Foundations for Geometry Chapter 1
advertisement

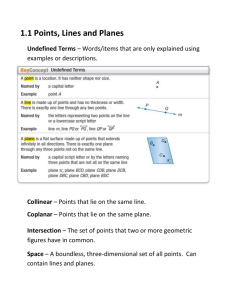
Foundations for Geometry Chapter 1 By: Peter Spencer Maria Viscomi Ian McGreal 1.1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Term-can not be defined by using figures Point- names a location and has no size, it is represented by a dot; named with a capital letter Line- is a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever; named with a lowercase letter or two points on the line Plane-a flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever; named by a script capital letter or three points not on a line Collinear- points on the same line Coplanar- points on the same plane 1.1 Continued Segment (or line segment)- the part of a line consisting of two points and all the points between them; named by its two endpoints Endpoint- point at the end of a segment or the starting point of a ray; named by a capital letter Ray- part of a line that starts at an endpoint and extends forever in one direction; named by its endpoint and any other point on the ray Opposite Rays- two rays that have a common endpoint and form a line; named by common endpoint and any other point on each ray Postulate- a statement that is accepted as true without proof 1.2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Coordinate- a number used to identify the location of a point Distance- absolute value of the difference of the coordinates Length- distance between two points Congruent Segments- segments that have the same length Construction- way of creating a figure that is more precise Between- a point in between two points is between them Midpoint- point that bisects Bisects- divides a segment into two congruent segments Segment bisector- any ray, segment, or line that intersects a line at the midpoint 1.3 Measuring and Constructing Angles Angle- figure formed by two rays, or sides, with a common endpoint Vertex- the common endpoint in an angle Interior of an angle-the set of all points between the sides of an angle Exterior of an angle- the set of all points outside the angle Degree- 1/360th of a circle; what angles are measured in 1.3 Measuring and Constructing Angles Acute Angle- an angle measured greater than 0 but less than 90 Obtuse Angle- an angle measured greater than 90 but less than 180 Right Angle- an angle measured 90 Straight Angle- an angle measured 180 Congruent Angles- angles with the same measure Angle Bisector-a ray that divides and angle into two congruent angles 1.4 Pairs of Angles Adjacent angles- two angles in the same plane with a common vertex and a common side, but no common interior points Linear pair- pair of adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays Complementary angles- two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 Supplementary angles- two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 Vertical angles- two nonadjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines 1.5 Using Formulas in Geometry Perimeter- sum of the side lengths of the figure Area- number of non-overlapping square units of a given size that exactly cover the figure Base- any side of a triangle Height- segment from a vertex that forms a right angle with a line containing the base Diameter- a segment that passes through the center of a circle and whose endpoints are on the circle Radius- a segment whose endpoints are the center of the circle and a point on the circle Circumference- distance around a circle Pi- an irrational number; 3.14159265….. 1.6 Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane Coordinate plane- a plane that is divided into four regions by a horizontal and a vertical line Leg- two sides that form the right angle of a right triangle Hypotenuse- the side across from the right angle that stretches from one leg to the other 1.7 Transformations In the Coordinate Plane Transformation- change in the position, size, or shape of a figure Preimage- the original figure before transformation Image- the figure after transformation Reflection- (flip) a transformation across a line Rotation- (turn) transformation about a point Translation- (slide) transformation in which all points move the same distance and direction