CHAPTER 5 NOTES
advertisement

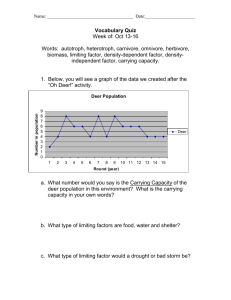
Mrs. Yanac Biology 1B DENSITY – The number of individuals in particular area GROWTH RATE – The rate at which the population increases GEOGRAPHIC DISTRIBUTION – The area inhabited by the population # of BIRTHS (Birth rate) # of DEATHS (Death rate) # of individuals that ENTER (Immigration) a population # of individuals that LEAVE (Emigration) a population Under IDEAL conditions with UNLIMITED resources, a population will grow & grow (exponentially) As resources become LESS available, the growth of a population SLOWS or STOPS Leveling off is known as carrying capacity (total # of individuals a population can support) EX: White-Tailed Deer Habitat Food Source = 10 deer Carrying Capacity = 10 deer Although the water, cover & space are sufficient for more deer, the limiting factor of the food supply determines what this habitat will support. Carrying capacity does not exceed the number that the most limiting factor will allow Any factor that causes the population to decrease Younger or weaker animals die (-) There may be fewer animals born (-) Takes more energy just to survive Animals could get burned (-) Food & cover burned (-) Water source may evaporate (+) Re-growth of nutritional vegetation (+) Encourages grass cover (+) Cleans out debris (-) Movement is difficult, requires more energy (-) Food is difficult, often impossible, to find (-) Thermal cover is difficult to reach & often ineffective (+) Insulates plants & animals from extreme cold (-) Vegetation withers, food disappears (-) Water sources dry up (-) Cover thins (-) Habitat & wildlife washed away or inundated. (-) Vegetation drowns (+) Disperse seeds & soil (-) Crowding and trampling of vegetation (-) Disease spreads easily (-) Vegetation is stripped Factors that depend on the size of a population Examples: Competition Predation Parasitism Disease Affect all populations regardless of size. Examples Natural disasters Weather Human activities RECAP: 1. What are 4 factors that affect population growth? 2. What are 3 characteristics of a population? 3. What type of growth goes through a period of rapid growth, then slows down or stops? 4. What is the term for the largest # of individuals a population can hold? 5. What type of growth grows at a constant rate? 6. What are some densitydependent limiting factors? 7. What are some densityindependent limiting factors?