Nitrogen Compounds
advertisement

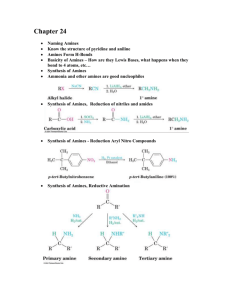
Amines Ammonia derivatives Specification from OCR o o o o o Explain the basicity of amines in terms of proton acceptance by the nitrogen lone pair. Describe the reactions of amines with acids to form salts Describe the preparation of: i) aliphatic amines by substitution of halogenalkanes with excess ethanolic ammonia ii) aromatic amines by reduction of nitroarenes using tin and conc. hydrochloric acid Describe the synthesis of an azo-dye State the use of reactions in the formation of dyestuffs Amines Amines are essentially molecules of ammonia One or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced with an alkyl group. H H N H Amines Replace one hydrogen atom with an alkyl group = primary amine, replace 2 = secondary amine etc. R NH2 Primary amine R NH R' Secondary amine R R N R'' R' Tertiary amine N R' + R''' R'' Quaternary ammonium salt The LONE PAIR on the nitrogen atom in amines makes them ... BRØNSTED-LOWRY BASES - they can be proton acceptors RNH2 + H+ ——> RNH3+ GOOD NUCLEOPHILES – able to attack the positive end of a polarised bond. Amines as bases Bases are proton acceptors. Amines don’t actually accept protons, they donate a lone pair to the hydrogen atom to form a dative bond. Ammonia and bases can do this with any suitable acid to give a salt. H3N H Cl NH4+Cl- Replacing a hydrogen in ammonia has the following effect Causes increased electron donation in the C-N bond Becomes polar, and nitrogen becomes slightly negative Lone pair on nitrogen slightly repelled Can be donated to a proton more easily 1° amines are more basic than ammonia What about secondary and tertiary? So following the same argument, 2° amines will be more basic still, as the lone pair will be repelled even more. In phenylamine, the lone pair becomes involved in the aromaticity, so it is less basic. The lone pair as part of the ring’s delocalised system, it is less readily donated to a proton. A tertiary amine will be more basic still. Reaction of amines with acids A standard Acid Base reaction. CH3CH2NH2 + HCl + CH3CH2NH3 - + Cl The preparation of amines 1. Reduction of nitrobenzene to give phenylamine NO2 NH2 i) conc. HCl/Sn + 6[H] ii) NaOH(aq) + H2O Conditions are reflux, this is important in the production of compounds called azo-dyes. Substitution of haloalkanes with excess ethanolic ammonia AMMONIA Reagent Conditions Product Nucleophile Equation Aqueous, alcoholic ammonia (in EXCESS) Reflux in aqueous , alcoholic solution under pressure Amine Ammonia (NH3) e.g. C2H5Br + 2NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + NH4Br (i) C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr (ii) HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br Mechanism Notes The equation shows two ammonia molecules. The second one ensures that the HBr is removed. NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION AMMONIA Why excess ammonia? The second ammonia molecule ensures the removal of HBr which would lead to the formation of a salt. A large excess ammonia ensures that further substitution doesn’t take place - see below Problem Amines are also nucleophiles (lone pair on N) and can attack another molecule of halogenoalkane to produce a 2° amine. This too is a nucleophile and can react further producing a 3° amine and, eventually an ionic quarternary ammonium salt. C2H5NH2 + C2H5Br ——> HBr + (C2H5)2NH (C2H5)2NH + C2H5Br ——> HBr + (C2H5)3N (C2H5)3N + C2H5Br ——> (C2H5)4N+ Br¯ diethylamine, a 2° amine triethylamine, a 3° amine tetraethylammonium bromide a quaternary (4°) salt Diazonium Salts Diazonium: there are 2 nitrogen atoms joined together in the positive ion. In French, nitrogen is still called by its old name ‘azote’ which means unable to support life. N N Cl diazonium chloride Formation of a Diazonium salt. Formed by reacting phenylamine with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid below 10◦C. These reagents form in situ nitrous acid HNO2. Diazonium Salts Notice the triple bond between the nitrogen atoms The positive charge is on the nitrogen that is attached to the benzene ring N N Cl diazonium chloride Why are they important? They look pretty weird! They are essential in the dye industry. A Diazonium salt is produced then reacted with a phenol. If the correct phenol is used, almost any colour can be produced. OCR specify this as a reaction you need to know. Formation of the Diazonium salt. The Diazonium salt is unstable above 10°C, so the reaction is normally carried out in ice. An aliphatic Diazonium salt is very unstable, so only aromatics are used. The lone pairs present in the salt can participate in the benzene ring, making it more stable. More correctly this is due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with the p-system in the ring. So phenylamine would give benzenediazonium chloride. Formation of the Diazonium salt. NH2 N N Cl + HONO(aq) + HCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) Formation of the Diazonium salt. The conditions are below 10◦C and remember the HNO2 (nitrous acid) is prepared in situ by reacting sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid. The diazonium salt can then do one of two things depending on the temperature Reactions of aromatic diazonium salts OH hydrolysis room temperature N N Cl OH Coupling reaction 5 degrees Celcius with phenol N N Hydrolysis The following occurs if a solution of a diazonium salt is warmed up: C6H5N2+Cl-(aq) + H2O(l) → C6H5OH + N2(g) + HCl(aq) Coupling reactions The mechanism is for interest only, you do not need to know it. OH N N N N H O H H O H OH N N General method for synthesis of azo dyes Add a cold aqueous solution of sodium nitrite slowly (with cooling and stirring) to a cold solution of the amine compound in excess hydrochloric acid The temperature must not rise above 5°C. This solution (still cold) should then be added slowly with stirring to a solution of the coupling compound. This should be kept below 5°C the whole time. Amino Acids These are bi-functional compounds. The contain 2 functions groups: A primary amine (in most cases) –NH2 The carboxylic acid group –COOH An amino acid must contain at least both of these functional groups. Amino Acids The simplest amino acid is glycine. H H H N C H O C O H Amino Acids All the amino acids (the twenty vitally important ones biologically) are 2-amino acids. The amine and acid groups are both attached to the same carbon. All can be names systematically, but in most cases the old names are used. Alanine is also known as 2-aminopropanoic acid, but alanine is the acceptable name to use. Alanine H H H O N C C H C O H H H General Formula H H H N C R O C O H Physical Properties White solids With relatively high melting points glycine (the simplest) has a melting point of 235°C. Normally readily soluble in water Almost totally insoluble in non-polar solvents Acid – Base Properties They are very largely ionic compounds. The carboxyl group can lose a proton The amine group can gain a proton The result is a ZWITTERION. From the German for hermaphrodite, hybrid or mongrel! Zwitterions Glycine mainly exists as. H3N + CH2 COO - Zwitterions The strong attractions in the crystal cause the high melting point In aqueous solution depending on the pH, they form either the neutral form, or the carboxylate will lose a proton, or the amino group will gain a proton. Zwitterions H H3N + C C H O + + H in strong acid H O H H H N C C H O + -H in strong alkali O H H H H N C C H O O- Isoelectric Point For each amino acid there is a definite pH – the isoelectric point at which the acid and basic ionisations are equal. The molecule is effectively neutral – it carries equal and opposite charges This is rarely near pH 7 because the molecule ionisation tendencies are affected by the other groups in the molecule. Isoelectric Point Aspartic acid – which has 2 –COOH groups – is acid in aqueous solution. Lysine with more amino than carboxyl groups is alkaline. Due to this dual functionality, they are able to act as buffer solutions (able to maintain a reasonably constant pH with small additions of acid or alkali). They also have optical activity. How amino acids join together Amino acids join together in specific ways to form specific proteins. One amino acid can join to another to form a substituted amide. H H H2N C COOH + H2N C COOH R' R'' H O H H2N C C N C COOH + H2O R' H R'' How amino acids join together This kind of bond between 2 amino acids is called a peptide bond or a peptide link. O C N H How amino acids join together H H O N C C H R' H H O R' O + N C C OH OH H R' N C C H H H H O N C C H R' OH How amino acids join together Two joined amino acids = dipeptide Three = tripeptide Many = polypeptide At some point a polypeptide becomes a protein. This can be put at 40 amino acids. Acid Hydrolysis of proteins Proteins and peptides can be hydrolysed with hot concentrated (6 mol dm-3) HCl. The protein is refluxed for about 24 hours. This hydrolysis is the exact reverse of the formation of the peptide bond. A molecule of water is in effect added across the linkage to regenerate the original amino acid and carboxyl groups. Acid Hydrolysis of proteins O C R O R' O N CH C CH C H + H2O N N H H O R' R C O N CH C H + OH H O CH C N H H N