Job Analysis - acehrm.edu.np
advertisement

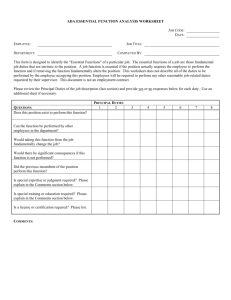
Job Analysis A Prelude to Recruitment and Placement Job Analysis – What is it and how is it used? The procedure for determining the duties skill requirements person specification of a job for making hiring decisions Jobs: Analyze, Describe and Provide Specifications Determining duties and skills Listing job duties, responsibilities, reporting, conditions, supervision “Human requirements” Are there Legal Issues Related to Job Analysis? The need to consider the legal context that requires the organisation to address No. of hours of work per week. Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act Equal Employment Opportunity Act (1972) Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures (1978) Americans with Disabilities Act (1990) What Information do I Collect? Work activities Human behaviors Machines, tools, equipment and work aids Performance standards Job context Human requirements Work activities Cleaning Selling Teaching Painting How, why and when the activities are performed Human behaviors Sensing Communicating Deciding Writing Job demands Lifting Walking Jumping jacks? Machines, Tools, Equipment, Work Aids Products made Materials processed Knowledge Services Job Context Working conditions Schedule Organizational context Social context Human Requirements Job-related knowledge and skills Education Training Work experience Personal attributes Aptitudes Physical characteristics Personality Interests Uses of Job Analysis Information Job Analysis Job Description and Job Specification Recruiting and Selection Decisions Figure 3-1 Performance Appraisal Job Evaluation— Wage and Salary Decisions (Compensation) Training Requirements Uses of Job Analysis Information Recruitment and selection Compensation Performance Appraisal Training Discovering unassigned duties Other compliance requirements Recruitment and Selection Executive recruiting Electronic recruiting Monster International How to recruit Assessment and selection Compensation Job value Salary Bonus Relative job worth Performance Appraisal How to do it Standards Self-appraisal The discussion Setting goals How to get a raise Training The job description should show the activities and skills—and therefore the training—that the job requires. Discovering Unassigned Duties Job analysis can also help reveal unassigned duties that are or are not being recognized EEO Compliance Job analysis also plays a big role in EEO compliance Steps in Job Analysis Decide how to use the information Review relevant background information Select representative positions Conduct the analysis Verify with the worker and supervisor Develop a job description and job specification Process Chart for Analyzing Work Flow Input from Plant Managers Input from Suppliers Job Under Study— Inventory Control Clerk Information Output to Plant Managers Inventory Output to Plant Managers Methods of Collecting Job Analysis Information The interview Questionnaire Observation Participant diary/logs U.S. Civil Service Procedure Quantitative techniques Multiple sources of information Collecting Job Analysis Information Joint effort between HR, the worker and the supervisor “SME’s” (Subject Matter Experts) Employees may be Concerned Because of – Resistance to change Possible changes to job duties Changes to pay Lack of trust of consequences The same job title may have different responsibilities and pay rates in different departments Widely Used: The Interview Individual interviews with each employee Group interviews with groups of employees who have the same job Supervisor interviews with one or more supervisors who know the job. Sample Interview Questions What is the job being performed? What are the major duties of your position? What exactly do you do? What physical locations do you work in? What are the education, experience, skill, and [where applicable] certification and licensing requirements? In what activities do you participate? What are the job’s responsibilities and duties? Sample Interview Questions (continued) What are the basic accountabilities or performance standards that typify your work? What are your responsibilities? What are the environmental and working conditions involved? What are the job’s physical demands? The emotional and mental demands? What are the health and safety conditions? Are you exposed to any hazards or unusual working conditions? Interviewing Questions after the clip: How well was the interview planned? Was rapport established? Were needs uncovered? Did the interviewer relate? What did the non-verbal behaviors suggest? How to Conduct a Questionnaire Session Use a specific questionnaire Establish rapport Follow a structured approach List duties in order of importance or frequency of occurrence Review and verify the data Observation Observation may be combined with interviewing Take complete notes Talk with the person being observed – explain what is happening and why Ask questions Diaries and Logs Time-consuming Self-reporting Remembering what was done earlier Can use dictating machines and pagers U.S. Civil Service Commission 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Knowledge Skills Abilities Physical activities Special environmental conditions Typical work incidents Worker interest areas Quantitative Job Analysis Techniques Position Analysis Questionnaire The U.S. Department of Labor approach Functional job analysis Sample Position Analysis Questionnaire Position Analysis Questionnaire Items Information Input Mental Processes Work Output Relationships with Other Persons Job Context Other Job Characteristics U.S. Department of Labor Procedure Data examples People examples Synthesizing Copying Instructing Persuading Things examples Setting up Tending Basic Department of Labor Worker Functions Basic Activities DATA PEOPLE THINGS 0 Synthesizing 1 Coordinating 2 Analyzing 0 Mentoring 1 Negotiating 2 Instructing 0 Setting up 1 Precision working 2 Operating—controlling 3 Compiling 4 Computing 5 Copying 3 Supervising 4 Diverting 5 Persuading 6 Speaking— signaling 7 Serving 8 Taking instructions — helping 3 Driving—operating 4 Manipulating 5 Tending 6 Comparing 6 Feeding—offbearing 7 Handling Functional Job Analysis Used beginning in the 1940’s Seven scales to describe what workers do in jobs: (1) (2) (3) (4) Things Data People Worker Instructions (5) Reasoning (6) Math (7) Language Writing Job Descriptions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Job Identification Job Summary Relationships Responsibilities and Duties Standards of Performance Working Conditions and Physical Environment Sample Job Description Figure 3 - 7 Sample Job Descriptions, Dictionary of Occupational Titles Job Identification Title Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) Date Approvals Supervisor’s title Salary Grade level Job Summary General nature Major functions or activities Includes general statements Responsibilities and Duties Examples Establishes marketing goals to ensure share of market Maintaining balanced and controlled inventories Defines the limits of job holder’s authority Purchasing authority Discipline Interviewing and hiring Standards of Performance Example Duty: Meeting Daily Production Schedule Work group produces no fewer than 426 units per working day Next workstation rejects no more than an average of 2% of units Weekly overtime does not exceed an average of 5% Job Descriptions Check this web site for sample job descriptions. What do you like about them? What, if anything, is missing? Using the Internet for Writing Job Descriptions The Dictionary of Occupational Titles (DOT) is being replaced by the U.S. Department of Labor by O*NET Writing Job Specifications What human traits and experience are required to do the job well? Specifications for trained versus untrained personnel Specifications based on judgment Specifications based on statistics Job Related Behaviors Industriousness Thoroughness Schedule flexibility Attendance Off-task behavior Unruliness Theft Drug misuse Statistics and Job Analysis Analyze job Select personal traits Test Measure subsequent job performance Statistically analyze relationship between trait and performance Job Analysis – a Practical Approach 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Decide on a plan Develop an organization chart Use a job analysis questionnaire Obtain lists of job duties from O*NET Compile the job’s human elements Complete your job description Step 1: Decide on a Plan Broad outline What do you expect your sales revenue to be next year? What products will you emphasize? Internally, what will expand, reduce, consolidate or grow What new positions will you need? Step 2: Develop an Organization Chart Step 3: Use a Job Analysis Questionnaire JOB ANALYSIS Job Title: Description of the Job: Tasks Tools Used Standards for Performance Conditions for Performance Step 3: Continued CONTENT ANALYSIS Subject Area Title: Content Description and Relevant Definitions: Tasks Tools Used Standards for Performance Conditions for Performance Step 4: Obtain Lists of Job Duties Check out O*.NET Find the description of a retail salesperson Then, complete Step 5: Compiling the job’s human requirements and Step 6: Completing your job description. Part 5: Job Analysis in a “Jobless” World From specialized to enlarged jobs Why managers are “de-jobbing” their companies Specialized to Enlarged Jobs Job Enlargement = same-level activities Job Rotation = moving from one job to another Job Enrichment = redesigning to experience more responsibility, achievement, growth and recognition Traditional Organization Chart President Chief Executive Officer Executive Assistant Vice President Sales Director East Region Vice President Marketing Director West Region Director Public Relations Vice President Human Resources Director Compensation and Benefits Manager Manager Manager Clerk Manager Manager Manager Administrator Vice President Operations Vice President Finance Director Training and Development Director Manufacturing Driector Audit and Accounting Manager Logistics Tax Plant Manager Finance Plant Manager Accounting Tech. Writer Manager Manager Sr. Trainer Manager Manager Sr. Trainer Sales Sales Sales Sales Sales Clerk Accounting Accounting Flatter Organizations Executive and Operations Team Technical Development Team Manufacturing Engineering Team People Systems Team Finance Team Purchasing and Sales, Service and Suppllier Quality Marketing Team Team How Organizations are Responding The boundaryless organization Re-engineering “Broadbanding” job descriptions Performance-based job descriptions Empowered employees Skills matrices The Skills Matrix for One Job at British Petroleum H H H H H H H G G G G G G G F F F F F F F E E E E E E E D D D D D D D C C C C C C C B B B B B B B A A A A A A A Business Awareness Communication & Interpersonal Decision Making & Initiative Leadership & Guidance Planning & Organizational Ability Problem Solving Technical Expertise The highlighted boxes indicate the minimum level of skill required for the job.