Networking Test
advertisement

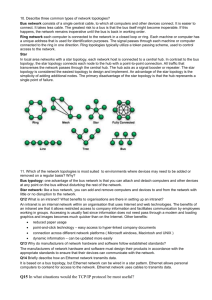
Networking Test Fill in the Blanks 1. In a network, a ____CLIENT_____ is a computer that requests or orders information from a server. 2. A ___client-server or server____ provides many different services to its client computers. 3. In a ____peer-to-peer_________ network, computers function as both clients and servers. 4. __A Network___ is the way computers are cabled together. 5. A bus network consists of a single cable, or ___Backbone cable___. 6. A ___terminator____ absorbs the signals and keeps them from bouncing back along the trunk. 7. ____Lag_______ happens when two signals are sent at the same time and run into each other keeping the signal from being delivered. 8. A device called a ___Bridge_____ can be used to connect two cables. 9. The ___HUB________ connects the nodes in the arms of a star network. 10. A small collection of bits is called a ____byte___________. Short Answer 1. Define the following words: a. Thin client : a computer or a computer program which depends heavily on some other computer (its server) to fulfill its traditional computational roles. b. Server : three definitions – see below… a computer program running as a service, to serve the needs or requests of other programs (referred to in this context as "clients") which may or may not be running on the same computer. a physical computer dedicated to running one or more such services, to serve the needs of programs running on other computers on the same network. a software/hardware system (i.e. a software service running on a dedicated computer) such as a database server, file server, mail server, or print server. c. Bandwidth : a rate of data transfer d. Synchronous communication : both the sender and receiver are synchronized with a click or a signal encoded in the data stream. e. Barrel connector : Mini power connector used for attaching extra low voltage devices to external electricity. 2. Give an example to describe the following two types of communication in a network: Not needed for final exam. a. Synchronous : b. Asynchronous : 3. What is a network? What 4 things does a network let a business or home do? A means of connecting two or more computers or devices together. A network allows for: Sharing of data Sharing of a centralized printer or other peripheral devices Connecting email on a central server Allowing storage/back up of files through a central server Better security through a server hardware (the computers and peripherals are protected better) Multiple computers hooked up as a network can have a tendency to speed up a system. Efficient communication between people across the internet – people do not have to be in the same room to share the files on the network. 4. Explain how a document is sent across a network. This depends on the type of network, but 5. What are two ways that communication can be broken when looking at cabling? During the sending or receiving phase of transmission, communication can be broken. This can be caused by defective cables. This can also be caused by errors in networking software. Critical thinking – short answer 1. Describe the differences between dedicated and non-dedicated servers. Please refer to the handout, Introduction to Computer Networking 2. List three examples of a dedicated server. Managed dedicated server Source dedicated server Half-life dedicated server 3. What makes a good network? Reliability coupled with proper speed, security, and ease of use. 4. Draw an example of each of the following and list an advantage and a disadvantage of each: Read in the handout for advantages and disadvantages a. Centralized b. Peer-to-peer 5. Briefly describe the four topologies. BUS: A bus network topology is a network architecture in which a set of clients are connected via a shared communications line, called a bus. There are several common instances of the bus architecture, including one in the motherboard of most computers, and those in some versions of Ethernet networks. STAR: Star networks are one of the most common computer network topologies. In its simplest form, a star network consists of one central switch, hub or computer, which acts as a conduit to transmit messages.[1] Thus, the hub and leaf nodes, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star. If the central node is passive, the originating node must be able to tolerate the reception of an echo of its own transmission, delayed by the two-way transmission time (i.e. to and from the central node) plus any delay generated in the central node. An active star network has an active central node that usually has the means to prevent echo-related problems. RING: A ring network is a network topology in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals through each node - a ring. Data travels from node to node, with each node along the way handling every packet. MESH: Mesh networking is a type of networking wherein each node in the network may act as an independent router, regardless of whether it is connected to another network or not. It allows for continuous connections and reconfiguration around broken or blocked paths by “hopping” from node to node until the destination is reached. 6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each topology? Advantages of a bus network Easy to implement and extend. Easy to install. Well-suited for temporary or small networks not requiring high speeds (quick setup), resulting in faster networks. Cheaper than other topologies (But in recent years has became less important due devices like a switch) Cost effective; only a single cable is used. Easy identification of cable faults. Reduced weight due to fewer wires. Disadvantages of a bus network Limited cable length and number of stations. If there is a problem with the cable, the entire network breaks down. Maintenance costs may be higher in the long run. Performance degrades as additional computers are added or on heavy traffic (shared bandwidth). Proper termination is required (loop must be in closed path). Significant Capacitive Load (each bus transaction must be able to stretch to most distant link). It works best with limited number of nodes. Commonly has a slower data transfer rate than other topologies. Only one packet can remain on the bus during one clock pulse. Advantages of a STAR Network Better performance: star topology prevents the passing of data packets through an excessive number of nodes. At most, 3 devices and 2 links are involved in any communication between any two devices. Although this topology places a huge overhead on the central hub, with adequate capacity, the hub can handle very high utilization by one device without affecting others. Isolation of devices: Each device is inherently isolated by the link that connects it to the hub. This makes the isolation of individual devices straightforward and amounts to disconnecting each device from the others. This isolation also prevents any non-centralized failure from affecting the network. Benefits from centralization: As the central hub is the bottleneck, increasing its capacity, or connecting additional devices to it, increases the size of the network very easily. Centralization also allows the inspection of traffic through the network. This facilitates analysis of the traffic and detection of suspicious behavior. Simplicity: This topology is easy to understand, establish, and navigate. Its simplicity obviates the need for complex routing or message passing protocols. Also, as noted earlier, the isolation and centralization it allows simplify fault detection, as each link or device can be probed individually. Easy to install and wire. Easy to detect faults and to remove parts. No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices. Disadvantages of a STAR network High dependence of the system on the functioning of the central hub Failure of the central hub renders the network inoperable The performance and scalability of the network depends on the capabilities of the hub Network size is limited by the number of connections that can be made to the hub Other nodes may see a performance drop if traffic to another node occupies a significant portion of the central node's processing capability or throughput. Wiring up of the system can be very complex and expensive. Advantages of a RING Network Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit Performs better than a bus topology under heavy network load Does not require network server to manage the connectivity between the computers Disadvantages of a RING Network One malfunctioning workstation or bad port in the MAU can create problems for the entire network Moves, adds and changes of devices can affect the network Network adapter cards and MAU's are much more expensive than Ethernet cards and hubs Much slower than an Ethernet network under normal load Advantages of a MESH Network the network may act as an independent router, regardless of whether it is connected to another network or not allows for continuous connections and reconfiguration around broken or blocked paths by “hopping” from node to node until the destination is reached. Mesh networks are self-healing: the network can still operate when one node breaks down or a connection goes bad typically be very reliable Disadvantages of a MESH Network the component parts can all connect to each other via multiple hops, and they generally are not mobile 7. What are three things that would need to be considered when deciding on a network for a company? Cost Security Usability