Chapter 1
advertisement

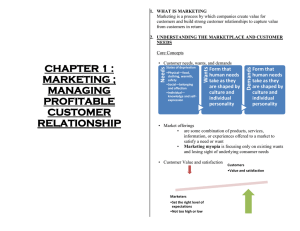
Chapter 1 Marketing in a Changing World: Creating Customer Value and Satisfaction Road Map: Previewing the Concepts Define what marketing is and discuss its core concepts. Explain the relationships between customer value, satisfaction, and quality. Define marketing management and understand how marketers manage demand and build profitable customer relationships. Compare the five marketing management philosophies. Analyze the major challenges facing marketers heading into the new “connected” millennium. 1-2 What is Marketing? Simply put: Marketing is the delivery of customer satisfaction at a profit. Goals: Attract new customers by promising superior value and keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction. 1-3 Core Marketing Concepts (Fig. 1-1) 1-4 Marketing Defined Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. 1-5 What are Consumers’ Needs, Wants, and Demands? Needs - state of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs i.e hunger Wants - form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality i.e. bread Demands - human wants backed by buying power i.e. money 1-6 What Will Satisfy Consumers’ Needs and Wants? Products Anything that can be Offered to a Market to Satisfy a Need or Want Experiences Persons Organizations Activities Places Ideas Services Activity or Benefit Offered for Sale That is Essentially Intangible and Doesn’t Result in the Ownership of Anything 1-7 How Do Consumers Choose Among Products and Services? Value Gained From Owning a Product and Costs of Obtaining the Product is Customer Value Product’s Perceived Performance in Delivering Value Relative to Buyer’s Expectations is Customer Satisfaction Total Quality Management Involves Improving the Quality of Products, Services, and Business Processes 1-8 How Do Consumers Obtain Products and Services? Exchanges Transactions Relationships Building a Marketing Network by Adding: •Financial Benefits •Social Benefits •Structural Ties •Profitable Customers 1-9 Consider the following thought questions, formulate an answer, pair with the student on your right, share your thoughts with one another, and respond to questions from your instructor. When was the last time you were completely satisfied with something you purchased? What was it? Why were you satisfied? What did a marketer have to do with this? 1-10 Modern Marketing System (Fig. 1-2) 1-11 Marketing Management Marketing Management Demand Management Profitable Customer Relationships Involves managing demand, which involves managing customer relationships Finding and increasing demand, also changing or reducing demand such as in Demarketing Attracting new customers and retaining and building relationships with current customers 1-12 Marketing Management Practice Stage 1. Entrepreneurial Marketing Stage 2. Formulated Marketing Stage 3. Intrepreneurial Marketing 1-13 Marketing Management Philosophies Production Concept Product Concept Selling Concept Marketing Concept Societal Marketing Concept 1-14 Marketing and Sales Concepts Contrasted (Fig. 1-3) 1-15 Societal Marketing Concept (Fig. 1-4) http://www.johnsonandjohnson.com/ 1-16 What are the major differences between the Marketing Concept and the Societal Marketing Concept? 1-17 Marketing Challenges in the New “Connected” Millennium (Fig. 1-5) 1-18 Technologies for Connecting Learn About & Track Customers With Databases Create Products & Services Tailored to Meet Customer Needs Connecting Technologies in Computers, Telecommunications, Information, & Transportation Help To: Communicate With Customers in Groups Or One-on-One Distribute Products More Efficiently & Effectively 1-19 The Internet The Internet has been hailed as the technology behind a New Economy. New applications include: “click-and-mortar” companies “click-only” companies Business-to-business e-commerce Business-to-business transactions online are expected to reach $3.6 trillion in 2003. By 2005, 500,000 companies will use the Internet to do business. 1-20 Connections With Customers Most marketers are targeting fewer, potentially more profitable customers. Asking: What value does the customer bring to the organization? Are they worth pursuing? Connecting for a customer’s lifetime. 1-21 BankOne (Marketing at Work 1-3) BankOne focuses on connecting with customers they can serve profitably. Premier One customers know that they are “special, exclusive, privileged, valued.” http://www.bankone.com/ 1-22 Direct Connections With Customers Many companies use technologies to let them connect more directly with their customers. Products available via telephone, mail-order catalogs, kiosks and e-commerce. Some firms sell only via direct channels (i.e. Dell Computer, http://www.amazon.com/), others use a combination. Direct marketing is redefining the buyer’s role in connecting with sellers. Buyers are active participants in shaping the marketing offer and process; some buyers design their own products online such as at http://www.landsend.com/. 1-23 Connections With Marketing’s Partners Connecting Inside the Company Every employee must be customer-focused Teams coordinate efforts toward customers Connecting With Outside Partners Supply Chain Management Strategic Alliances 1-24 Connections With the World Around Us Global Connections Broadening Connections Value Connections Social Responsibility Connections 1-25 Rest Stop: Reviewing the Concepts Define what marketing is and discuss its core concepts. Explain the relationships between customer value, satisfaction, and quality. Define marketing management and examine how marketers manage demand and build profitable customer relationships. Compare the five marketing management philosophies. Analyze the major challenges facing marketers heading into the next millennium. 1-26