Prices and Decision Making
advertisement
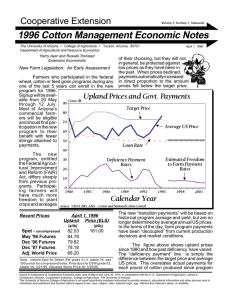
Prices as a System Prices help consumers and producers make decisions Tells sellers where to sell and consumers where to buy Prices serve as signals Allocate resources between markets Can impact many markets Fixed Prices Why are prices fixed? Special policies interest groups influence government Economists believe the costs of fixed price often outweighs the benefits Price Ceilings Maximum legal price that can be charged Result in shortages Prices no longer allocate resources Threatens profits of supplier Positive for people who receive the good Negative for those who do not Price Floors Lowest legal price Ex. Minimum wage Can decrease demand Predicting Prices Use models to explain and predict Predict changes in supply Ex. Agriculture Factor in demand elasticity Considered with a change in supply Illustrate possible changes in demand Ex. Gold Agricultural Price Supports Government will try to stabilize prices Use loan supports and deficiency payments in the 1930s Commodity Credit Corporation Loan Supports Put crop up as security Repay loan after selling crop, or give crop and keep loan money If unable to repay, they just forfeit the crop Non-recourse Creates loan large stockpiles of food Agricultural Price Supports Deficiency Payments Encouraged CCC farmers to sell on the open market would make up payment differences between actual price and target price Reforming Price Supports Federal Agricultural Improvement and Reform Act – 1996 Cash payments took place of price supports and deficiency payments LDP – Loan Deficiency Payment