Chemical Bonding Notes
advertisement

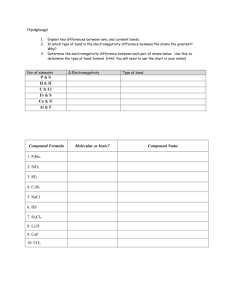
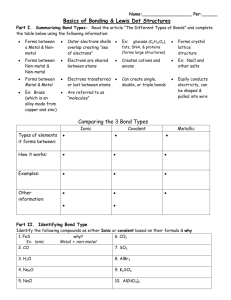
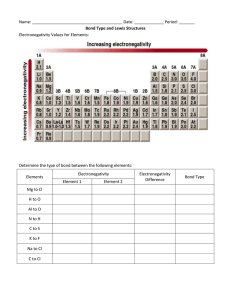
Chemical Bonding Mr. Guerrero LFHS • Bond-an attractive force that keeps two atoms or ions together. • Chemical bonds form, because it gives the two atoms lower Potential Energy. The bond length-the distance where two bonded atoms attain lowest PE. • 3 Types of Bonds: 1) Ionic bond-Involves a transfer of electrons, with cation/anion attraction. 2) Covalent-Involves sharing electron pairs between atoms. 3) Metallic- a special type of covalent with many stationary nuclei, surrounded by loosely held electrons(sea model) Bond Type can be predicted by: Metal + Nonmetal = Ionic Nonmetal + Nonmetal = Covalent This is very simplistic, Bonds actually have a bond character which is more accurately calculated by the electronegativity difference: Electronegativity Difference Electronegativity Difference 0.0------------------1.7---------------4.0 I Covalent I ionic I 0.0-Nonpolar-0.3-Polar------------------->4.0 Predict the bond type & find bond character Prediction N—Cs Mg—F C—N Fe—P Cl—K O—Br Bond Character Ionic Bonding: Bond energy- the energy required to break a chemical bond. • The strength of an ionic bond can be calculated using a different form of Coulomb’s Law: (FORCE OF ATTRACTION) (BOND ENERGY) The distance between a Na+ and a Cl- nucleus is .276nm. Find the bond energy in a Na-Cl bond. The distance between a Mg2+ and O2- is .212nm. Find the bond energy of the Mg—O ionic bond. What is the major reason one bond is stronger than the other? Use Coulomb’s law to predict ionic bond strength: • Arrange the following ionic bonds by increasing bond energy(strength): Mg—O K—Cl Al—N Ca—O Cs—Cl Weakest: Strongest: Cs—Cl K—Cl Ca—O Mg—O Al—N Properties of Ionic bonding • 1) transfer of e- due to a large difference in electronegativity between nuclei • 2) Ions form large repeating patterns called a crystal lattice. • 3) Ionic Compounds have very high melting & boiling points(Always solids at 25oC) • 4) Formula is always an Empirical Formula (lowest whole # ratio of cations and anions that has zero charge) • 5) Groups of cation/anions are called Formula Units • 6) Conduct electricity only when melted(free flowing ions) or dissolved in water(electrolytes-free flowing ions in water) Properties of Covalent Bonds: 1) Sharing e- pairs due to similar electronegativity between nuclei. 2) Form groups of atoms called molecules. Molecules are independent groups of bonded atoms . Neighboring molecules are held together with weaker Intermolecular Forces of Attraction.(IMF’s) 3) Covalent(AKA molecular) Compounds have very low melting and boiling pts.(could exist as a solid, liquid or gas at 25oC.) 4) Formulas are true(molecular) formulas. 5) Do not conduct electricity under any conditions. Lewis Structures-a drawing that represents the structural formula of a molecule. • Draw the following Lewis structures: • H2S N2 CO2 BH3 CO32- Molecule Lewis Central sigma/pi structural molecular(polar?) Struct. Hybridization Formal C. bonds formula Geometry N2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------CO2 H2O ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------BF3 Molecule Lewis Central sigma/pi structural molecular(polar?) Struct. Hybridization Formal C. bonds formula Geometry NH3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------NH4+ ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SbCl5 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------SF6 Molecule Lewis Central sigma/pi structural molecular(polar?) Struct. Hybridization Formal C. bonds formula Geometry SF4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ClF3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- I3- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------BrF5 Molecule XeF4 ClF4+ NO2 Lewis Central sigma/pi structural molecular(polar?) Struct. Hybridization Formal C. bonds formula Geometry Finding DH(Enthalpy) from bond Energies • How much heat is transferred when 25.0 grams of O2 combine with excess H2 to form water? DH = Bonds Broken – Bonds Formed (p. 374) Finding DH(Enthalpy) from bond Energies How much heat is lost when 25.0 grams of ethene are completely combusted?(Use bond energies on p. 374) • Ammonia decomposes to nitrogen and hydrogen. Use the bond energy table to find the enthalpy of reaction and how much heat is gained or lost if 3.50 grams of hydrogen are produced?