those who lacked representation in politics. Lyndon B. Johnsons Great Society – Hoped to open up opportunities and improve the quality of life for all Americans. Civil Rights: Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibited discrimination in businesses. Voting Rights Act of 1965 ended poll taxed, suspended literacy test and increased African American voter registration. Affirmative Action increased minority representation in colleges, the professions, and many businesses. Declared a “War on Poverty” and gave money to cities for urban planning. Medicare Act of 1965 – Government provided medical care for people over age of 65. Domino Theory under President Kennedy Domino Theory – If South Vietnam fell to Communism, neighboring Southeast Asian countries would fall to Communism like a row of dominos. Kennedy sent aid and U.S. military advisors to assist the South Vietnamese in fighting the Vietcong. Kennedy felt that a successful democracy in South Vietnam might serve as a model for other developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Crisis and Resurgence, 1969-2000 Nixon Presidency, 1969 – 1974 Environmental Protection Agency The EPA sets air and water pollution standards for cities, and engages in monitoring and enforcement activities. Private citizens can file lawsuits against polluters under the EPA ERA – “Equality of rights under the law shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of sex.” Women’s Liberation Movement Phyllis Schlafly – ERA would reduce the rights of wives and harm family life as well as women serving in combat roles. Watergate – [The Nixon Presidency 1969-1974] 1972 CIA agents, working for Nixon’s re-election as President [Committee to RE-Elect the President] were caught breaking into Democratic Party headquarters at the Watergate complex. Nixon secretly recorded all of his White House conversations. When Nixon was asked for the tapes, he claimed executive privilege – the right of the president to keep information private. United States v. Nixon – ruled that Nixon must turn over the tapes, reaffirming the principal of checks and balances and that no one is above the law. The Impact of Watergate Lowered public confidence in government (1st Amendment – Freedom of the Press) Reaffirmed the role of the press in uncovering government misconduct The Ford Presidency 1974 – 1977 According to many economists an important effect on the American economy with the increase of oil prices in the 1970s was the onset of Stagflation – High unemployment combined with inflation. 1973 the Arab nations of OPEC used oil as a political weapon for U.S. siding with Israel in the 1973 war. Overnight the price of oil shot up. The impact could be felt across the entire energy industry. Cost of heating a home, the prices of food, to electricity and gasoline all went up in price The Carter Presidency, 1977 - 1981 Camp David Accords Israel agreed to return the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt, which Israel had taken in the Six-Day War in 1967. Egypt offered a peace treaty and the establishment of normal diplomatic relations with Israel – ending 30 years of warfare. After breaking promises for reform, Shah Pahlavi, ruler of Iran was forced into exile in 1979. Ayatollah Khomeini (pictured above) took over. The U.S. government allowed Shah Pahlavi to enter the U.S. for medical treatment. This perceived support for the Shah of Iran resulted in angry Iranian students seizing the staff of the U.S. embassy in Tehran, Iran and taking them hostage for more than a year. The fundamentalists Shiite Muslims were generally hostile to Western Influence. They resented America for interfering in Iranian affairs, for helping the Shah and for backing Israel. America’s image suffered because of its inability to free the hostages. An attempt to rescue the hostages with a surprise helicopter raid failed. The Impact of Geography on History Technological developments allowed for the transition from the “Rust Belt” (mostly states in grey) to the “Sun Belt” (mostly states in blue). Government-built dams made water available to western cities. Air conditioning and hydro-electric power made it possible to keep homes, offices, and factories cool in the summer. The environment of the area changed. Shopping malls replaced grasslands and deserts. Cities demanded more resources such as water and energy which placed a greater burden on the environment. North Atlantic Treaty Organization Benefits of Participation in International Organization Global Cooperation – Improves economies and promotes peace in the nuclear age. Global Platform – Provides the United States with a place to state its views and helps spread its democracy. Environmental – International cooperation is required to tackle global problems, such as the environment. Costs/Risks of Participation in International Organizations Limitations – International organizations may place limitations on nation’s sovereignty or ability to act. Problems – International organizations involve the United States in problems around the world. Costs – International organizations cost the United States billions $$$$ of dollars to support America in the New Millennium Multinational Corporations – A corporation that has set up local companies, or subsidiaries, in several countries and sell their products in every corner of the world. Globalization – Multinational corporations has contributed to globalization. This has had a serious impact on government policies such as deciding to allow a company to produce in their country. If a company pollutes a government might ban that company but that company will just move to another country. Think NIKE – Home office is in Oregon but they make everything in China because of cheaper labor and fewer regulations. American culture has spread thank to technologies such as Google, Facebook, Twitter, and Wikipedia.