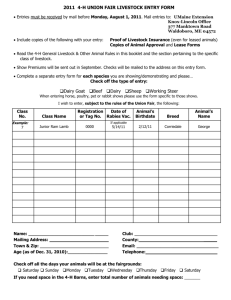
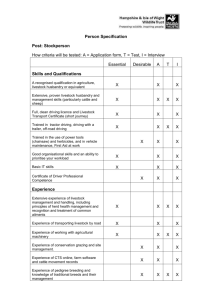
Livestock & Dairy Development Board (LDDB)
advertisement

Livestock & Dairy Development Board (LDDB) – A Profile Akram Khalid Company Secretary LDDB: The Genesis Part of Livestock Development Policy presented to the Prime Minister (April, 2005) Part of Agribusiness Development and Diversification Project (July 2005) Not-for-profit company under Section 42 of Companies Ordinance 1984 established 27-10-2005 Prime Minister approved summary of nominations of BOD (Nov 2005) 15 member Board of Directors(8 private sector - 7 public sector) LDDB: The Objectives Plan, promote, facilitate and coordinate accelerated development of and investment in livestock and dairy sectors Promote and facilitate marketing of livestock & livestock products Encourage private sector investment in livestock and dairy Undertake capacity building of all stakeholders Facilitate, promote and support the development and dissemination of improved technologies LDDB: Proposed Activities Player in implementation of livestock development policies (livestock development programs) Advise government on legal and policy framework International cooperation Identification and dissemination of new technologies Facilitate and promote livestock marketing Programs for producer organizations Stakeholders capacity building Livestock market information system Advice on re-orientation of public sector institutions LDDB – Immediate Business Plan Making Board operational entity Ensuring sustained financial resource Supervision of livestock sector study under Agribusiness development and diversification project Initiation of projects Livestock Production and Development for Meat Production Milk Collection/Processing and Dairy Production and Development Program Supervision of livestock sector study Identify livestock and dairy production areas, determine if they show comparative advantage and identify the major problems and constraints in the specified areas; Develop a database for different animal species and breeds with specific reference to production and processing potential; Identify the requirements and parameters for restructuring and reforming post-production technologies and operations related to livestock and dairy products, including milk, mutton, beef and by-product business in the private sector; Review previous work undertaken in the dairy and livestock sub-sectors and assess lessons learned and ways to benefit form such work; Recommend measures that can address constraints identified regarding breeds used, marketing, export compliance and their harmonization with the relevant WTO agreements; and, Develop proposals concerning livestock and dairy agribusiness components, and appropriate interventions for a possible follow-up project or second phase of the Agribusiness Development Project. Prepare a plan for the required restructuring of the government livestock institutions so that these become more responsive to the needs of the stakeholders. Livestock Production and Development for Meat Production Project Executed by Livestock & Dairy Development Board The project activities may jointly be undertaken with public and private sector institutions Facilitation and support to the farmers Demand driven Project Components Feedlot Fattening Farms Lead/Nucleus Beef Farms (150) Small Beef Farms (600) Feeder Beef Farms (300) Veal Production Farms (50) Lead Mutton Farms (250) Small Mutton Farms (600) Feeder Mutton Farms (400) Slaughter houses (8) and butcheries (20) in Private Sector Capacity Building of all stakeholders Awareness Program Legislation Project Implementation LDDB – overall guidance, supervision and execution Consultancies for feasibilities & SOPs of small medium and large fattening farms for beef & mutton Advertisement in the newspaper Technical services for setting up farms Contract with interested farmers Project provides for free technical and partial financial assistance (max. 15 %) Capacity building of farmers Project cost Duration – 5 years (2006-11) Establishment cost – 192.960 M Farmers support – 1024.343 M Slaughter house/butcheries – 61.34 M Training – 25.84 M Other operational costs – 216.364 Total Cost – 1520.847 M Milk Collection/Processing and Dairy Production and Development Program Executed by Livestock & Dairy Development Board The project activities may jointly be undertaken with public and private sector institutions Facilitation and support to the farmers Demand driven (cluster approach) Project Components Milk Collection and Marketing from Small and Landless Farmers Support to Market-oriented Rural Dairy Farmers Production of Quality Breeding Animals Production of Progeny-tested Bulls Milk Collection and Marketing Milk cooling units (300) Guaranteed purchase of milk from registered farmers Support for collection, cooling and transportation of milk Facilitate sale of milk to dairy plants and others Veterinary cover and breeding facility Improved animal nutrition Capacity building Farmers’ organization Market-oriented Rural Farmers Support rearing of quality heifers and bull calves Veterinary and breeding services Training in various aspects of dairy farming Support for silage/hay making and fodder production Technology support Production of quality breeding animals Support for rearing of heifers by small and market oriented dairy farmers Support for rearing of bull calves Support for silage/hay making and fodder production Facilitate sale of quality heifers and future breeding bulls Training in various aspects of heifer and bull calf management Production of Progeny Tested Bulls Technical and financial support for expansion of progeny testing program for Nili-Ravi buffalo and Sahiwal cattle Initiation of progeny testing program for Kundi buffalo and Red Sindhi cattle Public-private partnership in progeny testing program Link production of progeny tested bulls to the breeding program with farmers Support to semen production centres Strengthening of selected AI centres Project Implementation LDDB – overall guidance, supervision and execution Component I 500 villages (identification in collaboration with PMSIL, PDDC, provinces) 300 milk cooling units farmers’ organization Milk collection centre to act as focus for veterinary cover, breeding (AI) and feed/fodder seed availability VLW and farmers training Component II & III Newspaper advertisement for farmers selection Cluster approach Technology support & capacity building Facilitation of sale of heifers & bull calves Component IV Strengthening of on going activity in Punjab Initiate progeny testing program Project cost Duration – 5 years (2006-2011) Establishment cost – 244.560 M Equipment cost – 260.100 M Field activities – 855.600 M Other operational cost – 228.090 M Total Cost – 1588.350 M Thank You Livestock Development Policy Vision Promoting livestock to provide safe and quality products at competitive prices, covering entire value chain with focus on market and poverty reduction Policy Private sector led development with public sector providing enabling environment Strategy for development Private sector led Increase in productivity Moving from subsistence farming to market-oriented and commercial farming Covering entire value chain Features of Livestock Policy – 1 Legal Framework De-regulation of milk and meat prices Rationalization of taxes at local govt level Sale of meat animals on live weight basis Quality control of livestock products Regulation of urban ‘gawala’ colonies Level playing field for local dairy industry Features of Livestock Policy – 2 Livestock and Dairy Development Board Professionally run corporate body (free from unnecessary controls), will also act as holding company Facilitate and promote production, processing and marketing of milk and meat covering entire value chain Capacity building of the stakeholders Provision of technical and managerial services Sustained financial base Features of Livestock Policy – 3 Credit availability - Collateral issue Strengthening of policy and regulatory capacity at MINFAL headed by Animal Resource Development Commissioner Capacity Building for all stakeholders (LDDB, Jan 2006) Features of Livestock Policy – 4 Re-orienting Public Sector Institutions Government farms – superior male production Phased privatization of slaughter houses Self-sustaining/private-public partnership for vaccine production centres Improvement in research & development infrastructure as well as funding levels (Estab 50: Operational 50) Public Sector Programs – 1 Vaccine production facility and epidemiology of Foot and Mouth disease Improvement in quality of veterinary vaccines Market information system for livestock Infrastructure improvement in livestock markets Genetic potential of cattle and buffalo breeds for beef and sheep and goat breeds for mutton production Range and forage improvement programs Public Sector Programs – 2 Surveillance and monitoring system for animal diseases Expansion and modernization of diagnostic laboratories with quality control of milk facilities Fodder research and development programs in livestock production institutions Biotechnological interventions – Embryo transfer Drought mitigation strategies Promoting Livestock as a Source of Supplementary Income – 1 Support for: Establishment of a network of milk collection and chilling centres and refrigerated transport Cooperatives for meat animals marketing Seed availability of high yielding multi-cut fodder varieties Popularization of balanced feed and multinutrient molasses blocks for animals Farmers’ training particularly women in improved animal management Livestock help-line Promoting Livestock as a Source of Supplementary Income – 2 Expanding the progeny testing program for Nili-Ravi buffalo and Sahiwal cattle and initiation of genetic improvement of Kundi buffaloes and Red Sindhi cattle Expansion of genetic up-gradation of nondescript cattle through crossbreeding Expansion of artificial insemination network Bull calf raising centres and bulls for natural breeding Production of quality rams/bucks of indigenous sheep and goat breeds SME in Livestock – 1 Support for: Model dairy farms at district level Livestock business advisory service Salvage farming for dry animals of dairy colonies Support for private sector semen production units Wool production and processing Improved skins/hides processing SME in Livestock – 2 Support for: Feed-lot fattening for beef and mutton production Establishment of model butcheries in each city (grading system and commercial cuts) Encouraging building of slaughter houses in private sector Establishment of disease-free herds Establishment of slaughter house by-products plants Livestock Business Promotion Incentives for: Setting up large scale breeding farms Integrated meat production and processing Dairy zones in each districts (300 acres each) Meat export processing zones Programs for absolute poor Passing-on the gift program for absolute poor Distribution of livestock to destitute from Zakat and Bait-ul-Mal Restocking of sheep and goat herds lost during drought in Baluchistan Restocking of animals in quake-hit areas LDDB: Provisions in Agri-business Project Staff: Livestock & Dairy Development Advisor (1) Administrative & Support No. Rum/mo Personal Assistant Accounts/Admin Assistant Computer operators Receptionist Driver Messengers Security Guards Janitor (2) (1) (3) (1) (1) (2) (2) (1) 10,000 10,000 15,000 10,000 7,000 7,000 5,000 3,000 LDDB: Provisions in Agri-business Project Office: Equipment: Rental Refurbishment Furniture & Fixture Computers Multimedia Projector Photocopier Fax Vehicles: Saloon Car Motor cycle Rs. 1.000 million/year Rs. 2.000 million Rs. 0.190 million (2 (1 (1 (1 No) No) No) No) Rs. 1.200 million Rs. 80,000 LDDB: Provisions in Agri-business Project Operational Expenditure Travel Office supplies Communications Utilities Vehicle operating cost Repairs & maintenance Contingency (Million Rs for 5 years): 3.450 0.900 1.200 1.080 0.925 0.050 10.245 Livestock Business Development Support under Agribusiness Development Project Agriculture Support Services Provision Through ASF Business Development Services Private sector information service Agribusiness Finance Development Agribusiness capacity building Matching funds for enterprises, farmers, research & extension service providers (50:50) Grant to farmers organizations for agribusiness or marketing enterprises (100%) Dairy & livestock sector particularly higher level knowledge & skill development Capacity building including farmers field schools Livestock agribusiness study INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES IN LIVESTOCK LIVESTOCK IN NATIONAL ECONOMY Agriculture in Pak GDP 23.1 % Livestock in Pak GDP 10.8 % Share in agri GDP 46.8 % Livestock in export 8.5 % Provides raw material for industry Creates market and capital Social security for rural poor Security against crop failure in barani areas Dependent population > 6.5 m families Economic Survey (2004-05) LIVESTOCK PRODUCTION Milk Beef Mutton Poultry meat Eggs Wool Hair Skins and hides 29.472 M ton 1.115 M ton 0.740 M ton 0.416 M ton 8.529 billion 40.2 T ton 21.5 T ton 51.2 millions Economic Survey (2004-05) LIVESTOCK POPULATION (2004-05) (Million Heads) PROVINCE CATTLE BUFFALO SHEEP GOAT CAMEL PAKISTAN 24.2 26.3 24.9 56.7 0.8 Per cent distribution NWFP PUNJAB SINDH BALOCHISTAN 21.5 43.2 28.9 6.4 6.3 60.8 31.8 1.1 13.3 24.3 18.2 44.2 17.5 37.1 23.8 21.6 8.3 18.6 29.7 43.4 Economic Survey (2004-05) Livestock population trends 50000 POPULATION (000) 40000 30000 Cattle Buffaloes Sheep 20000 Goats 10000 0 1955 1960 1972 1976 1986 1996 2004 CENSUS YEAR 2004 data is estimated Livestock by Herd Size in Pakistan (Census 1996) LARGE RUMINANTS Herd Size Percent share in population Buffalo Cattle 1-2 18.1 16.3 3-4 24.5 (42.6) 5-6 SMALL RUMINANTS Herd Size Percent share in population Sheep Goat 1-5 6.5 21.4 22.0 (38.3) 6-15 13.2 (19.7) 28.5 (49.9) 17.4 (60.0) 17.2 (55.5) 16-30 15.7 (35.5) 16.3 (66.2) 7-10 19.6 (79.6) 20.0 (75.5) 31-50 12.8 (48.2) 9.9 (76.1) 11-15 10.2 (89.8) 9.9 (85.4) 51-75 8.5 (56.7) 5.7 (81.8) 16-20 4.2 (94.0) 4.8 (90.2) 76-100 6.8 (63.5) 4.2 (86.0) 21-30 2.9 (96.9) 4.3 (94.5) 101-150 9.1 (72.6) 4.9 (90.9) 31-50 1.6 (98.5) 2.9 (97.4) 151-200 7.5 (80.1) 3.1 (94.0) > 50 1.5 (100.0) 2.5 (99.9) 201-350 12.2 (92.3) 4.3 (98.3) > 350 7.9 (100.2) 1.5 (99.8) Values in parentheses indicate cumulative value indicating %age of total animals up to that herd size . Why investing in livestock sector ? Demand for livestock products is increasing Technologies for increasing production and processing are available Processed food is in demand Cost of production and profitability issue Export market in Gulf and South-East Asia International subsidies are lowering Niche markets Supply and Demand Parameter Growth rate (%) Milk Current Supply* Demand* (2004-5) (2010) (2010) 2.9 (milk) 3.2 (meat) 3.2 (milk) 4.3 (meat) 5.0 (milk) 6.5 (meat) 29.472 35.86 38.30 2278 2806 3228 (million tons) Meat (thousand tons) *Projected Government Initiatives Improving legal framework Access to bank credit Govt guaranteed private sector-led two companies for promotion and facilitation Re-orienting public sector institutions Livestock development policy Increasing public-sector investment to facilitate and promote the sector development Investment opportunities – 1 Setting up large scale breeding farms Farms for crossbred cattle Salvage farming for dry animals of dairy colonies Semen production units Artificial insemination service Establishment of milk collection and chilling centres and refrigerated transport Specialized dairy farms Vaccine production units especially for Foot and Mouth disease Seed production and sale of high yielding multicut fodder varieties Cattle feed mills Diversification of dairy products Investment opportunities – 2 Feed-lot fattening for beef and mutton production Establishment of model butcheries in each city (grading system and commercial cuts) Breeding rams/bucks production farms Slaughter houses in private sector Establishment of slaughter house by-products plants Integrated poultry production units High tech broiler and layer production Poultry processing (chilled and frozen, cuts) Value added units (processed products) Veterinary pharmaceuticals Thank You Livestock Production Constraints Unavailability of superior germplasm Inadequate feed resources (short by 30%) Epidemics of infectious diseases Livestock herd structure Un-organized farmers and lack of lobbying Poor marketing infrastructure Low investment by government (<1% of PSDP) Poor institutional infrastructure Inadequate regulatory framework Unavailability of credit to the livestock farmers (11% of agricultural credit) Livestock production systems Buffaloes and Cattle Sheep and Goats Poultry - Rural subsistence small holdings Rural market oriented small holdings Rural commercial farming Peri-urban commercial dairying - Nomadic - Transhumant - Sedentary / household - Traditional rural poultry - Industrial poultry Production Supply and Demand Issue Demand for livestock products is increasing Population growth rate and increased income are the real reasons Increase in red meat prices clearly indicate supply gap Tremendous scope of export (rising trend each year) Technology gap shows scope for increased production Supply and Demand Parameter Current (20032004) 2010 (MTDF) 2010 (High Road) Growth rate (%) 2.5 (milk) 3.1 (meat) 3.2 (milk) 4.3 (meat) 5.0 (milk) 6.5 (meat) 28.62 35.86 38.30 2212 2806 3228 Milk (million tons) Meat (thousand tons) Prospects and Potentials Rangelands Current fallow 23.5 m Ha 6.53 m Ha Farmers Milk Yield Average 1800 191 Elite animals 3500 250 Developed countries 6500 293 (kg/305 days) Meat Yield (kg/carcass) FAO Yearbook 2002 Government Initiatives Livestock Development Policy (Private sector led development with public sector providing enabling environment) Legal Framework Livestock and Dairy Development Board Capacity Building Credit availability Re-orienting public sector Institutions Incentives for enterprisers Poultry Development Policy Development Projects Strengthening of Livestock Services Agribusiness Development Improvement in Meat Production & processing Improvement in Milk Production, collection and Processing FAO – TCP projects Provincial Government Initiatives Livestock and Dairy Development Board Professionally run corporate body (free from unnecessary controls) registered under Companies Act Facilitate and promote production, processing and marketing of milk, meat and poultry covering entire value chain Facilities and promote producers controlled organization Capacity building of the stakeholders Provision of technical and managerial services Sustained financial base Summary Livestock has great potential for economic growth, export and poverty alleviation Main features of proposed Livestock Development Policy are: Enactment of enabling legal framework Establishment of Livestock and Dairy Development Board Ensuring credit availability to livestock farmers Thrust on capacity building of all stakeholders Improving technical back-stopping at MINFAL Restructuring livestock related public sector institutions Promoting commercial livestock farming Action Plan for increase in Milk and Meat production with combined efforts of Private Sector, Federal Government, Provincial Governments and Livestock & Dairy Development Board Features of Livestock Policy – 1 Legal Framework Review & update existing laws – Federal laws (FG, July 2005) Review & update existing laws – Provincial laws (PG, July 2005) De-regulation of milk and meat prices (PG, Jan 2006) Rationalization of taxes at local govt level (PG, Jul 2006) Sale of meat animals on live weight basis (PG, Jan 2006) Quality control of livestock products (PG, Jan 2006) Regulation of urban ‘gawala’ colonies (PG, Jan 2006) for Equitable Rural Development Healthy Nation and Poverty Alleviation Invest in Livestock Development Livestock Development Policy Vision Promoting livestock to provide safe and quality products at competitive prices, covering entire value chain with focus on market and poverty reduction Policy Private sector led development with public sector providing enabling environment Strategy for development Private sector led Increase in productivity Moving from subsistence farming to market-oriented and commercial farming Covering entire value chain Progress in hand Strengthening of livestock services project (EU-GOP funding) Agribusiness development project Up-scaling of Hala from 500 to 1200 villages Milk collection and marketing initiative of LEADS at Thatta (FAO-IFAD funding) PSDP (2004-05) – 5 new projects Hala Model by Idara Kissan Milk Collection Centre Producer/Member Services (subsidized) 1. Vaccination & Health cover 2. Breed Improvement - AI 3. Feed & fodder seed 4. Training 5. Mother & child Program + Fixed price and assured purchase Milk Plants Processing & Marketing -Pasteurized Milk -UHT milk -Dairy products Retailer Consumer POLICY VISION Provide the people of Pakistan wholesome livestock products at competitive prices along with exploring export markets in Gulf and South East Asian countries and use livestock as a tool for poverty reduction in the country PROPOSED POLICY “Livestock development in Pakistan will be led by private sector with public sector providing enabling environment and capacity building role” STRATEGY FOR DEVELOPMENT Increase in per unit animal productivity Moving from subsistence farming to market-oriented farming and finally commercial farming Improving per unit animal productivity Balanced Feed Health Management Improvement in Genetic Potential Fair Marketing Government Initiatives Legal Framework De-regulation of milk and meat prices Sale of meat animals on live weight basis Level playing field for local dairy industry Electricity and other tariffs/local taxes Quality control of livestock products National standards for livestock and livestock products Features of Livestock Policy – 2 Livestock and Dairy Board Professionally run corporate body (free from unnecessary controls) Facilitate and promote producers owned and controlled organizations for milk and meat production Capacity building of the stakeholders Provision of technical and managerial services Rs. 5 billion endowment fund Features of Livestock Policy – 3 Credit availability Separate credit line Collateral issue Capacity Building Very important All stakeholders Features of Livestock Policy – 4 Technical back-stopping at MINFAL Animal Resource Development Commissioner similar to ADC Separate commissioners for Milk Meat Poultry Diseases Inland fisheries Marine Fisheries Features of Livestock Policy – 5 Restructuring Institutions Private-public partnership for slaughter houses Self-sustaining/private-public partnership for vaccine production centres Government farms – superior male production Improvement in research & development infrastructure as well as funding levels (Estab 50: Operational 50) Incentives for Commercial Farming Allocation of marginal state land Rationalization of Taxes Regulation of Functioning of Dairy Colonies Action Plan For Milk Increase Immediate (Ist Year) Establishment of a network of milk collection and chilling centres and refrigerated transport (LB,PS) Model dairy farms at district level (LB,PS) Vaccine production facility and epidemiology of Foot and Mouth disease (FG) Quality control of veterinary vaccines (FG) Seed availability of high yielding multi-cut fodder varieties (PS,PG) Popularization of balanced feed for animals (LB,PG) Farmers’ training particularly women in improved animal management (LB,PG) Use of media (print and electronic) in livestock extension activities (LB,PG) Livestock help-line (LB,PG) Feed advisory service (LB,PG) Action Plan For Milk Increase Short-term (2-3 Years) Re-organizing dairy cattle colonies particularly at Karachi (PG,LB) Expanding the progeny testing programme for Nili-Ravi buffalo and Sahiwal cattle and initiation of genetic improvement of Kundi buffaloes and Red Sindhi cattle (PG,LB,PS) New summer fodder varieties for animals (PG,PS) Popularization of legume fodders and legume-cereal mixed fodder cropping system (PG,LB,PS) Modernization of vaccine production facilities (PG,FG,PS) Expansion of artificial insemination network (PG,PS) Bull calf raising centres (PG,PS) Salvage farming for dry animals of dairy colonies (PS,LB,PG) Distribution of livestock to destitutes from Zakat and Bait-ul-Mal (FG,PG) Surveillance and monitoring system for animal diseases (FG,PG) Action Plan For Milk Increase Medium-term (3 to 5 Years) Genetic up-gradation of non-descript cattle through crossbreeding (PS,PG) Setting up large scale breeding farms (PS,LB) Dairy zones in each districts (300 acres each) (PG) Sexual health control programme (PG,LB) Fodder research and development programmes in livestock production institutions (PG) Support for private sector semen production units (LB) Genetic characterization and sustainable use of indigenous livestock genetic resources (FG,PG) Expansion and modernization of diagnostic laboratories with quality control of milk facilities (FG,PG) Market information system for livestock (LB,PG) Action Plan For Meat Increase Immediate (Ist Year) Feed-lot fattening for beef and mutton production (PS,LB) Establishment of model butcheries in each city (grading system and commercial cuts) (PS,LB) Farmers’ training in commercial meat production (PG,LB) Butchers’ training in improved flaying techniques (PG,LB) Infrastructure improvement in livestock markets (DG,PG) Meat production service centres (PG,LB) Action Plan For Meat Increase Short-term (2-3 Years) Production of quality rams/bucks of indigenous sheep and goat breeds (PS,PG,LB) Nuclear and multiplier flocks for sheep/goat male production (PS,LB) Meat export processing zones (PG,FG) Cooperatives for meat animals marketing (PS,LB) Evaluation of Narimaster in the field (PG) Popularization of multi-nutrient molasses blocks (PS,LB,PG) Drought mitigation strategies (FG,PG) Action Plan For Meat Increase Medium-term (3 to 5 Years) Genetic potential of cattle and buffalo breeds for beef production (PG,FG) Genetic potential of sheep and goat breeds for mutton production (PG,FG) Modernization of slaughter houses (PS,DG) Encouraging building of slaughter houses in private sector (PS,FG) Establishment of slaughter house by-products plants (PS,PG,FG) Establishment of disease-free herds (PS,PG,FG) Range and forage improvement programmes (PG,FG) Restocking of sheep and goats herds lost during drought in Baluchistan (PG,FG) In-service training for professional and paraprofessional staff (PG,FG) Transport for live animals and carcasses (PS,PG) Summary Livestock has great potential for economic growth, export and poverty alleviation Main features of proposed Livestock Development Policy are: Enactment of enabling legal framework Establishment of Livestock and Dairy Development Board Ensuring credit availability to livestock farmers Thrust on capacity building of all stakeholders Improving technical back-stopping at MINFAL Restructuring livestock related public sector institutions Promoting commercial livestock farming Action Plan for increase in Milk and Meat production with combined efforts of Private Sector, Federal Government, Provincial Governments and Livestock & Dairy Development Board for Equitable Rural Development Healthy Nation and Poverty Alleviation Invest in Livestock Development