Self Assessment
advertisement

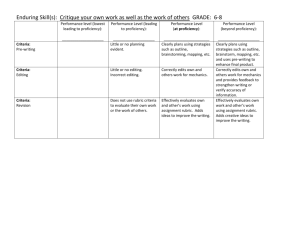
DIVINE MERCY COLLEGE FOUNDATION INC. Caloocan City Professional Education ASSESSMENT AND RATING OF LEARNING OUTCOMES UNDER THE K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM Presented by: CHRISTIAN D. EVANGELISTA MARIANNE T. EVANGELISTA, MSHRM DepEd ORDER No. 73 S. 2012 General Guidelines for the Assessment and Rating of Learning Outcomes • Effective School Year () 2012-2013, the standards-based assessment and rating system shall be implemented to support the progressive roll-out starting with grades 1 and 7 of the K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum in public and private elementary and secondary schools nationwide. OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION • • • • • • • • Philosophy of Assessment Nature of Assessment and Its Purpose Levels of Assessment Assessment Tools Levels of Proficiency and Equivalent Numeric Value Rating System Assessment Rubric Frequency of Assessment WHAT IS “K TO 12 PROGRAM”? K TO 12 PROGRAM • The K to 12 Program covers: • Kindergarten and 12 years of basic education (six years of primary education, four years of Junior High School, and two years of Senior High School [SHS]) A. PHILOSOPHY • Assessment shall be used primarily as a quality assurance tool to track student progress in the attainment of standards, promote self-reflection and personal accountability for one’s learning, and provide a basis for the profiling of student performance B. NATURE AND PURPOSE OF ASSESSMENT • Assessment shall be holistic, with emphasis on the formative or developmental purpose of quality assuring student learning. • It also standards-based as it seeks to ensure that teachers will teach to the standards and students will aim to meet or even exceed the standards. • The students’ attainment of standards in terms of content and performance is, therefore, a critical evidence of learning. LEVEL OF PERFORMANCE AND UNDERSTANDING C. LEVELS OF ASSESSMENT • The attainment of learning outcomes as defined in the standards shall be the basis for the quality assurance of learning using formative assessments. • They shall also be the focus of the summative assessments and shall be the basis for grading at the end of instruction. LEVEL OF LEARNING OUTCOMES • • • • Knowledge Process or Skill Understanding Products and Performances – The levels of Assessment are defined as follows: KNOWLEDGE • The substantive content of the curriculum, the facts and information that the student acquires PROCESS • Skills or cognitive operations that the student performs on facts and information for the purpose of constructing meanings or understandings. UNDERSTANDING(S) • Enduring big ideas, principles and generalizations inherent to the discipline, which may be assessed using the facets of understanding which may be specific to the discipline PRODUCTS / PERFORMANCES • Real-life application of understanding as evidenced by the student’s performance of authentic tasks. LEVELS OF ASSESSMENT These levels shall be the outcomes reflected in the class record and shall be given corresponding percentage weights as follows: LEVEL OF ASSESSMENT PERCENTAGE WEIGHT Knowledge Process or Skills Understanding (s) Products / Performances TOTAL 15% 25% 30% 30% = 100% ASSESSMENT TOOLS KNOWLEDGE PROCESS / SKILLS UNDERSTANDINGS PRODUCTS & PERFORMANCES Traditional Tools: Transform a Textual Presentation into a Diagram Facets of Understandings Authentic products or performance tasks that a student is expected to do to Paper and Pencil Tests ~ Outline, Organize, Analyze, Interpret, Translate, Convert or Express Information ~ Self Knowledge Demonstrate his or her understanding. ~ Multiple Choice ~ Flow Chart ~ Empathy ~ Self Understanding ~ True or False ~ Construct Graphs ~ Perspective ~ Self Monitoring ~ Matching Type ~ Graphic Organizers ~ Explanation ~ Self Assessment ~ Constructed Response Tests ~ Draw Analogies ~ Interpretation ~ Permit choices of combinations of oral, written, visual and kinesthetic modes LEVELS OF PROFICIENCY AND ITS EQUIVALENT NUMERICAL VALUE The performance of the students shall be described in the report card, based on the following levels of proficiency LEVEL OF PROFICIENCY Beginning (B) Developing (D) Approaching Proficiency (AP) Proficient (P) Advanced (A) While, the level proficiency shall be based on a numerical value which arrived form summing up the results of the student’s performance on the various level of assessment. EQUIVALENT NUMERICAL VALUE 74% and Below 75 - 79% 80 - 84% 85 - 89% 90% and Above LEVELS OF PROFICIENCY LEVELS OF PROFICIENCY FEED BACK • Results of the assessment across levels should be fed back immediately to the students, so that they know what to improve further, and then they can plan strategically how they can address any learning deficiency PROTOTYPE RUBRICS FOR THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF ASSESSMENT WHAT IS RUBRIC: • A rubric is a guideline for rating student performance. • It must define the range of possible performance levels. • Within this range, there are different levels of performance which are organized from the lowest level to the highest level of performance. • Usually, a scale of possible points is associated with the continuum in which the highest level receives the greatest number of points and the lowest level of performance receives the fewest points. BENEFITS OF RUBRIC – The rubric provides assessment with exactly the characteristics for each level of performance on which the students and the teacher should base their judgment. – The rubric provides the students with clear information about how well they performed and what they need to accomplish in the future to better their performance. RUBRICS CRITERIA & PERCENTAGE CRITERIA PERCENTAGE Knowledge Skills Understanding (s) Transfer of Understanding 15% 25% 30% 30% TOTAL: 100% LEARNING OUTCOME #O1 KNOWLEDGE PAPER AND PENCIL INSTRUMENTS • Paper-and-pencil instruments refer to a general group of assessment tools in which candidates read questions and respond in writing. • This includes tests, such as knowledge and ability tests, and inventories, such as personality and interest inventories. MOST COMMON RESPONSE FORMATS ARE: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. MULTIPLE CHOICE TRUE OR FALSE MATCHING TYPE IDENTIFICATION CONSTRUCTED RESPONSE / ESSAY A. KNOWLEDGE (15%) LEARNING OUTCOME #O2 SKILLS TRANSFORM TEXTUAL PRESENTATION INTO A DIAGRAM • Outline, Organize, Analyze, Interpret, Translate, Convert or Express Information by using: 1. 2. 3. 4. Flow Chart Graphs Analogies Graphic Organizers PROTOTYPE PIE GRAPH PERCENTAGE LEVEL OF PROFICIENCY 5% 10% LEGEND 15% B D AP 40% 30% P A Result of Midterm Exam B. SKILLS (25%) CONTINUATION: CONTINUATION: #02 CONTINUATION: #03 PROTOTYPE ASSESSMENT MATRIX FOR “TLE” (Technology Livelihood Education) BASIS FOR PROMOTION AND RETENTION LEVEL OF PROFICIENCY EQUIVALENT NUMERICAL VALUE Beginning (B) 74% and Below Developing (D) 75 - 79% Approaching Proficiency (AP) 80 - 84% Proficient (P) 85 - 89% Advanced (A) 90% and Above PROMOTION AND RETENTION • Promotion and Retention of students shall be by subject • Students whose proficiency level is Beginning (B) at the end of the quarter or grading period shall be required to undergo remediation after class hours so that they can immediately catch up as they move to the next grading period • If by the end of school year, the students are still at the Beginning level, then they shall be required to take summer classes RATING SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOME #O3 UNDERSTANDING UNDERSTANDING • Understanding as expressed using any three of the six facets of understanding • The facets are explained (adapted from the paper, “Understanding by Design Framework in the Philippines” by Mc Tighe and Grant Wiggins, p.5) FACETS OF UNDERSTANDING EXPLAIN SELF KNOWLEDGE INTERPRET CONCEPT EMPATHY APPLY PERSPECTIVE FACET # 01 • Concepts, principles, and processes by putting them in their own words, teaching them to others, justifying their answers and showing their reasoning. “EXPLANATION” FACET # 02 “INTERPRETATION” • By making sense of data, text, and experience through images, analogies, stories and models; FACET # 03 “APPLICATION” • Effectively using and adapting what they know in new and complex texts FACET # 04 “PERSPECTIVE” • Demonstrate perspective by seeing the big picture and recognizing different points of view. FACET # 05 “EMPATHY” • Display empathy by perceiving sensitively and putting one’s self in someone else’s shoes; FACET # 06 “SELF KNOWLEDGE” • Have self knowledge by showing met cognitive awareness, using productive habits of mind and reflecting on the meaning of the learning and experience. UNDERSTANDING MAYBE ASSESSED BASED ON THE FOLLOWING CRITERIA Continuation: LEARNING OUTCOME #O4 PRODUCT / PERFORMANCES TRANSFER OF UNDERSTANDING • Transfer of understanding to life situations maybe assessed as demonstrated through the following: 1. PRODUCTS – Outputs which are reflective of learner’s creative application of understanding; 2. PERFORMANCES – skillful exhibition or creative execution of a process, reflective of masterful application of learning or understanding. STUDENT IS EXPECTED TO DEMONSTRATE HIS/HER UNDERSTANDING BY MEANS OF: • Self Understanding • Self Monitoring • Self Assessment SELF UNDERSTANDING • Also known as Self knowledge • Is the ability to understand one's own actions SELF MONITORING • Used in behavioral management where a person will keep a record of behavior patterns. • A personality trait for the ability to change behavior in response to different situations. SELF ASSESSMENT • It is the process of gathering information about yourself in order to make an informed career decision. • A self assessment should include a look at the following: values, interests, personality, and skills. Continuation: PROTOTYPE FORMATIVE AND SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOOLS PRE ASSESSMENT TOOL • Pre-assessment allows the teacher and student to discover what is already known in a specific topic or subject. • It is critical to recognize prior knowledge so students can engage in questioning, formulating, thinking and theorizing in order to construct new knowledge appropriate to their level. PROTOTYPE PRE-ASSESSMENT TOOL FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT The goal of formative assessment is to gather feedback that can be used by the instructor and the students to guide improvements in the ongoing teaching and learning context. These are low stakes assessments for students and instructors. Examples: 1. Asking students to submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture 2. Have students submit an outline for a paper. 3. Early course evaluations 4. Giving quizzes to check student understanding • SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT • The goal of summative assessment is to measure the level of success or proficiency that has been obtained at the end of an instructional unit, by comparing it against some standard or benchmark. • The outcome of a summative assessment can be used formatively, however, when students or faculty take the results and use them to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses. • Examples of summative assessments include: a midterm exam a final project a paper a senior recital PROTOTYPE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TOOL THROUGH AUTHENTIC PERFORMANCE TASK Presented to: DR. BELLA LAUREANO And the students under Professional Education of The Divine Mercy College Foundation Inc (Batch 2013)