Physics 1230: Light and Color Chapter 1
advertisement

Physics 1230: Light and Color
Ivan I. Smalyukh, Instructor
Office: Gamow Tower, F-521
Email:
ivan.smalyukh@colorado.edu
Phone: 303-492-7277
Lectures:
Tuesdays & Thursdays, 3:30 PM - 4:45 PM
Office hours:
Mondays & Wednesdays, 3 PM - 4 PM
Grading Assistants:
Jian Yao,
Yiheng Lin,
Hao Song
Lectures
Homeworks
Exams
Hands-on experience
Demonstrations
Peer Instruction (with extra credit)
Fun
Course Business
• Website
http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1230/phys1230_fa09/
• Syllabus
– Science of light and color
– HW assignments, reading and exam dates
• Course info
– Grades
– Clicker technology
• Another kind of invisible wave
2
Physics 1230: Light and Color
Ivan I. Smalyukh
• What is "science"?
• Why is learning science
like learning a foreign
language?
– Words have new and precise
meanings
– Wave, image, ray, lens, white, exposure, file, see,
reflection, refraction, dispersion, particle
– What does it mean for the
"sun to set?" Is there really
global warming? How could
complex and magnificent
creatures like us have evolved
from lower species?
•
•
•
•
•
We all have scientific curiosity:
Why the sky is blue?
What is rainbow?
What is sunset?
How my laptop display works?
Ornithoptera chimaera chimaera
Ornithoptera priamus urvillianus
Ornithoptera goliath supremus, f. titan
Papilio blumei blumei
What will be tested in this class?
How can I get a good grade?
Ability to:
Memorize
"Understand" new
Deeper understanding: Be able to
new facts
concepts at a
figure out new things using concepts
and
mi nim al level
definitions
Percent of grade:
25%
25%
50% (only 15% uses math)
HW#1 due next Thursday
Survey to be answered by clickers
1. What is your background
for light and color?
Choose the one which
best describes your
science background
a)
I have had no physics in high
school or college
b) I have had physics in high
school but not in college
c) I have taken a physics course
OR a psychology course at the
college level
d) I have taken more than one
physics or psychology courses
(high school and/or college
level)
e) I am a science major
Survey to be answered by clickers
2. Why did you take this
course? Give the answer
which best describes your
reason.
a) Because of requirements
by the university
b) Because it was
recommended to me
c) Because it looked easy
d) Because it looked
interesting
e) I don't know why
Scientific notation and metric system
• Powers of 10 give a
shorthand notation for
very large numbers.
•
•
•
•
103 = 1000
102 = 100
10 1 = 10
100 = 1
• Or very small numbers
10-1
•
= 0.1
• 10-2 = 0.01
• 10-3 = 0.001
• Scientists don't use feet or miles
to indicate distances
• They use
– meters (m)
• 1 meter = 39.4 inches
– kilometers (km)
• 1 km = 1000 m = 0.625 mi
– centimeters (cm)
• 1 cm = 10-2 m = 0.394 inches
– millimeters (mm)
•
1 mm = 10-3 m
– nanometers (nm)
•
1 nm = 10-9 m
Clicker question
•
What Lottery Prize you
prefer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
$ 103
$ 10-8
$ 107
$ 100
$ 10-18
• wavelength = 500 nm =
5 x 102 x10-9 m =
5 x 10-7 m
• Hence 1 m =
wavelength/(5 x 10-7) =
107/5 wavelengths =
2 million wavelengths
• Since 1 cm is 1/100 of a
meter there are 2 x
106/100 = 20,000
wavelengths in a cm
Clicker question
•
The wavelength of green
light is around 500 nm.
How many wavelengths
of green light fit into one
cm (or a fingertip)?
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
20 thousand
50 thousand
Two million
Two billion
5 billion
• 500 nm = 5 x 102 x10-9 m
= 5 x 10-7 m
• 1 cm = 10-2 m;
• Hence, 10-2 /(5 x 10-7) =
20,000 wavelengths in a
cm
Intro and Chapter 1 Continued
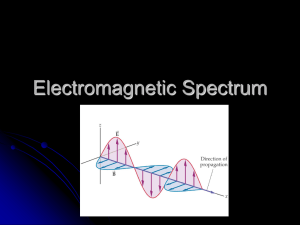
• Light belongs to a family of
waves called electromagnetic
(EM) waves (Physics 2000)
– Other waves: rope waves,
water waves, sound waves, etc.
• Sometimes EM waves are
called EM radiation
– Radio waves
– Radar and similar waves
• microwaves
• cell phone waves
–
–
–
–
Infrared or heat waves
Ultra-violet (suntan) waves
X-rays
Gamma rays
• EM waves are created and
destroyed by emission and
absorption
– Classical picture (Phys 2000)
• wiggling electrons radiate radio
waves or radar waves
• electrons in an atom are
resonant with emitted or
absorbed light waves or X-rays
– Quantum picture (Phys 2000)
• change of state of electrons in
atoms when bundles of wave
energy (photons) are emitted or
absorbed
• Light sources
– Incandescent light bulb
– Neon light
– Fluorescent light
Rays (a single beam of light, for example)
• Single light ray
– Ray from a laser acts like a
single light ray
– Illustrate by laser light
through fog
– Bounce off mirror
– Bounce off white card
– Put through water (bending)
• We only see light when a
ray enters into our eye
– Laser light is visible from
side because it is scattered
into our eyes
• Rays from a flashlight
• Rays from a light bulb
• What about light coming
from everything in this
room? Two kinds of objects:
– Self luminous objects (lights)
– Objects which are not selfluminous are seen because of
light reflected off them
• Turn out the light and we
don't see anything in the room
• It's all reflected light with
many rays coming from
diffuse surfaces
Light rays are invisible unless they enter
directly into our eye or are scattered by
smoke, fog or some object into your eye!
Laser
Flashlight
Light
bulb
MANY reflected rays come
from all parts of Alex, including
his nose - a diffuse object
Incident ray from a light bulb
Bob sees Alex's nose because a reflected light ray enters Bob's eye!
Rays bounce when they reflect off a mirror or
shiny surface
• This is called specular reflection.
• How is it different from
diffuse reflection?
Mirror
Rays bounce when they reflect off a mirror or
shiny surface
• This is called specular reflection.
• How is it different from
diffuse reflection?
Mirror
http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/string-wave/string-wave_en.html
Waves
• Rope waves
– Created by oscillation of
my hand holding the rope
– Finite speed of wave, but
rope segments do NOT
move in direction of wave
– Rope segments move up
and down, not along wave
– Note the change that occurs
when I oscillate my hand
faster
• Radio wave transmitter
– 3 meters wavelength
– (100 Mhz frequency)
• Google search under
keyword "physics"
– Water waves (circular
pattern)
– Stadium waves
Period and frequency of a wave and
relation to wavelength and speed
• The period, T, is the time for
the wave to make one complete
cycle (say, top-bottom-top) AT
ONE FIXED SPOT
Think of my hand moving to make the rope
wave. The period is the time for my hand
holding the rope to make one complete topbottom-top (or bottom-top-bottom) motion.
• The frequency, f, of the wave is equal
to one over the period: f = 1/T
f has the units of 1/secs, which we
call Hertz (Hz)
• The frequency, f, is related to the
speed of the wave, c and its
wavelength, (lambda):
f=c
What would happen if sound waves could
propagate through empty space???
We see color when waves of different
wavelengths enter enter our eyes!
Light with wavelength of 650 nm
appears red when it enters a viewers eye
Light with wavelength of 520 nm
appears green when it enters a viewers eye
Light with wavelength of 470 nm
appears blue when it enters a viewers eye
The speed of light in empty space is the same for all wavelengths
Clicker questions
•
•
•
Which of the light waves has
the longest wavelength?
Which of the light waves is
brightest?
Which of the light waves has
the highest speed in empty
space?
a)
b)
a) b) c)
d) They all have the same
speed
c)
Clicker question
•
What does Alex see when
the wave at left with
wavelength 650 nm goes
by him?
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Red
Blue
Green
White
Nothing
What happens when two or more waves with
different wavelengths reach your eye?
Light with both wavelengths 650 nm and
520 nm appears yellow when it enters
a viewers eye
Light with only wavelength 580 nm
ALSO appears yellow when it enters
a viewers eye (A DEEPER YELLOW
THAN FOR THE CASE ABOVE)
What is white light?
Light which is a mixture of 650,
520 and 470 nm wavelengths
(and possibly more wavelengths)
appears WHITE when it reaches
your eye
No single wavelength (monochromatic) wave appears white
when it reaches your eye!
Light at
wavelengths
which we see
as colors are
part of a
wider family
of electromagnetic
waves
It's a good idea to remember some rough
wavelengths associated with colors
• Violet and blue are
what we see when
shorter wavelength
visible rays enter
our eyes.
– They have
relatively higher
frequencies
• Red is how we see
longer wavelength
visible rays
– Red has a relatively
smaller frequency
What happens when those other
electromagnetic waves enter our eyes?
Wavelength = 10 million nm
Note that the frequency is
f = c/
=(3 x 108 m/s)/(10-2 m)
= 3 x 1010 Hz
• We don't see anything because
electromagnetic waves at this
frequency cannot excite a
resonance in the atoms in our eyes.
• Note that this wavelength is on
the order of a centimeter
• These are microwaves just like
those sent out and received by your
cellphones (or used in a microwave
oven).
• We cannot see them even
when they enter our eyes because
their wavelength is too long to
excite a resonance.
How much time it takes for the wave
to travel distance of 9000 km?
• Speed of sound
340 m/s
• Speed of
electromagnetic waves
300,000 km/s ;
How does an ordinary incandescent
light bulb work?
Filament with current of electrons which hit
into atoms causing light to be emitted
Gas
Atom
Atom
Electrons
Electrode leading to
the other side of
the wall plug
Atom
Light emitted at
many different
resonance
frequencies of atoms
appears as white
light
Electrode leading to one
side of the wall plug
Neon lights have atoms with resonances at special colors
inside. They use alternating (AC) household current
(Demo)
Atom
Atom
Electrons
Atom
Neon light
When rays come out in various different directions
from an object or objects, the wavefront is defined as
a curve or surface perpendicular to all the rays
Wavefront
Rays
Light
bulb
• In this case the wavefront is
expanding out spherically from
the light bulb.
• Wherever it intersects a ray the
wavefront is perpendicular to
that ray
– More technically, the tangent
to the wavefront at the point of
intersection is perpendicular to
the ray
• The wavefront may be easier to
visualize than the rays
– You throw a pebble into a
pond. The circularly
expanding water waves are the
wavefronts
How are wave wiggles related to rays?
They are perpendicular
Amplitude {
Wiggles
Speed of light in empty space is
c = 186,000 miles/sec
= 3 x 108 meters/sec
Wavelength {
ray
Light with a SINGLE
wavelength is called
monochromatic light
Waveform
Ray
Note, the wave is NOT "red." I have colored it red.
We perceive it as red because of its wavelength.
HW #1 is due today