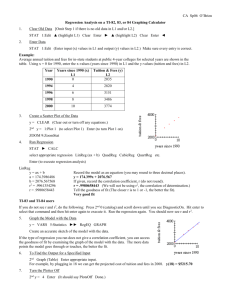
Statistic 4.1.1
advertisement
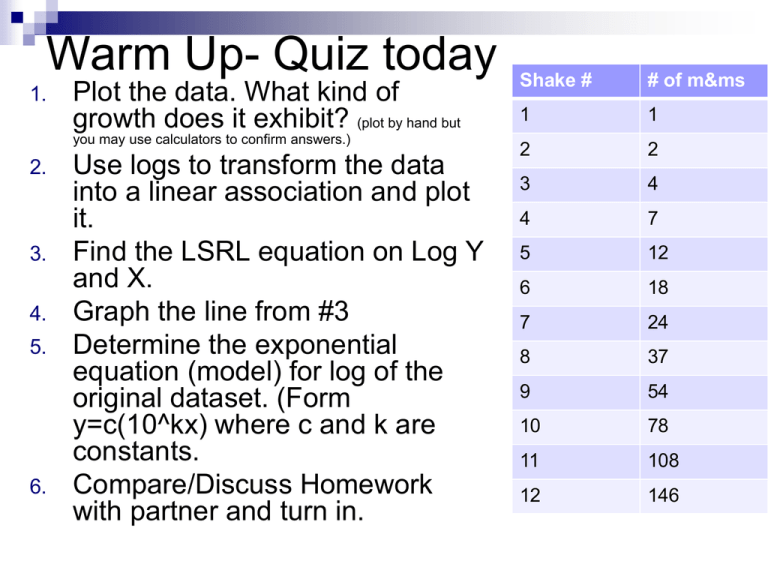
Warm Up- Quiz today 1. Plot the data. What kind of growth does it exhibit? (plot by hand but you may use calculators to confirm answers.) 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Use logs to transform the data into a linear association and plot it. Find the LSRL equation on Log Y and X. Graph the line from #3 Determine the exponential equation (model) for log of the original dataset. (Form y=c(10^kx) where c and k are constants. Compare/Discuss Homework with partner and turn in. Shake # # of m&ms 1 1 2 2 3 4 4 7 5 12 6 18 7 24 8 37 9 54 10 78 11 108 12 146 Warm Up 1. Plot the data. What kind of growth does it exhibit? (plot by hand but you may use calculators to confirm answers.) 2. 3. 4. Use logs to transform the data into a linear association and plot it. Find the LSRL equation on Log Y and X. Write the equation and Draw this line on your second (linear graph) Determine the exponential equation (model) for the original dataset. (Form y=c(10^kx) where c and k are constants. Age # Savings 5 12 10 78 15 506 20 3,300 25 21,000 30 90,000 Get ready…you or your partner need to… Take out a sheet of binder paper and cut in half. Half for you half for your partner. Label with name, date period on top right corner. AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 3 Reading Quiz 4.2 1. 2. Correlation and regression are used for what kind of relationships? Are correlation, r, and least squares regression line resistant or not? 3. What do we call a ‘hidden’ variable that is not among the explanatory or response variables in a study and yet may influence the interpretation of relationships among those variables? 4. A high correlation, r, does imply causation. True or False. 4 Reading Quiz 4.2 1. 2. Correlation and regression are used for what kind of relationships? _____________is the use of a regression line for prediction far outside the domain of values of the explanatory variable x that you used to obtain the line or curve. Such predictions are often not accurate. 3. What do we call a ‘hidden’ variable that is not among the explanatory or response variables in a study and yet may influence the interpretation of relationships among those variables? 4. Correlation, r, and least squares regression line are not resistant. True or False Correlations based on averages are usually too ______ when applied to individuals. 5 5. Key to Reading Quiz 4.2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Linear Relationships Extrapolation Lurking Variable True High AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 6 Section 4.2.1 Cautions AP Statistics Cautions, Part 1 Regression and correlation describe only linear relationships Not resistant measures AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 8 Cautions, Part 2 Extrapolation is the use of a regression line for prediction far outside the domain of values of the explanatory variable x that you used to obtain the line or curve. Such predictions are often not accurate. Examples Keeping track of a child's growth Speed continues to decrease when running the mile. AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 9 Cautions, Part 3 Lurking Variable is a variable that is not among the explanatory or response variable in a study and yet may influence the interpretation of relationships among those variables. AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 10 Basketball example Piston Points vs. Piston Fouls P o i n t s Fouls Since we have a positive slope we say that for every 4.28 fouls the team gets a point. So the more fouls the more points??? Lurking Variable? Lurking variable: Playing Time AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 11 Piston Minutes vs. Piston Points AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 12 Piston Minutes vs. Piston Fouls AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 13 Another Example In the 1600-1800s the number of English Ministers in America increased The consumption of rum increased So the Ministers caused the people to drink more rum? Lurking Variable? Increase in population. AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 14 Clustering can allow us to see correlation that exist within subgroups The more education the get the lower the salary??? So drop out of school now??? Solid circles indicate Phd. Economist Education and Salary S a l a r y Years of Education AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 15 Can the number of students in math classes be used to predict the number enrolled? Maybe the number of required math classes changes AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 17 Good residual plot? AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 18 Residuals vs. Time. Different conclusion? AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 19 Caution, Part 4 Avoid using averaged data. Correlations based on averages are usually too high when applied to individuals. Example Take the mean height of my six class vs. all 180 heights from all students. Don’t use average data` when you can use raw data. AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 20 Assignment Exercises: 4.27, 4.28, 4.31, 4.32 AP Statistics, Section 4.2, Part 1 21