Circulatory System_Modified for website
advertisement

Major Function
The major function of the circulatory system is to pump
blood and other nutrients from the heart through the rest
of the body. Other functions of blood include:
• Carries oxygen and nutrients throughout body
• Takes secretions and metabolic waste away from the
cells
• Helps maintain normal body temperature
• Regulates internal pH
• Fights infection with phagocytic cells
Components of Blood
• Red blood cells- blood cells that transport oxygen and
contain hemoglobin. Hemoglobin makes blood red.
• White blood cells- blood cells that defend against
pathogens (infection and disease)
• Platelets- cell fragments that contain chemicals and
enzymes, which are important for blood clotting
• Plasma- part of blood that contains metabolic wastes,
salt and proteins and transports them where needed
http://ebooks.bfwpub.c
om/phelanphys2e.php
Blood Vessels
Arteries
•
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to be used in other parts of the body
•
Made up of endothelium, smooth muscle and connective tissues
•
•
This allows arteries to adjust with blood flow
Two main arteries
•
•
Pulmonary, which bring oxygen depleted blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen
Coronary, which branch off from the aorta and split off into a network around the body
Veins
•
Move blood away from the body back to the heart
•
Made up of the same material as arteries, however they are thinner
•
Pulmonary veins brings oxygenated blood to the heart
•
Smallest are venules and receive blood from arteries
Capillaries
•
Tiny section that connects veins and arteries
•
Play a key part in delivering nutrients to cells as well as waste removal
•
Are made up of a single layer endothelial cells
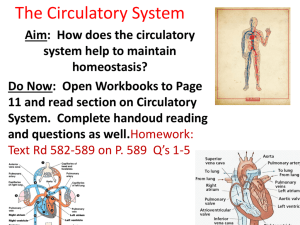
Heart
• The main job of the heart is to
pump blood throughout the body
• Electrical pulses from the
sinoatrial node cause the heart to
beat
• The right side of the heart pumps
deoxygenated blood to the lungs,
then is goes back into the heart on
the left side
• Four main Chambers
• Left ventricle and right ventricle
•
•
•
Separated by the interventricular
septum.
Lower part of heart
These pump blood out of the heart.
• Left atria and right atria
•
•
•
where blood enters the heart.
Separated by atrioventricular valve
Upper part of heart
Lungs
• The oxygen used in this system comes from the lungs, as well as carbon
dioxide being released from this system
• The pulmonary artery merge into smaller sections called arterioles which
connect to the alveoli. Oxygen diffuses across the tissue and into the
capillaries. Conversely the carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the
alveoli
• The pulmonary vein brings the oxygenated blood to the heart
http://learn.fi.edu/learn/heart/systems/
pulmonary.html
Fun Fact
Red blood cells have no nuclei, so they can carry more
oxygen. However because of this, they cannot multiple
and after around 120 days the cell will die from damage or
aging.
http://www.proteinstructure.net/reading-244-Hemolysisand-Fragility-of-Red-Blood-Cells.html
Interdependence of Systems
• Transports hormones, produced in the endocrine cycle,
around the body
• Helps dispose of the waste and carbon dioxide
• Nutrients from the digestive system are released into
the circulatory system and used as energy for cells
• The circulatory system works with the muscular system,
in the heart, a muscle, pumps blood through the body
• The marrow inside of the skeletal system produces the
white and red blood cells. These make up the blood
stream and fight off disease and carry oxygen
• The immune system consists of white blood cells, which
fight off diseases and infections
Pathway of Blood
Blood flows throughout the body
through a system of blood
vessels(veins & arteries). The blood
vessels carry blood to every part in
the body. The blood begins to
contract in the right ventricle and
eventually travels to pulmonary
artery and then to the lungs. The
blood picks up oxygen from the
lungs and travels to a main artery of
the body, the Aorta. This artery
distributes the blood to other parts
of the body such as the head, liver,
and gut. The Aorta also dispenses
blood back to the heart. The heart
continually pumps blood which is
used throughout the body.
•
HowStuffWorks "Blood Flow". (n.d.).
HowStuffWorks. Retrieved May 30, 2014,
fromhttp://health.howstuffworks.com/huma
nbody/systems/circulatory/heart3.htm
How the Circulatory System and
Respiratory System Are Related
• Oxygen is gathered through the circulatory system
and then transported through the circulatory
system
• These two systems work together to eliminate
carbon dioxide
• The lungs are important in both systems
• The alveoli and capillaries in the lungs are where
the two systems meet
• The oxygen from the lungs is moved through the
blood to the heart
• Both cycles start with inhalation and exhalation
• Both cycles are controlled in the brain but are
involuntary
Whiteboard review
1
2
3
4
10
5
6
9
8
7
Label
the
diagram
Bibliography Khosla, N. (2014). Introduction to the Cardiovascular System. Retrieved from
http://www.ck12.org/user:Y21vc2J5QHRtc2FjaGFydGVyLm9yZw../book/7th-gradeNC-essential-standards/r2/section/10.1/
Castro, J. (2013, September 25). 11 Surprising Facts About the Circulatory System.
Retrieved from http://www.livescience.com/39925-circulatory-system-factssurprising.html
(2009). Circulatory System. Retrieved from
http://userpages.umbc.edu/~farabaug/sokolo3.html
Durani, Y. (2013, January). Heart and Circulatory System. Retrieved from
http://kidshealth.org/parent/general/body_basics/heart.html
(2000-2014). Blood Flow in Human Circulatory System. Retrieved from
http://www.dreamstime.com/stock-images-blood-flow-human-circulatory-systemillustration-white-background-image35501514
Phelan, J. (2011). What is life?: a guide to biology with physiology. New York, New
York: W.H. Freeman.
American Society of Hematology. (2009, January 29). The Components of Blood and
Their Importance. Retrieved from http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-sKZWqsUpw
Bibliography
• Anatomy of the human heart. (n.d.). . Retrieved June 2, 2014, from
http://images.wisegeek.com/diagram-of-the-anatomy-of-the-humanheart.jpg
• Fox, C., & Barwick, S. (2014, June 1). What Is the Connection Between the
Circulatory System and Respiratory System?. WiseGeek. Retrieved June 3,
2014, from http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-connection-betweenthe-circulatory-system-and-respiratory-system.htm
• Heart disease. (n.d.). Definition. Retrieved May 27, 2014, from
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heartdisease/basics/definition/con-20034056
Bibliography•
The Circulatory System. (n.d.). BBC News. Retrieved June 3, 2014, from
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/pe/appliedanatomy/0_anat
omy_circulatorysys_rev3.shtml
•
Circulatory System Working With Other Systems! - Delta Science. (n.d.). <i>Circulatory
Working With Other Systems! - Delta Science</i>. Retrieved June 2, 2014, from
https://sites.google.com/a/apps.svsu.org/waterwheel- science/home/the-circulatorysystem/circulatory-system-working-with-othersystems
•
Concept 1 Review: Structure and Function of Arteries, Capillaries, and
Veins.
(n.d.). Concept 1 Review: Structure and Function of Arteries,
Capillaries, and Veins. Retrieved
June 2, 2014, from http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cardio2/
structure.html
•
Durani, Y. (2013, January 1). Heart and Circulatory System. KidsHealth - the
site about children's health. Retrieved June 3, 2014, from
http://kidshealth.org/teen/your_body/body_basics/heart.html
•
Phelan, J. (). <i>What is Life? A to Biology with Physiology </i>. : Ebooks.
•
Thadani, R. (n.d.). Circulatory System Organs. Buzzle. Retrieved June 3, 2014,
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/circulatory-system-organs.html
•
36 Interesting Facts About . . . var addthis_config =
{"services_compact":"email,fark,digg,delicious,linkedin",
"services_expanded":"email,fark,digg,delicious,linkedin"}; (36 Interesting Facts about the
Human Heart)
Web's
System
most visited
from