Name Bioenergetics Review Draw the ATP cycle. Label ATP, ADP +
advertisement
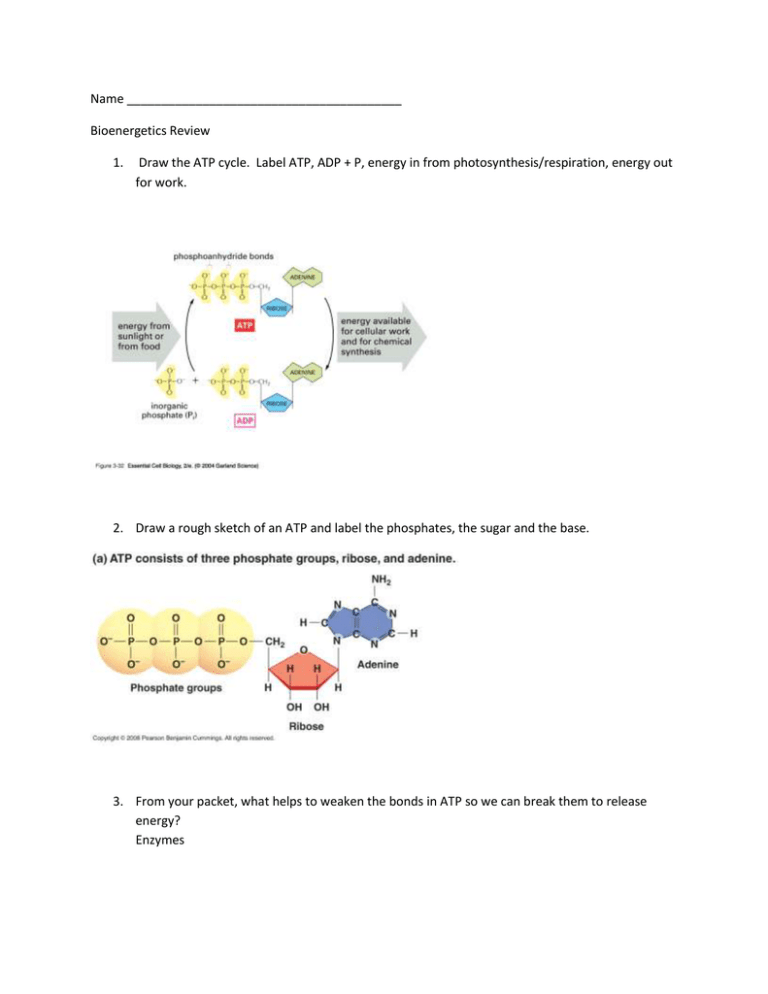
Name ________________________________________ Bioenergetics Review 1. Draw the ATP cycle. Label ATP, ADP + P, energy in from photosynthesis/respiration, energy out for work. 2. Draw a rough sketch of an ATP and label the phosphates, the sugar and the base. 3. From your packet, what helps to weaken the bonds in ATP so we can break them to release energy? Enzymes 4. What is the overall equation (in words) for photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide + water + light sugar and oxygen 5. What is the equation for respiration? Sugar and oxygen water + carbon dioxide + ATP 6. How do the two equations relate to each other? The products of one are the reactants of the other (they are reverse processes) 7. What is the energy conversion in photosynthesis? Light into chemical energy in the form of sugar 8. What is the energy conversion in respiration? Chemical energy in the form of sugar into chemical energy in the form of ATP 9. What class of molecules do plants use to absorb light energy? Pigments 10. What colors of light does chlorophyll absorb? Reflect? It absorbs primarily red and blue (some purple) It reflects all green light 11. What happens when chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight (what does it give its energy to?) It gives the energy to electrons 12. What molecule carries high energy electrons from the light reactions to the Calvin Cycle? NADPH (I remember this one by associating the P with photosynthesis or plants) 13. What molecules carry high energy electrons from glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle to the ETC in respiration? NADH and FADH2 14. The energy from the high energy electrons in the ETC (in either photosynthesis or respiration) is used to make what? ATP 15. What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic respiration? Aerobic respiration requires oxygen. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. 16. What are the products of the light reactions? ATP, NADPH, and O2 17. What are the products of the Calvin Cycle? ADP, NAD+, and SUGAR 18. Draw three graphs to represent the relationship between light and photosynthesis, CO2 and photosynthesis and temperature and photosynthesis. Explain why each shows that relationship. Light and photosynthesis have this relationship because photosynthesis requires light for energy. Initially as light increases photosynthesis does, too. Eventually all of the photosynthetic enzymes are busy already and more light doesn’t help them. CO2 has the same relationship for the same reasons. Temperature and photosynthesis have this relationship because temperature and enzymes have this relationship. Like all else in the cell, photosynthesis is largely performed by protein workers. At too low a temp, these proteins and enzymes (also proteins) don’t have enough energy to work. At too high a temp, the proteins are denatured (lose their shape—aka melt). 19. How do organisms get the energy they need? By breaking down food slowly to release chemical energy. 20. What process is needed to produce NAD+ for glycolysis but does not actually produce any energy? Fermentation 21. The presence of what determines whether your cells will do cellular respiration or fermentation? oxygen 22. What are the two kinds of fermentation? Alcoholic and lactic acid 23. What valuable products are made with alcoholic fermentation? Bread, alcohol, kimchi 24. What kind of fermentation do your muscle cells do when they don’t have enough oxygen? Lactic acid 25. List the three stages of cellular respiration, where they occur, and how much ATP they make. Glycolysis (ALL CELLS DO THIS) – cytoplasm 2 net ATP Kreb’s Cycle (only go down this path if you have oxygen) – mitochondria – 2 ATP Electron transport chain (the step that absolutely requires oxygen) – mitochondria – 32-34 ATP 26. In the snail lab, what color would you see with the following combos after 24 hours? a. 1 snail – yellow (high CO2) b. 1 elodea light (blue – low CO2, the CO2 was used up by photosynthesis) c. 1 elodea dark (green – no photosynthesis so the plant is not using up CO2) d. 1 snail two elodea light (blue – there are more elodea than snails so overall they’d use more CO2 than the snail would produce) e. 1 snail two elodea dark (yellow – in the absence of photosynthesis, the snail’s CO2 would turn the indicator yellow) 27. In the snail lab, what did the snails produce for the elodea? CO2 Essays on the Test 1. How is a molecule of ADP like a rechargeable battery? ADP is like a rechargeable battery because you can store energy in it through photosynthesis or respiration. It constantly cycles between the high energy ATP and the low energy ADP, so you can constantly re-use it and recharge it just like a battery. 2. Describe the relationship between the light dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle There are two major relationships. The first is that the light dependent reactions supply the energy for the Calvin Cycle (if you want to be technical, in the form of ATP and NADPH). The other relationship is that each produces something the other uses. The light reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which the Calvin Cycle uses for energy. The Calvin Cycle in turn produces ADP and NADP+, which the light cycle recharges back into ATP and NADPH. 3. Explain how the ultimate source of energy for heterotrophs is the sun even though they cannot make their own food. All food chains have to start with plants. Plants use the energy from the sun to create sugars. These sugars are the basis for all large carbon molecules in the plant (e.g. proteins, lipids, sugars, etc). Sugar in a way is just stored solar energy. 4. Would a muscle cell or a skin cell have more mitochondria and why? This is one you are going to have to think about yourself.







