Phases of Matter and Particle Motion
advertisement

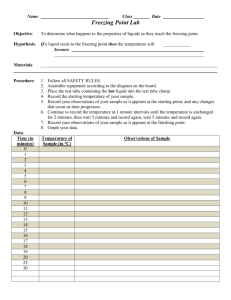
SPS5 Phases of matter (SPS5phasesandmotion) Name:_____________________________________________ Date:________________________ 1.The formation of water droplets on the inside of a window pane during a cold night is an example of A. dehydration. B. sublimation. C. condensation. D. fermentation. 2. The process in which a liquid changes to gas is called A. condensation. B. evaporation. C. freezing. D. precipitation. 3. The process which changes water into a vapor or gas is called A. condensation. B. evaporation. C. precipitation. D. sublimation. 4. Carolyn was walking on the sidewalk in front of a store and had to step over a melting ice cream cone. What type of change was the ice cream undergoing? A. chemical B. molecular C. organic D. phase 5. The illustration below shows a hot-air balloon. The pilot can change the altitude of the hot-air balloon by changing the temperature of the gas inside the balloon. When the gas is heated, the balloon rises. Which of the following best explains this phenomenon? A. Heating the gas reduces its pressure. B. Heating the gas decreases its density. C. Heating the gas decreases its molecular motion. D. Heating the gas reduces the frequency of the gas molecules' collisions. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education. 6. Which of the following occurs when a rigid container of gas is heated? A. The pressure inside the container increases. B. The pressure inside the container decreases. C. The pressure inside the container stays the same. D. The pressure inside the container changes the composition of the gas. T. 7. The illustration below shows the lab equipment set up by a student to find the melting and freezing points for naphthalene, a chemical used as an insect repellent. A small sample of solid naphthalene (C10H8) is placed in the capillary tube attached to the thermometer and is heated in the water bath until the white solid melts. The student then turns the heat off and observes the sample as it cools, recording the temperature at regular intervals. What will most likely happen to the colorless liquid naphthalene when the temperature reaches the freezing point of naphthalene? A. The naphthalene will change into a yellow liquid. B. The naphthalene will crystallize into a white solid. C. The naphthalene will begin to form small bubbles. D. The naphthalene will disappear from the capillary tube. This online assessment item contains material that has been released to the public by the Massachusetts Department of Education. 8. Perfume sprayed from a bottle spreads more easily in a warm room of 25°C than in a cool room of 15°C. Which of the following correctly compares perfume molecules at 25°C to those at 15°C? A. At 25°C, they have more mass. C. At 25°C, they have less kinetic energy. B. At 25°C, they are moving faster. D. At 25°C, they are decreasing in volume. . 9. As a substance changes from a liquid to a solid A. the average kinetic energy decreases. C. the potential energy decreases. B. the average kinetic energy increases. D. the temperature increases. 10. As you view the illustrations from left to right, from one state of matter to another, which of these statements is correct? A. The average kinetic energy of the molecules decreases. B. The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. C. The attractive force between the molecules increases. D. The average temperature decreases. 11. If the volume of a hot air balloon remains constant, what happens as the temperature of the air inside the balloon increases? A. The pressure inside the balloon decreases. C. The kinetic energy of the air inside decreases B. The pressure inside the balloon increases. D. The attractive force between the air particles inside increases. 12. An ice-skating rink has tubes under its floor to freeze the water. Salt water is cooled well below the freezing point of water and pumped through the tubes to freeze the water in the rink. Why can the salt water be cooled so low without freezing? A. Salt has a very low freezing point. B. Adding salt to water lowers its freezing point. C. Movement of the salt water through the tubes keeps it in the liquid state. D. The salt water is constantly absorbing energy from its surroundings. 13. Water molecules have the greatest kinetic energy in — A. ice at 0° C B. water at 373° K. C. water at 98° C D. steam at 150° C 14. The graph shows the pressure of an ideal gas as a function of volume. According to the graph, increasing the volume from 100 mL to 150 mL — decreases the pressure by 80 kPa decreases the pressure by 160 kPa increases the pressure by 80 kPa increases the pressure by 160 kPa its A. B. C. D. 15. According to Boyle's law, the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature is — A. numerically equivalent. C. positively correlated. B. inversely proportional. D. totally unrelated. Answer Key 1. C) condensation. 2. B) evaporation. 3. B) evaporation. 4. D) phase 5. B) Heating the gas decreases its density. 6. A) The pressure inside the container increases. 7. B) The naphthalene will crystallize into a white solid. 8. B) At 25°C, they are moving faster. 9. A) the average kinetic energy decreases. 10. B) The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. 11. B) The pressure inside the balloon increases. 12. B) Adding salt to water lowers its freezing point. 13. D) steam at 150° C 14. A) decreases the pressure by 80 kPa 15. B) inversely proportional.