Demand - WordPress.com
advertisement

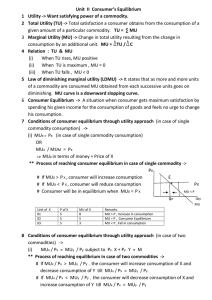
Demand • Meaning of Demand: Demand of commodity refers to the quantity of a commodity which a consumer is willing to buy at a given price, and time. • Market Demand: Market Demand refers to the sum total of the quantities demanded by all the individual households in the market at various prices in given time. • Demand Function: Demand Function is the functional relationship between demand and factors affecting demand. • Dx = f (Px, Po, Y, T, E) Factors affecting Demand Following are the factors which affect the Demand. • • • • • • • • • • • • Price of Commodity: When the price of commodity rises demand of commodity will decrease and viceversa. Price of other related commodity: Price of other commodity affect the demand of commodity in two ways: Substitute Goods:- In the case of substitute goods, the demand for a commodity rises with a rise in the Price and fall with the fall in price. Example- Tea and coffee Complementary Goods:- In case of complementary goods, the demand for a commodity rises with fall in the Price and decreases with the rise in the price of complementary goods. Example: Car and Petrol, Ink and Pen, Bread and Butter. Income of Consumer:- When the Income of Consumer rises the demand of normal goods increases and if the income decreases the demand of normal good decreases. In case of Inferior good the demand will decrease with rise in income and increase with decrease in income. Taste and Preference: - If the taste and preference of consumer develop for a commodity the demand will rise. Expectation: - If the consumer expects that price in future will rise the demand will rise and vice-versa Population:- More population, more demand, less population less demand. Climate: - The demand of commodity changes according to the climate. Law of Demand Other things are equal, the demand for a good rises with a decrease in price and decreases with increase in price. Px Qx Y Price D 10 100 P1 9 150 P P2 8 200 Q1 O Q Demand Q2 D X Change in Demand It is also called shift in demand curve. When quantity of commodity chang due to change in factor other than price. It has two types Y Y Price D Contraction of Demand 3 (A) Price Expansion of Demand Px 2 D1 D 1 D1 Increase in dd D2 decrease in dd. D2 10 O 20 QD 30 D X O Q.D. X Elasticity of Demand The elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded due to change in price of the commodity Measurement of elasticity of demand Total Expenditure Method/Total outlay method If no change in total expenditure as change in price than Ed=1 If total expenditure and price changes in opposite direction Ed>1 If total expenditure and price changes in same direction Ed<1 Proportionate or Percentage Method Under this method elasticity of demand is measured by the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage in price. Ed = Percentage change in Quantity Demanded Percentage change in Price Geometric Method/ Point Elasticity Method If elasticity of demand is to be measured on the point of demand curve following formula is to be used. ed = Lower segment from the point Upper segment from the point Factors effecting elasticity of Demand • • • • • • Nature of Goods Availability of Substitutes Postponement of Consumption Number of Uses Time period Habit of consumer Degrees of elasticity of Demand Perfectly elastic Demand Perfectly Inelastic Demand Elastic Demand Price Flatter Demand Curve E > 1 D Quantity Thanks • Prepared by:• HANS RAJ MEENA • K.V. BSF POKARAN