Bilingualism without diglossia Bilingualism without diglossia
advertisement

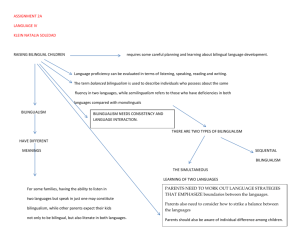
Essential Concepts for Researching Bilingualism and Bilingual Education Dr Anwei Feng Email: Anwei.Feng@durham.ac.uk School of Education, Durham University Two Questions Why is it important to study bilingualism and bilingual education? What do we need to know to study the issues related to bilingualism and bilingual education? Common (Mis)perceptions Issues related to bilingualism and bilingual education are perhaps basically linguistic issues. So let’s leave them to the ‘language people’ or linguists. Concepts related to the notions are easy and only relevant to minority groups. Why Important? Activity 1 – Discuss whether and, if yes, why it is important to study bilingualism and bilingual education and what counter-arguments there are. Importance Counter Arguments •Response to globalisation •Intercultural communication •Minority education •Language provision policies •FL education •Personal needs •For nation-building •For social stability and racial harmony • etc. •Cause of underachievement •Potential catalyst for Quebec-style separationism •Detrimental to cognitive development •High cost •Split personality •Identity and emotional problems • Etc. What do we need to know? A revisit to WHY question tells us research into these issues is interdisciplinary. SLA for sure Psychology (bilingualism and emotions) Sociology (language and society) Politics (language and politics) Cultural studies (intercultural communication) An Example If you wish to discuss the case of CMI versus EMI schools in Hong Kong, what literature will you need to review in order to gain a relatively full view of the phenomenon? Language and politics Language and identity Mother tongue education and empowerment Effectiveness of each model Emersion: total or partial Strong form or weak form Bilingualism and intelligence Bilingualism and economic development Globalisation and language policy Another Example If you wish to discuss Putonghua education in Hong Kong schools, what literature will you need to review in order to gain a relatively full view of the phenomenon? Language and national identity Bilingualism and economic development Bilingualism, biculturalism and/or interculturalism Language and power Effectiveness of Putonghua education A weak form A strong form How complex concepts can be? Activity 2 – What is “bilingualism”? Write a simple definition or key words to “bilingualism” Bilingualism 1 Common definition - The use of two languages by individuals ‘use’ can range from native speaker competence to incipient ability to survive with a foreign/second language ‘two’ is not accurate as the term is used also to refer to tri- or multi-. ‘language’ may include formal language, variety of language, or even dialect ‘individual’ is not accurate as the term is often used to refer to societal phenomena Bilingualism 2 If they are difficult to define, can we describe BILINGUALISM? (Baker’s (2001) dimensions, p.3) Ability (how proficient – incipient receptive productive native-like) Age (simultaneous, sequential, late ) Balanced (equally fluent in two) Development (Additive – Subtractive; Ascendant – Recessive) Contexts (Home, school, etc.) Circumstantial (forced to learn for survival because of circumstances) or Elective (choose to learn to add another language competence) Societal Bilingualism Diglossia – Situation where two languages, or varieties of a language (High-variety Vs Lowvariety) are used for different purposes in a society (Fishman, 1972; Baker, 2001) High variety (language or dialect) – Often used in formal domains Low variety (language or dialect) – Used in informal domains *The term is useful for analysis of language use in multilingual situations and power relationship between HV users and LV users Diglossia and Bilingualism Four language situations Diglossia + Individual Diglossia and bilingualism bilingualism Bilingualism without diglossia + - Diglossia without bilingualism Neither bilingualism nor diglossia (a political fiction) Diglossia with bilingualism Diglossia with bilingualism: exists and is stable if other factors support Examples? Most cities in China (H - Putonghua; L Local dialect or language) In London (H – RP English; L – Cogney or any other ethnic minority language) In Singapore (H – English; L – ethnic minority language?) In Hong Kong? Etc. Diglossia without bilingualism Diglossia without bilingualism Examples: Switzerland (German, French, Italian, Romansch speech communities in different area) India (power group speak English, masses their own languages) Bilingualism without diglossia Bilingualism without diglossia (unstable and likely to lead to creolisation?): Examples: Wales (bilinguals use either Welsh or English in any domain) In Ireland (same situation) Some places in North America Hong Kong? Neither/Nor Neither/nor: monolingual states – political fiction? Examples: Cuba (forced monolingual state by exterminating minority languages) The Dominican Republic (forced?) Natural ones (non-existent?) Limitations Difficult to categorise some communities into the ‘cells’ (Boyd and Latomaa, 1999) Multilingual societies/states (i.e. politically unified): using more than one official language Bilingualism without diglossia may not be unstable. Stability of diglossia with bilingualism may be affected by increasing communication with otherness. Bilingual Education Write several words to show your working definition of the term. Write a few examples of bilingual education according to your definition Are they defined as bilingual education? A classroom with both local students and students from other countries using the local language as MoI? A classroom dominated by minority students but taught in the majority language? A classroom dominated by students of the majority group but taught in a foreign language? A classroom mainly taught in the native language with a second/foreign language as a school subject? Are they defined as bilingual education? A classroom taught simultaneously by two teachers in two different languages? A classroom taught in a foreign language but gradually changed to be taught in a local majority language? Etc. Introductory Texts C. Baker (2006) Foundations … J. Cummins (2000) Language, power, and pedagogy. … J. Edwards (1994) Multilingualism … A. Feng (2007) Bilingual education in China … A, Pavlenco & A. Blackledge (2004) Negotiation of identity … A, Pavlenco (2006) Bilingual minds … Durham Module Bilingualism and Bilingual Education Thanks