Document 10033929
advertisement

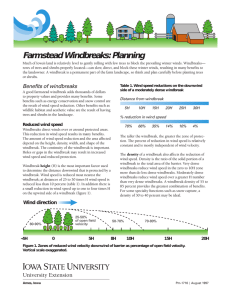
Chapter 5-part 1 • • • • • Physical Properties of Building Materials Physics of Home Insulation Selection of Home Site Physics of Window Design Effects of Energy Conservation on Heating and Cooling Costs Energy in the News Uses CO2 and a Surfactant What else is a Surfactant? Drawbacks: Need high pressure (900 psi) Machines cost more BUT Only waste:CO2 + surfactant Less heat: Less damage to fabric, less energy use Less water used. Radiation of Heat-Effect of Color Which radiates heat faster: coffee with cream or Coffee without cream? How does heat move in a vacuum? Conduction of Heat Q/t = k * A * Delta T/ delta Q=heat flow, k = thermal conductivity, A= area Delta T = temperature difference New formulation: Q/t = 1/R * A * DeltaT R is an insulation factor that is a function of material Properties and thickness. R values add-this is very useful. Changes in Insulation Requirements After WWII, who granted large numbers of home mortages? Differences in R value of Common Materials Table of R Values What has the highest R Value at a 1 inch thickness? Polyurethane board = High R sheathing Sick Building syndrome? Composite R Values Preventing Convection Infiltration of Air Heat loss from infiltration=Cp * V * K * Delta T Where Cp is heat capacity of the air, V is house volume K is number of air changes per hour, T is temperature difference Add up size of air slots Around the edge of a Door. Infrared pictures of a House on a cold day Weather Stripping Heating and Cooling Degree Days • Heating Degree Day = 65°F - T average • Cooling Degree Day = 75°F - T average • T average = average temperature for the day. Heating and Cooling DD in the United States R-Values Transmittance/Reflectance of Glass Glass transmits visible light, but is opaque to long wavelength infrared light. Table of Optical Properties Which is the best material for energy efficient windows? Convection in Windows Heat can be Transferred by conduction, Convection and radiation. Low E (emissivity) coatings are to prevent radiation of heat. Optimum Air Space Thickness Results for A double paned Window: Minimum heat loss is for a 15-20 mm Thickness of Air space Between two panes of glass Energy Savings from Conservation Savings and Payback Times What sort of payback times are short enough to convince the average person to invest in energy conservation? What is the lifetime of a house? Radiant Slab Heat Reducing Cooling Needs Coober Piedy Passive Cooling Methods Radiant Barriers What form of heat gain or loss is being prevented? Savings from Energy Efficient Landscaping Savings depend On your location Savings from Planting for wind shielding and sun Shading. Effects of Windbreaks House should be within 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. Trees should be evergreens. Don’t break with A driveway. No shadows on south walls. More on Windbreak Design Length must be greater Than 11 times windbreak height. Driveway is curved to preserve windbreak effectiveness. Plant perpendicular to Prevailing wind direction. Summer Shading Use deciduous trees Find the hottest week Of the year Calculate sun angle At mid afternoon If sun angle is 75 Degrees, trees should be no closer than on a line 75 degrees from true South. Shade East and West Walls (more important Than South walls!!) Winter: Let the Sun Shine In! Plant trees outside Of south wall of House. Avoids unwanted Shade in winter. Funneling Summer Wind Summer Wind Goes past moist shrubs and cool bricks before Entering house. Remind you of some Mediterranean houses?