Chapter 5: The Structure of Matter
advertisement

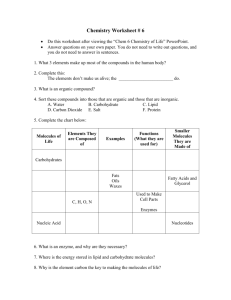
Objectives Be able to describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic compounds Be able to identify the names and structures of groups of simple organic compounds and polymers Be able to identify what makes up the polymers that are essential to life and how they are essential Important Vocabulary Organic compound Hydrocarbon Alkanes Alkenes Alcohol Monomer Polymer Biochemical compound Carbohydrate Protein Lipid Nucleic acid Organic Compounds Are compounds that originate from living things They are covalently bonded molecules They always contain carbon, and almost always hydrogen Oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus are also found in organic compounds Examples of Organic Compounds Acetylsalicylic acid, C9H 8O4 is the effective ingredient in aspirin Sugarless chewing gum also has organic compounds as ingredients. The sweeteners sorbitol, C6H14O6, and aspartame, C14H18N2O5 Organic Compounds Carbon atoms form 4 covalent bonds in organic compounds Compounds only made of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons Carbon can form single, double and triple bonds The type of bond that forms between carbon atoms determines the name of its organic compound Alkanes Are hydrocarbons that have only single covalent bonds Methane, ethane & propane all line up in a row structurally Above 3 carbons, alkanes can have branches or rings Alkane Structures More Alkane Structures Alkenes Are hydrocarbons with at least one double covalent bond Their names end in –ene instead of –ane Examples: ethylene and propylene Ethylene is formed when fruit ripens Propylene is used to make rubbing alcohol & plastics Alcohols Are organic compounds that are made up of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen They have a hydroxyl groups ( –OH ) Their names end in –ol Alcohol molecules behave similar to water molecules: Alcohol molecules are attracted to each other They are liquids at room temp. They also have high boiling points Alcohols Polymers Are long chains of repeating subunits called monomers Some are natural and others are man-made Rubber, wood, cotton, wool, starch, protein and DNA are all natural polymers Plastics & fibers are man-made polymers The properties of a polymer are determined by its structure Hard Plastics Nylon Fibers Polyester Fibers Polyethene Biochemical Compounds Are naturally occurring organic compounds that are very important to living things There are 4 types of biochemical compounds: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Are made of monomers of simple sugars like glucose and fructose Glucose provides energy to living things Glucose that is not needed right away for energy is stored as glycogen Starch is made of many bonded glucose molecules in chains pack closely together Starch is stored by plants Proteins Are polymers of different amino acids in chains Amino acids are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and (some) sulfur There are 20 different amino acids that can make up proteins The way that amino acids combine determines which kind of protein is made Most proteins are enzymes which break down substances or speed up chemical reactions Lipids Are large, non-polar organic molecules They do not dissolve in water Include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, waxes, and pigments Have a higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms than carbohydrates They store more energy Nucleic Acids Are very large & complex molecules They store & transfer important information in the cell 2 types DNA RNA DNA Is a polymer with a complex structure DNA determines your genetic makeup It contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus It is made up of monomers called nucleotides Each nucleotide is made of a sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base There are 4 types of nitrogen bases: adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine The nucleotides are paired together and form a 2stranded ladder-like structure that is twisted This structure is called a double helix DNA Nucleotides Know the three parts of a nucleotide: A sugar, a phosphate & a nitrogen base RNA Ribonucleic Acid Composed of nucleotides Stores and transfers information from DNA to make proteins It also act as enzymes