What is the process of developing assessment?
advertisement

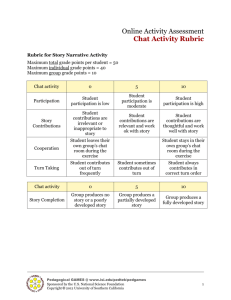
Designing and Developing Online Course Assessments :: Webcast Dr. Veronica Diaz, Maricopa Community Colleges Dr. Patricia McGee, The University of Texas at San Antonio Day 2 Agenda Welcome Part 4: What are the types of effective assessments in an online course? Part 5: How can we select the appropriate assessment strategy? Q&A What are the types of effective assessments in an online course? PART 4 Review of Day 1 Assessment and Learning P. McGee Assessment Toolkit Online vs. Face-to-face Progressive online learner assessment Self-Assessment Peer review Individual Team What are the types of effective assessments in an online course? Part 4 Effective uses of rubrics: content, processes, attitudes, etc. Rubrics Specifically state the criteria for evaluating student work Are more specific, detailed, and disaggregated than a grade and can help students to succeed before a final grade Can be created from Language in assignments Comments on students’ papers, or Handouts intended to help students complete an assignment Development Steps Identify what you are assessing (e.g., critical thinking, writing, process, participation) Identify the characteristics/behavior of what you are assessing (e.g., presenting, problemsolving) Decide what kind of scales you will use to score the rubric (e.g. checklists, numerical, qualitative, or numerical-qualitative) Describe the best work you could expect using these characteristics: top category Describe the worst acceptable product using these characteristics: lowest category More Steps Develop descriptions of intermediate-level products and assign them to intermediate categories: 1-5: unacceptable, marginal, acceptable, good, outstanding 1-5: novice, competent, exemplary Other meaningful set Test it out with colleagues or students by applying it to some products or behaviors and revise as needed to eliminate ambiguities Rubric Tips Develop the rubric with your students Use same rubric that was used to grade Use examples to share with students, so they can begin to understand what excellent, good, and poor work looks like Have students grade sample products using a rubric to help them understand how they are applied In a peer-review process, have students apply the rubric to eachother’s work before submitting it for official grading Benefits Allows assessment to be more objective and consistent Focuses instruction to clarify criteria in specific terms Clearly shows the student how their work will be evaluated and what is expected Promotes student awareness of about the criteria to use in assessing peer evaluation Rubric Resources http://www.uwstout.edu/soe/profdev/rubrics.shtml http://www.calstate.edu/AcadAff/SLOA/links/rubrics.shtml http://www.iuk.edu/~koctla/assessment/rubrics.shtml http://www.csupomona.edu/~uwc/faculty/CSU-EPTScoringGuide.shtml http://condor.depaul.edu/~tla/html/assessment_resources.html http://www.winona.edu/AIR/rubrics.htm http://www.engin.umich.edu/teaching/assess_and_improve/handbook/direct/rubric.html http://www.seattleu.edu/assessment/rubrics.asp http://wsuctproject.wsu.edu/ctr.htm http://www.utexas.edu/academic/diia/assessment/iar/students/report/rubrics-types.php Rubric Template: http://edweb.sdsu.edu/triton/july/rubrics/Rubric_Template.html Activity Consider how you might use or modify one of these for your course Share in chat Peer Assessment Developing Good Feedback Asynchronous Synchronous Participation Completion Attendance Contribution Degree Participation Contribution Amount Completion Completion Criteria Deadline Completion Achievement Deadline Frequency of Feedback Pedagogical Timing Calendar Schedule After practice Indirect – weekly At completion/achievement of objective Direct - bi-monthly Where and how… From http://www.french-inaude.com/pages/skype.htm From http://www.thethinkingstick.com/?p=604 Student Self-Assessment Involving the learner… Incorporate metacognitive assessments Provide a strategy for selfassessment and progress Track progress Compare work to that of others Grade own performance Progressive Benchmarks • 4 to 6 times per semester • Checklist • Fill in map • Portfolio • Coded grade book • Instructor acknowledgement • Recognition Self-Assessment Techno CATs Increases accountability Before/after unit Engages students Reflection Starts discussions Feedback on design Early alert Feedback on technology Practice 1. What was the one most useful thing you learned in this assignment, unit or module? 2. What suggestions would you give other students on ways to get the most out of this assignment, unit or module? 3. In what area did you learn or understand the most? Least? 4. List three ways you think you have developed or grown as a result of this assignment, unit or module? 5. What did you learn about writing, research, (or any other skill) from this assignment, unit or module? 6. What problems did you encounter in this assignment, project, unit, or tool that was used? 7. What unit/module of this course was your best work and why? Examples Cases Case-based instruction Well-bounded cases are presented to students as a focus for discussion and analysis. One situation or case becomes the focal point for an instructional sequence. Cases can illustrate a real world situation that requires application of learned course content. Cases can be provided in segments, as learners become prepared to address different components of the case. Case Assessment Teams Final outcome against pre-determined criteria Completion Performance against other teams Individual Contribution Objective assessments Case-based Assessment Student Generated Instructor Provided Pre-determined and communicated context, focus, format Case is focus of formal assessment Peer review/critique Solution-resolutionoutcome is withheld Expert review/critique Students complete case Contest Projects Project-based learning A long term instructional activity in which students work as a group as they focus on a question, problem, event or interest, investigate and negotiate understanding, and produce a product that represents their understanding (Brown & Campione, 1994). Considerations for Online Collaborative Projects Virtual or field? Team or individual? Cooperative or collaborative? Progressive? Types of Projects Research Debate Presentation Teach/mentor Design-Develop Simulation (virtual worlds) Helpful techniques Set benchmarks Use peer review Provide regular and informative feedback if nor formal assessment Set criteria for performance, completion, scope, and achievement Student Portfolio What are they? A way to organize, summarize, and share artifacts, information, and ideas about [you decide] A sampling of the breadth and depth of a person's work conveying the range of abilities, attitudes, experiences, and achievements Uses Reflection Sharing Reference Employer oriented Progressive Course, unit, program based Evaluation Repository Tools & Considerations Tool Ideas Considerations Internal Interactive CMS Web pages External Wikis Google Sites Blogs Support multimedia Security and privacy Allows assessment (scoring and data aggregation based on a rubric) Portable (exportable) Storage space Peer Review Example: peer review in a research methods course Google Docs POLL: Which best describes your experience with student teams? Have used them successfully (students like them and I do too) Have used them, but students don’t like them Have never used them I’d use them more often if I could use them effectively They don’t fit well with my courses 45 How can we select the appropriate assessment strategy? PART 5 Team/Group Assessment 47 Using Teams Based on the work of Larry Michaelsen (University of Oklahoma) http://teambasedlearning.apsc.u bc.ca/ 3 Keys Promoting ongoing accountability Using linked and mutually reinforcing assignments Adopting practices that stimulate idea exchange 48 Promoting Ongoing Accountability Require pre-group work Require group members to express individual opinions and monitor via another member Include peer evaluation in grading Readiness Assurance Process Test over readings Group: Test, discuss, reach consensus and retest Provide information for peer feedback process 49 Using linked and Mutually Reinforcing Assignments 50 Adopting Practices that Stimulate Idea Exchange Use of assignments that create conditions that foster give-and-take interaction Diversity of opinion, ideas, and perspectives Assign roles Not too easy Use permanent groups Not too much writing Size: 4-7 Employ, select, apply concepts from the course 51 Team Teaching Tips Outline learning goals Teach team skills Clear and detailed instructions Rubric Stages of team development Forming - polite but untrusting Storming - testing others Norming - valuing other types Performing - flexibility from trust 52 Cooperation and Collaboration COOPERATION – Each team member takes on a specific and unique role, e.g., editor, task manager, researcher, etc. The instructor assign tasks, monitors accountability, sets a clear procedure, devices a strategy for oversight of parts as relate to the whole COLLABORATION – Team members contribute perform same role and compile contributed pieces, e.g. all students research, interview, collect, examine, etc. Assign roles, accountability, clear procedure Team Contracts Purpose, goals, and missions Expectations Roles Conflict resolution strategies Meetings Communication Decision-making policy Agendas Record-keeping 54 Other Resources Team Based Learning (Michaelsen) http://teambasedlearning.aps c.ubc.ca/?page_id=9 Video Demonstrations http://teambasedlearning.aps c.ubc.ca/v/michaelsenvid.html 55 56 4 Questions What do I want students to be able to DO after this unit of instruction (behavioral outcomes) What will students have to KNOW to do XYZ (learning outcomes) How can I ASSESS whether or not students have successfully mastered key course concepts? (feedback) How can I tell if students will be able to USE their knowledge of key course concepts? (application) 57 Polls/Surveys Poll/Survey Options Drill & practice activities with participation points (online quizzes) Polls Polldaddy.com Survey monkey Survey tools in CMS Individual Assessments Individual Classroom Assessment A method used to inform you on …. Students learning Effectiveness of course content Effectiveness of teaching methods Individual Assessement Benefits Learner-centered Teacher-prompted Mutually beneficial Formative Fast to administer and interpret Non threatening Ongoing Foster trust between student and instructor Basic Development Steps 1. Choose a learning goal to assess 2. Choose an assessment technique 3. Apply the technique 4. Analyze the data and share the results with students 5. Respond to the data, i.e., make modifications as necessary 5 Suggestions for Online CATs Customize to your specific needs and learning environment Should be consistent with your instructional philosophy Test out a CAT and assess their effectiveness Allow extra time to carry out and respond to the assessment Let students know what you learn from their feedback and how you and they can use that information to improve learning Online CAT Examples Chain notes One-sentence summary Application cards Student-generated test questions Can be easily modified or converted to an online environment CATS as Formative Assessments CATs (most can be easily converted) Classroom Assessment in Web-Based Instructional Environment: http://pareonline.net/getvn.asp?v=9&n=7 Teaching Tips: http://honolulu.hawaii.edu/intranet/committees/FacDev Com/guidebk/teachtip/teachtip.htm#assessment Assessment Resources http://honolulu.hawaii.edu/intranet/committees/FacDev Com/guidebk/teachtip/assess-2.htm http://www.ntlf.com/html/lib/bib/assess.htm http://www.ntlf.com/html/sf/vc75.htm http://technologysource.org/article/classroom_assessme nt_techniques_in_asynchronous_learning_networks/ http://www4.nau.edu/assessment/main/research/webto ols.htm Exercise Review the CATs and pick one Identify the goal for your CAT Explain why this CAT is helpful/necessary in this particular area of the course How and when will students receive feedback on the CAT Discussion Assessments Posting vs. processing But I posted six messages?? You didn’t tell me I had to respond to other posts I didn’t have anything to say! I didn’t understand the instructions!!! Start with.. General discussion criteria in the syllabus Reiterate criteria and instructions as first message in discussion thread Provide examples of an appropriate post Facilitate with public feedback to the group and private feedback to the individual Possible discussion criteria Number of posts (least effective) Number of words Type of responses: Answer a question Pose a question Respond to another post Provide new information, examples, or evidence Quality of response Chat Assessments Participation vs. contribution Did the learner arrive on time? What was frequency of contribution? Did the learner remain in chat room the entire time? Where chat expectations communicated? Did the learner contribute? How did student meet chat expectations? Did the learner interact with others? Did learner follow chat conventions? How was chat assessed? Chat strategies Breakout rooms with specific outcomes Presentations with per-determined criteria (Rubric) Debates (winner) Discussion (participation and contribution) Other chat assessments? [respond in chat] Bloom’s & Web 2.0 Processes Tools Attributes Remember Recognizing, recalling Visual/Text/Audio stimuli, selecting, feedback Understand Interpreting, classifying, comparing, summarizing, explaining Sorting, tagging, labeling, entering, selecting Apply Executing, implementing Manipulating, entering, feedback Analyze Differentiating, organizing, attributing Selecting, grouping, altering, tagging, labeling Evaluate Checking, critiquing Commenting, entering, responding Create Generating, planning, producing Adding, generating, combining, publishing Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy Blogs vs. wikis Blogs Wikis Typically individual Typically collective group Documentation of thinking, experiences, events, reporting, peer critique Production of ideas, reporting, collaborating/cooperating , publishing Measured by: frequency, critical/reflective thinking, quality of writing, etc. Measured by: amount, contributions, collective quality, group determined value, etc. Blogs http://gateway102.blogspot.com/ http://freshmancomp101.blogspot.com/ http://geckowriters.blogspot.com/ http://www.netvibes.com/wesch#Anthro_Blogs Wikis http://mcc-cis236.wetpaint.com/ http://enh241.wetpaint.com/ http://wiki.mc.maricopa.edu/anthrowiki/index.php/Main _Page http://www.squidoo.com/wikisinhighered http://www.netvibes.com/wesch#Intro_Class_Portal http://spring09.wetpaint.com/?t=anon Web 2.0 Tool Videos Blogs RSS Wikis Podcasting Social bookmarking Web searches Social networking Google Docs Social media Google Reader P. McGee Assessment Toolkit Q&A