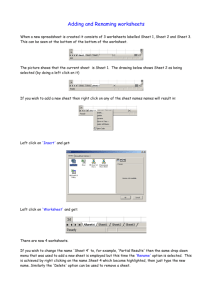
Unit B
advertisement

Microsoft Office 2003- Illustrated Introductory, Second Edition Building And Editing Worksheets Objectives Plan and design a worksheet Edit cell entries Enter formulas Create complex formulas Introduce Excel functions Building and Editing Worksheets 2 Objectives Use Excel functions Copy and move cell entries Understand relative and absolute cell references Copy formulas with relative cell references Copy formulas with absolute cell references Building and Editing Worksheets 3 Planning and Designing a Worksheet When planning and designing a worksheet, it is important to: – Determine the purpose of the worksheet – Determine the desired result – Collect all necessary information – Determine the calculations or formulas necessary to achieve the results – Sketch how you want the worksheet to look Building and Editing Worksheets 4 Planning and Designing a Worksheet (cont.) Sample worksheet Building and Editing Worksheets 5 Editing Cell Entries To edit a cell: – Select the cell, then click the formula bar or press [F2] to change to Edit mode • A blinking line called the insertion point appears in the formula bar – Edit data • The mode indicator on the status bar tells whether Excel is in Edit mode Building and Editing Worksheets 6 Editing Cell Entries (cont.) Insertion point Pointer used for editing Edit mode indicator Building and Editing Worksheets 7 Editing Cell Entries (cont.) Recovering a lost workbook file – Due to Excel or some other program freeze or a power failure – Document Recovery task pane opens the next time you open Excel • Displays original and recovered versions of the Excel file • Open and review any version of the file • Save the file version you want Building and Editing Worksheets 8 Entering Formulas A formula is used to perform numeric calculations – Adding, subtracting, multiplying, etc. – Formulas usually start with an equal sign (=), called the formula prefix followed by cell addresses or range names • Using a cell address or range name is called cell referencing • When the value in a cell is changed, any formula containing that cell reference will be automatically recalculated Building and Editing Worksheets 9 Entering Formulas (cont.) Click the cell where you want to enter the calculation – Enter the calculation by typing the cell addresses or by pointing • Use the mouse to point to cells Formula in formula bar Moving border Formula in cell Building and Editing Worksheets 10 Entering Formulas (cont.) Common arithmetic operators Building and Editing Worksheets 11 Creating Complex Formulas A complex formula is an equation that uses more than one type of arithmetic operator – A formula that uses both addition and multiplication – Arithmetic operators separate tasks in order of precedence Building and Editing Worksheets 12 Creating Complex Formulas (cont.) Formula in formula bar Formula calculates a 20% increase over the value of cell B8 Building and Editing Worksheets 13 Creating Complex Formulas (cont.) Order of precedence in Excel formulas – Excel performs calculations in a certain order based on these rules: • Operations inside parentheses are calculated first • Exponents are calculated next • Multiplication and division are calculated next (from left to right) • Addition and subtraction are calculated next (from left to right) Building and Editing Worksheets 14 Introducing Excel Functions A function is a predefined formula that makes it easy to perform a complex calculation – Begin with the formula prefix (=) – Type functions or use the Insert Function button – Can be used by itself or within a formula Building and Editing Worksheets 15 Introducing Excel Functions (cont.) The AutoSum button enters the most frequently used function: SUM – By default, AutoSum adds the values in cells above the cell pointer – If there are one or fewer values above the cell pointer, AutoSum adds values to its left Excel uses the information within parentheses, the argument, to calculate the function result Building and Editing Worksheets 16 Introducing Excel Functions (cont.) AutoSum button Insert Function button SUM Function Result of SUM Function Building and Editing Worksheets 17 Using Excel Functions Using the MIN and MAX functions – MIN calculates the smallest value in a range – MAX calculates the largest value in a range Frequently used functions Building and Editing Worksheets 18 Using Excel Functions (cont.) Click to use mouse to define an argument Building and Editing Worksheets 19 Copying and Moving Cell Entries Use the Cut, Copy, and Paste buttons or the drag-and-drop feature – Copy or move data within a worksheet or between worksheets – The Office Clipboard temporarily stores information that you copy or cut • Holds up to 24 items • Has its own task pane that displays all stored items Building and Editing Worksheets 20 Copying and Moving Cell Entries (cont.) Copying and pasting a range of information – Select the top-left cell of the range where you want to paste the information The drag-and-drop technique is useful for copying cell contents – An outline of the cell appears when you move the pointer Building and Editing Worksheets 21 Copying and Moving Cell Entries (cont.) Copy button Paste button Copied cell Outline of copied cell Drag-and-drop pointer Building and Editing Worksheets 22 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References Use relative references when cell relationships don’t change – Excel normally records the relationship of cell references to the cell containing the formula and not the cell references • Calculations are performed based on cell relationship – The formula results are calculated the same way even if the cell is moved • Called relative cell referencing Building and Editing Worksheets 23 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References (cont.) Formula contains relative cell references Cells contain relative cell references Building and Editing Worksheets 24 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References (cont.) Use absolute cell references when one relationship changes – Excel retrieves formula information from a specific cell which doesn’t change even if the formula is copied to another location • Called absolute cell reference • Created by placing a dollar sign ($) before both the column letter and the row number for the cell’s address Building and Editing Worksheets 25 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References (cont.) Relative cell reference Cell referenced in absolute formulas Absolute cell reference Building and Editing Worksheets 26 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References (cont.) Using a mixed reference – A mixed cell reference combines both relative and absolute cell referencing • When you copy a formula, you may want to change the row reference but keep the column reference – Created using the [F4] function key Building and Editing Worksheets 27 Understanding Relative and Absolute Cell References (cont.) Print worksheet formulas – View formulas rather than cell contents • Click Tools on the menu bar, click Options, click the View tab, select the Formulas check box, then click OK – Print the worksheet Building and Editing Worksheets 28 Copying Formulas with Relative Cell References Reuse formulas you’ve created – Use Copy and Paste commands or the Fill Right technique to copy formulas • Use the AutoFill feature to copy labels, formulas, or values – Copy a formula to a new cell • Excel substitutes new cell references so that the relationship of the cells to the formula remain unchanged in the formula’s new location Building and Editing Worksheets 29 Copying Formulas with Relative Cell References (cont.) Copied formula cell references Copied cell Copied formula result Paste options button Building and Editing Worksheets 30 Copying Formulas with Relative Cell References (cont.) Filling cells with sequential text or values – Months of the year; days of the week; or text plus a number (Quarter 1, Quarter 2, etc.) – Drag the fill handle to extend an existing sequence Building and Editing Worksheets 31 Copying Formulas with Absolute Cell References A cell reference in a copied formula always refers to a particular cell address – Press [F2] for the range finder to outline the equation’s arguments in blue and green Absolute cell reference in formula Building and Editing Worksheets 32 Summary Create simple and complex formulas Edit cell contents Use functions Copy and move entries Understand cell referencing Building and Editing Worksheets 33