Latin America
advertisement

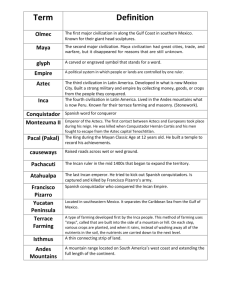
Latin America A diverse region-steeped in the heritage of three cultures, one language, and one religion. Environmental Changes: Pollution Mexico City has severe air pollution. Heavy smog is caused by overpopulation, a history of poor emissions and topography. one of the most polluted cities in Latin America as well as the most populous. Language Hispanic America speaks Spanish Brazil speaks Portuguese Why? Ans: Treaty of Tordesillas. Pope settled territorial disputes between Portugal and Spain. Rain Forests: HumanEnvironment Interaction. Much of this region is dominated by rain forests. The world’s rain forests are in serious trouble due to deforestation Impact of Physical; elements The Rio Grande is a natural border. Latin America: A Region Three Sub-Regions: 1. Central America 2. South America 3. The Caribbean Central America Mexico-Belize-Guatemala El Salvador-HondurasNicaragua Costa Rica-Panama (Isthmus) South America: largest landmass Colombia-Venezuela-Guyana Suriname-French Guiana-Ecuador Peru-Bolivia-Brazil (largest country) Paraguay-Argentina Uruguay-Chile Caribbean Cuba Haiti Jamaica Dominican Republic Puerto Rico (U.S.) (Part of the Greater Antilles) Physical Characteristics: South America = largest land area in region. Major Mountain Ranges The Andes Mountains run down the west coast of South America and are the longest mountain range in the world. More Mountain Ranges In Mexico you have the Sierra Madre Occidental in the west, the Sierra Madre Oriental in the east, and the Sierra Madre del Sur in the south. Rainforests The Amazon The largest rainforest in the world. The Atacama Desert The Atacama Desert is a coastal desert that is on the leeward side of the Andes Mountains. It is the driest place on earth – it hasn’t rained in 400 years! Reversed seasons south of the equator They have Summer when we have winter and vice versa. Amazon River Basin The Amazon River Basin is one of the largest river systems in the world. During the rainy season the Amazon river gets up to 350,000 sq km (3 times its size during the dry season) Grasslands - Pampas In the plains of Argentina and Uruguay there are the grassy, treeless areas known as Pampas. The Pampas have the rainfall and fertile soils needed for producing grain and grazing cattle and sheep. Grasslands - Llanos People of Venezuela and Colombia have been raising cattle for hundreds of years on the large, fertile plains areas called llanos (LAHnohz), which run along the Caribbean coast of South America. Tropical Climates predominate Volcanoes and earthquakes Location: Ring of Fire Archipelagoes: Greater and Lesser Antilles Vertical Climate Zones Climate and vegetation vary widely, depending on elevation. The following vertical climate zones exist the region: Tierra Caliente: 2,500-3,000 feet Tierra Templada: 6,000-6,500 feet Tierra Fria: 10,000-12,000 feet Tierra Helada: above 15,000 feet Economic Characteristics: Diverse economies Primary levels of economics – farming, oil Some tourism – ecotourism: e.g. rainforests. Disparity of income distribution Environmental concerns NAFTA Primary Economic Level Subsistence farming is farming at a basic level. Subsistence farming is farming to meet the needs of yourself and your family. Demographics that are typical of developing countries: 1. Low per capita GDP 2. Low life expectancy 3. High population growth rate 4. High infant mortality 5. Large percentage of the population under the age of 15 6. Low literacy rates Plantation Agriculture Commercial farming, which is farming for profit, exists on plantations. There are various cash crops and food crops but the major crop is COFFEE. Slash and Burn Farming Is a form of subsistence farming in which forests are cut and burned to plant crops. This adds to South America’s deforestation problem. Haciendas – large Spanish Plantations Gauchos: Argentine Cowboys They work on ranches in the pampas region. Deforestation South America’s rain forests are rapidly being destroyed. Brazil has some of the worst deforestation in the world. Oil Resources (nonrenewable) Venezuela Ecuador Mexico Disparity of Income Distribution A growing gap between the rich and the poor NAFTA North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). USA, Canada and Mexico all signed to open trade and improve the economies of the three nations. NAFTA is an example of: 1. How membership in military and political alliances provide access to markets. 2. An economic union. 3. Spatial divisions. 4. Cooperation Diverse mineral resources Copper in Chile Iron ore in Venezuela Iron ore in Brazil Cultural Characteristics Influence of European colonization, Indian civilizations and African traditions. Predominance of Roman Catholic religion. Rigid social structure: Spanish influence Cultural hearths: Ancient Native Civ. Indian Civilizations Maya: in the Yucatan Peninsula Aztec: near Mexico City Inca: in the Andean mountains of Peru African Traditions Cultural influences came with the slaves that were imported to work on the plantations European Colonization: 1. Spain 2. Portugal 3. England 4. France Roman Catholic religion Brought by the Spanish Mestizos – mixed white (mostly Spanish) and Indian Location of settlements Most people in South America live near the coasts. Why? Large Megacities like Rio de Janeiro occur along the coasts. Answer: because of physical barriers to farming and other economic development. For Example: the Andes Mountains and the Amazon rain forest. Impoverished Squatter settlements arise outside of the Megacities like this one. Rapid population growth – developing. Mexico in 2000 Out Migration People are leaving, many going to the U.S. in search of economic opportunity. Cultural heritage Music – African influences, calypso, steel drum bands, reggae Traditional Dances – Tango in Argentina Spanish is the dominant language Portuguese in Brazil (line of demarcation) Calypso Music from the Caribbean (Steel Drums) Reggae – Jamaica (Caribbean) Witness the passion of the Tango! AH, the Latin dance of love! Cultural Landscape Pyramids, cathedrals Haciendas, ejidos (communal land) Machu Picchu Tikal Cultural Lanscape Hacienda: large Spanish estate. Machu Picchu – Old Incan City high in the Andes Mountains. Tikal – largest known Mayan city Cities as centers of culture and trade: Mexico City: Capital of Mexicolocated high on the Mexican Plateau on the site of the Aztec Capital. Rio de Janeiro: Previous capital of Brazil-coastal port and center of Brazilian culture-carnival! When my baby smiles at me, I go to Rio….. Mexico City Rio de Janeiro Cities continued: Buenos Aires: Capital of Argentinalocated at the mouth of the Rio de La Plata as it enters the Atlantic Ocean. A major South American port. This is the outlet for major river systems: Parana, et.al. Cities continued: Santiago: Capital of Chile and a major South American Port on the West Coast: Pacific. An Example of a change in a cities function over time: Moving Brazil’s capital from Rio de Janeiro to Brasilia in order to promote development in the interior of the country. Brasilia THE END